Tupolev Design Bureau KJ-1 kōngzhōng yùjǐng
 |
|
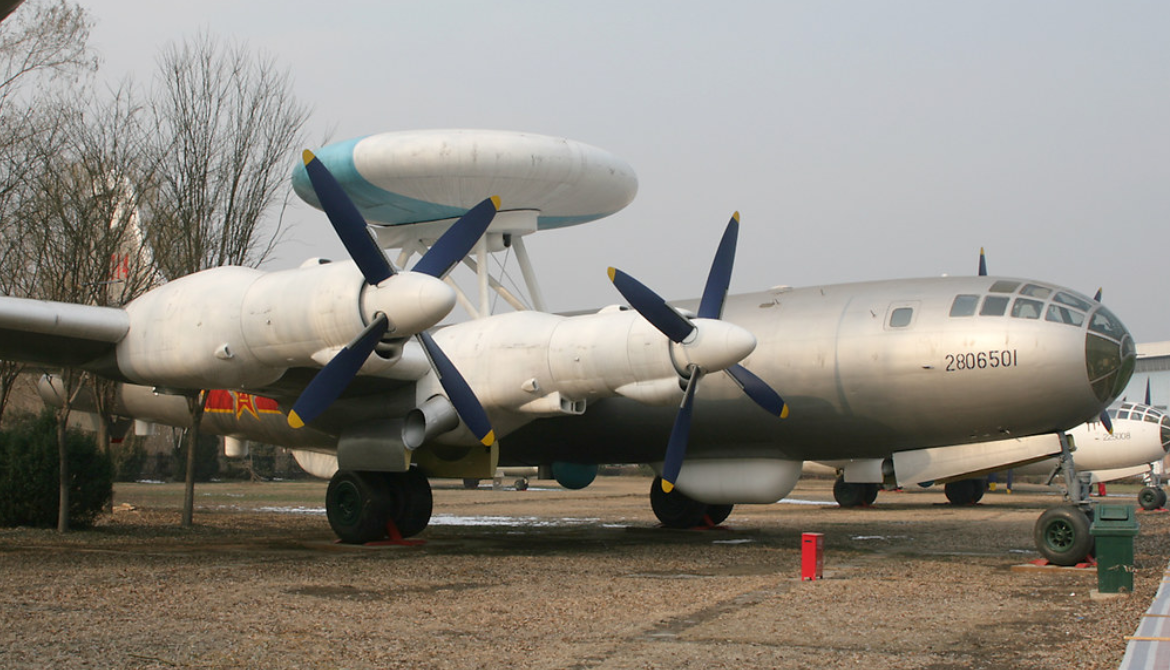
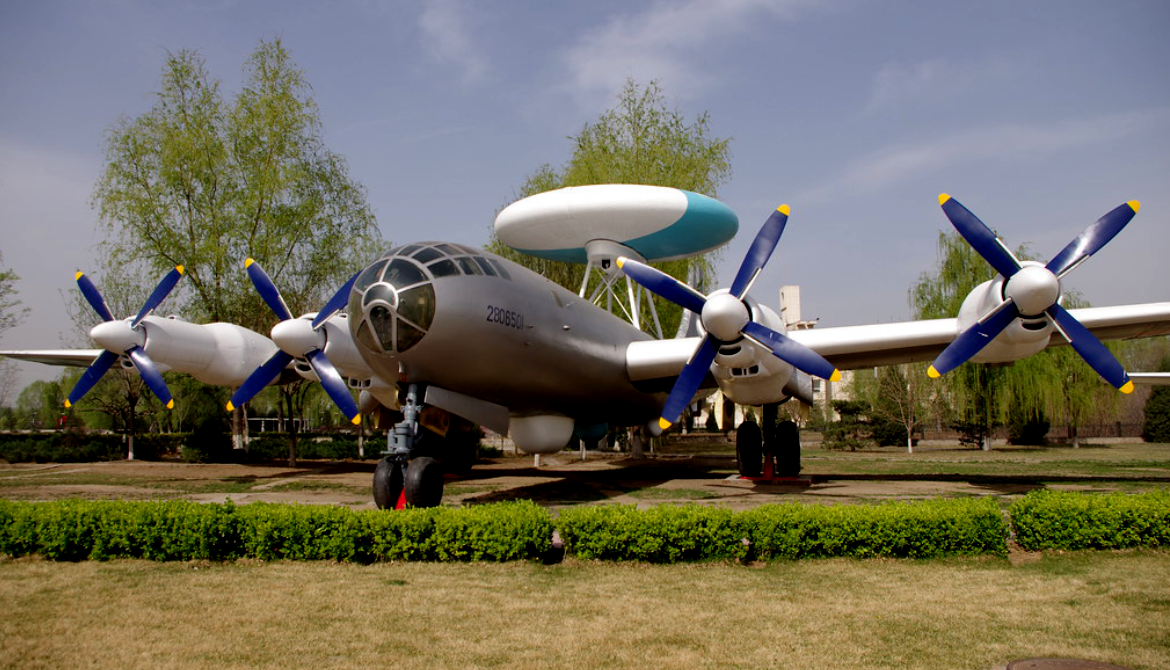
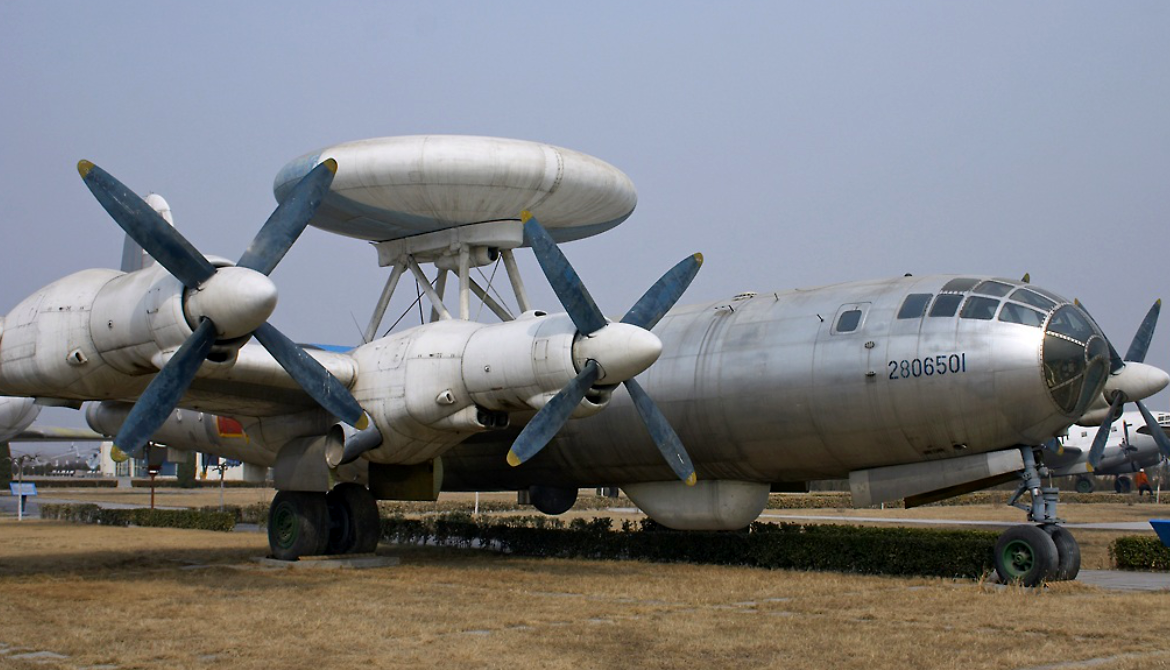
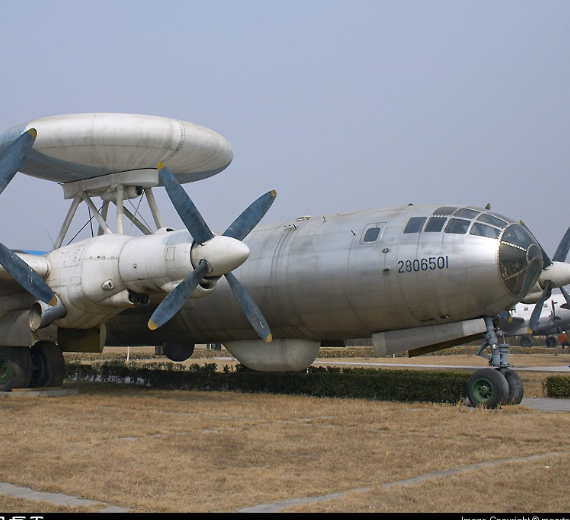
| KJ-1 AEWC (Tu-4 with radar) at China Aviation Museum | |
| Role | Airborne Early Warning and Control |
|---|---|
| National origin | People's Republic of China (PRC) |
| Status | cancelled |
| Number built | 1 |
| Developed from | Tupolev Tu-4 |
|
|
.
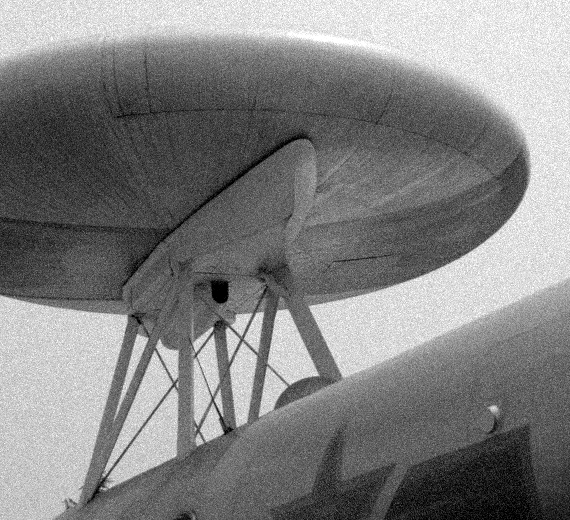
History PLAAF KJ-1 (from Chinese: 空警; pinyin: Kōng Jǐng, short for 空中预警 kōngzhōng yùjǐng

The KJ-1 (from Chinese: 空警; pinyin: Kōng Jǐng, short for 空中预警 kōngzhōng yùjǐng meaning "airborne early warning") was a Chinese experimental airborne early warning (AEW) aircraft, based on a Tupolev Tu-4 bomber aircraft. The project was started in 1969 under the code name "Project 926", but only one prototype was built before the project was put on hold indefinitely until it was finally cancelled in 1979.
Development
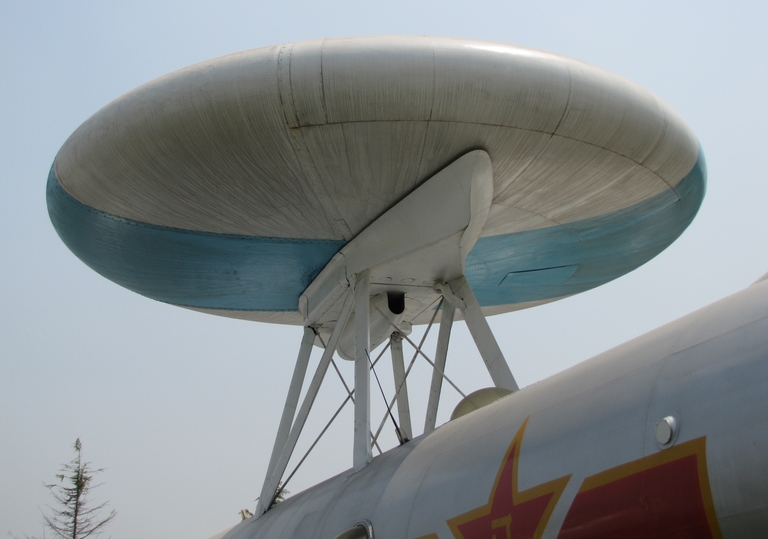

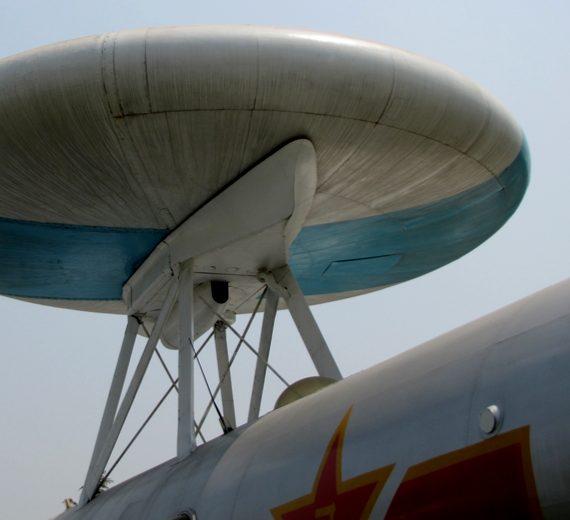
The KJ-1 was the first-generation AEW aircraft developed by the People's Republic of China. According to Chinese government claims, a single KJ-1 would have functions equivalent to more than 40 ground radar stations, but the test flight in the early 70s experienced severe mid-flight vibrations that could not be solved, and the development was stopped later amongst the political chaos of the Cultural Revolution.
During the Chinese economic reform, the project was once again put on hold due to cuts in military budget as economic development was given top priority. When the project was finally reviewed again in 1978 for the modernization of the People's Liberation Army Air Force, it was considered obsolete, and the project was terminated in 1979. The only KJ-1 aircraft built was dismantled after the project was scrapped, and the KJ-1 now on display at the China Aviation Museum in Beijing is actually a reconstructed replica converted using another Tu-4.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km.hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
PLAAF KJ-1 (from Chinese: 空警; pinyin: Kōng Jǐng, short for 空中预警 kōngzhōng yùjǐng


PLAAF KJ-1 (from Chinese: 空警; pinyin: Kōng Jǐng, short for 空中预警 kōngzhōng yùjǐng
General Info
-
-
-
-
- Crew: 11
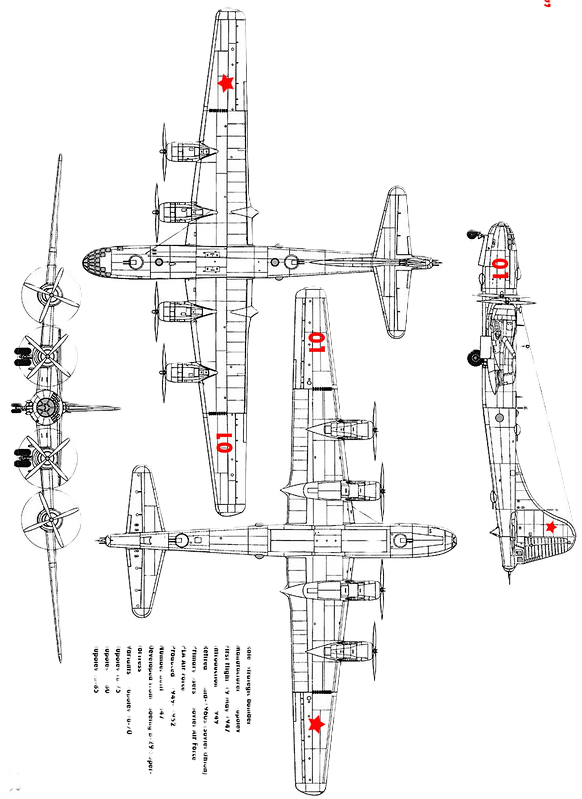
- Length: 30.18 m (99 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 43.05 m (141 ft 3 in)
- Height: 8.46 m (27 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 161.7 m2
-
-
-
Powerplant
-
-
-
- Empty weight: 36,850 kg
- Gross weight: 47,850 kg
- Max takeoff weight: 55,600 kg
- Powerplant: 4 × Shvetsov ASh-73TK 18-cyl. air-cooled radial piston engines, 1,790 kW (2,400 hp) each
-
-
-
Performance
-
- Maximum speed: 558 km/h
- Range: 5,400 km (3,400 mi, 2,900 nmi) at 3,000 m (9,800 ft) with 63,600 kg (140,200 lb) take-off weight including 3,000 kg (6,600 lb) of bombs and 10% fuel reserves
- Service ceiling: 11,200 m
Armament
-
- Guns: * 10 × 23 mm (0.91 in) Nudelman-Suranov NS-23 aircraft cannon, two cannon in each of the four turrets and two cannon in the tail barbette
- Missiles: * 2 × KS-1 Komet standoff missiles (Tu-4K only; these anti-ship missiles resembled a scaled-down MiG-15)
- Bombs: * 6 × 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) bombs
.
Links to Youtube & Others
Between 1970 and December 2016 there were 110 serious incidents involving the Tu-154, including 73 hull losses,
with 2,911 fatalities.
Tupolev Design Bureau Tupolev Tu-4 AEW
In October 2020 ALROSA, the last Russian passenger airline to operate this aircraft, retired its last remaining Tu-154
Youtube Link
In January 2010 Russian flag carrier Aeroflot announced the retirement of its Tu-154 fleet after 40 years, with the last scheduled flight being Aeroflot Flight 736 from Yekaterinburg to Moscow on 31 December 2009.