General Info
Tupolev Design Bureau
Tupolev Design Bureau
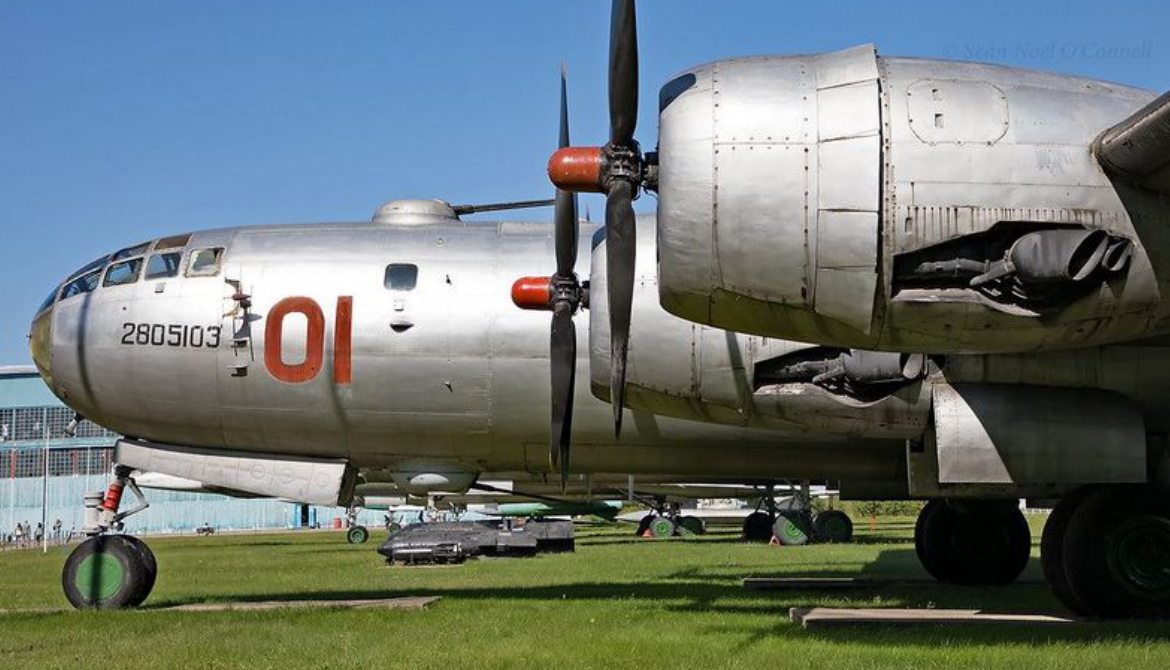
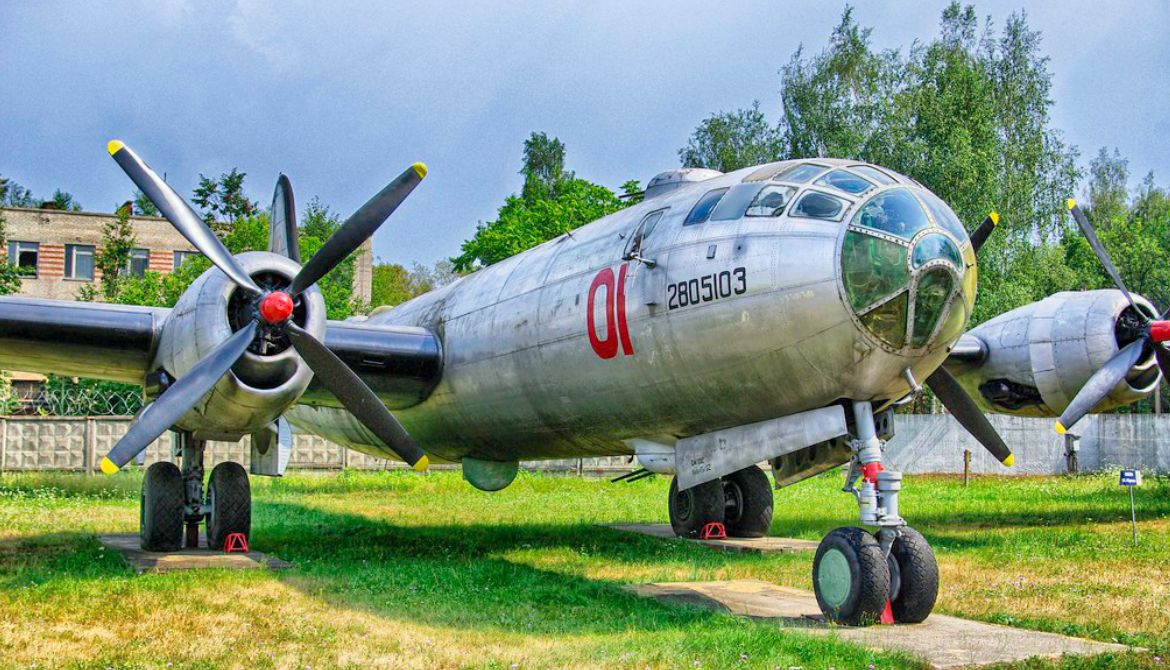
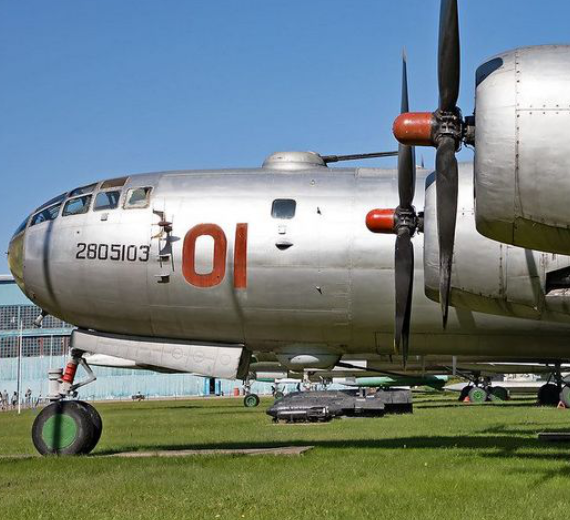
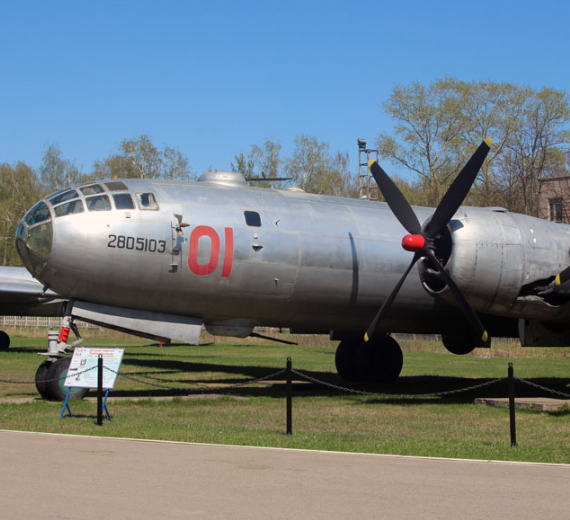
Tupolev Tu-4 Bull
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.
History Public Joint Stock Company Tupolev,
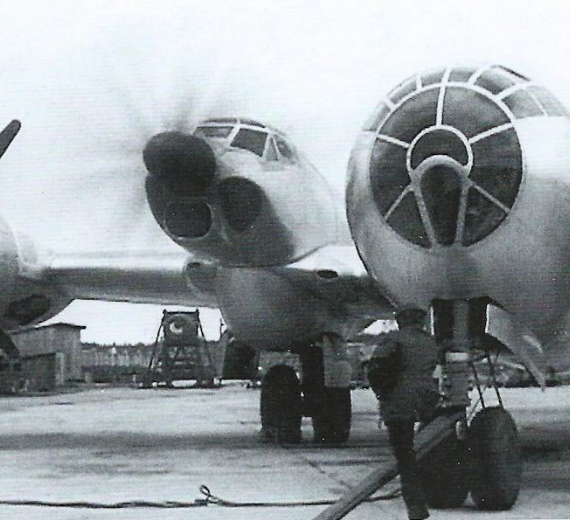
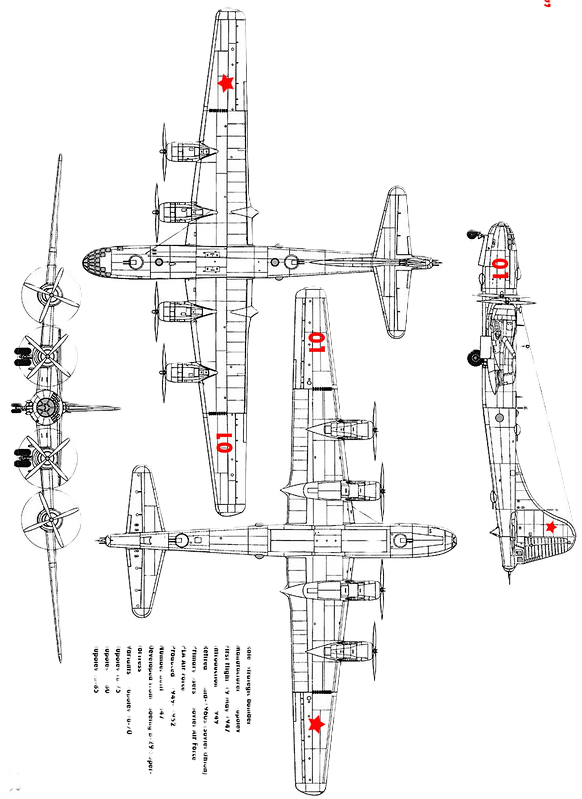
Tupolev Tu-4 (Туполев Ту-4; NATO reporting name: Bull)

Toward the end of World War II, the Soviet Union saw the need for a strategic bombing capability similar to that of the United States Army Air Forces. The Soviet VVS air arm had the locally designed Petlyakov Pe-8 four-engined "heavy" in service at the start of the war, but only 93 had been built by the end of the war and the type had become obsolete. The U.S. regularly conducted bombing raids on Japan, from distant Pacific forward bases using B-29 Superfortresses. Joseph Stalin ordered the development of a comparable bomber.
Development
Variants

- Tu-4
- main production version, originally designated B-4
- Tu-4 Variants without special designations:
- Tu-4 ELINT and ECM
- Tu-4 mothership for the DFS 346A.(Note:other DFS346 prototypes were carried by one of the Boeing B-29s interned during the war).
- Tu-4 escort fighter mothership (Project Burlaki)
- Tu-4 remotely controlled target drone converted from time expired bombers.
- Tu-4 fuel carrier
- Tu-4 in-flight refuelling testbeds (four different systems were trialled)
- Tu-4 radiation reconnaissance aircraft
- Tu-4 communications relay aircraft
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
MachAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Gallery
Photo Gallery
Photo Gallery
Public Joint Stock Company Tupolev,
upolev Tu-4 (Туполев Ту-4;
NATO reporting name: Bull)


Voronezh Aircraft Production Association
Public Joint Stock Company Tupolev,
Public Joint Stock Company Tupolev,
upolev Tu-4 (Туполев Ту-4; NATO reporting name: Bull)
1
General Info
-
-
-
-
- Crew: 11
- Length: 30.18 m (99 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 43.05 m (141 ft 3 in)
- Height: 8.46 m (27 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 161.7 m2 (1,741 sq ft)
-
-
-
2
Powerplant
-
-
-
- Empty weight: 36,850 kg
- Gross weight: 47,850 kg
- Max takeoff weight: 55,600 kg (122,577 lb) – 63,600 kg
- Powerplant: 4 × Shvetsov ASh-73TK 18-cyl. air-cooled radial piston engines, 1,790 kW (2,400 hp) each
-
-
-
3
Performance
-
- Maximum speed: 558 km/h
- Range: 5,400 km (3,400 mi, 2,900 nmi) at 3,000 m (9,800 ft) with 63,600 kg (140,200 lb) take-off weight including 3,000 kg (6,600 lb) of bombs and 10% fuel reserves
- Service ceiling: 11,200 m (36,700 ft)
4
Armament
-
- Guns: * 10 × 23 mm (0.91 in) Nudelman-Suranov NS-23 aircraft cannon, two cannon in each of the four turrets and two cannon in the tail barbette
- Missiles: * 2 × KS-1 Komet standoff missiles (Tu-4K only; these anti-ship missiles resembled a scaled-down MiG-15)
- Bombs: * 6 × 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) bombs
.
Special Links Public Joint Stock Company Tupolev, upolev Tu-4
(Туполев Ту-4; NATO reporting name: Bull)
(Туполев Ту-4; NATO reporting name: Bull)
Links to Youtube & Others
Between 1970 and December 2016 there were 110 serious incidents involving the Tu-154, including 73 hull losses,
with 2,911 fatalities.
Tupolev Design Bureau Tupolev Tu-4 Bull
In October 2020 ALROSA, the last Russian passenger airline to operate this aircraft, retired its last remaining Tu-154
Youtube Link
In January 2010 Russian flag carrier Aeroflot announced the retirement of its Tu-154 fleet after 40 years, with the last scheduled flight being Aeroflot Flight 736 from Yekaterinburg to Moscow on 31 December 2009.