Boeing Military
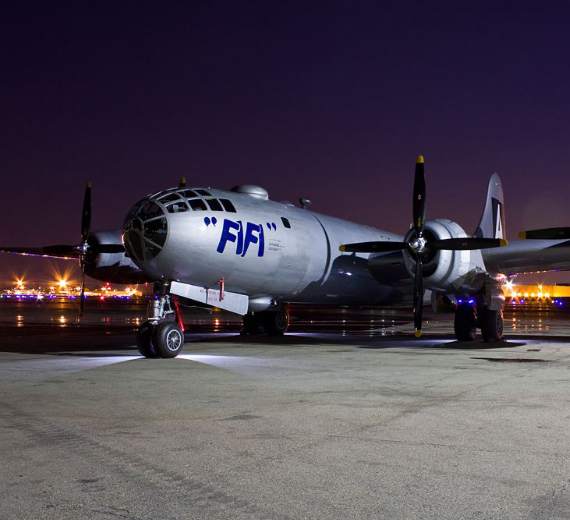
B-29 Super Fortress
Role Strategic bomber, heavy bomber
National origin United States
Manufacturer Boeing
First flight 21 September 1942
Introduction 8 May 1944
Retired 21 June 1960
Status Retired (see Surviving aircraft)
Primary users United States Army Air Forces
United States Air Force
Royal Air Force
Produced 1943–1946
Number built 3,970
Variants All models
Boeing KB-29 Superfortress
XB-39 Superfortress
Boeing XB-44 Superfortress Boeing B-50 Superfortress
Developed into Boeing C-97 Stratofreighter
Boeing 377 Stratocruiser
Tupolev Tu-4
.
History Boeing Military
Boeing B-29 Super Fortress

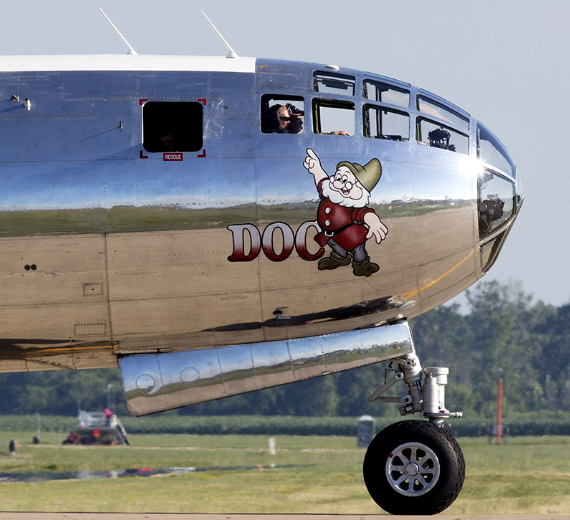
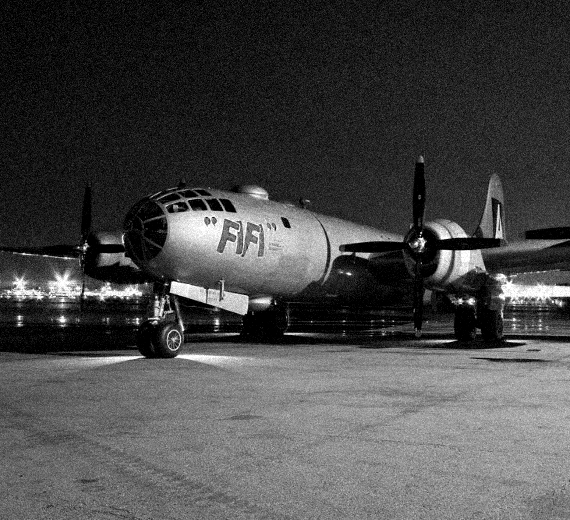
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the B-17 Flying Fortress, the Superfortress was designed for high-altitude strategic bombing, but also excelled in low-altitude night incendiary bombing, and in dropping naval mines to blockade Japan. B-29s dropped the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the only aircraft ever to drop nuclear weapons in combat.
One of the largest aircraft of World War II, the B-29 was designed with state-of-the-art technology, which included a pressurized cabin, dual-wheeled tricycle landing gear, and an analog computer-controlled fire-control system that allowed one gunner and a fire-control officer to direct four remote machine gun turrets. The $3 billion cost of design and production (equivalent to $49 billion today), far exceeding the $1.9 billion cost of the Manhattan Project, made the B-29 program the most expensive of the war.The B-29 remained in service in various roles throughout the 1950s, being retired in the early 1960s after 3,970 had been built. A few were also used as flying television transmitters by the Stratovision company. The Royal Air Force flew the B-29 with the service name Washington from 1950 to 1954 when the jet-powered Canberra entered service.
In response, Boeing began work on pressurized long-range bombers in 1938. Boeing's design study for the Model 334 was a pressurized derivative of the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress with nosewheel undercarriage. Although the Air Corps lacked funds to pursue the design, Boeing continued development with its own funds as a private venture. In April 1939, Charles Lindbergh convinced General Henry H. Arnold to produce a new bomber in large numbers to counter the Germans' bomber production. In December 1939, the Air Corps issued a formal specification for a so-called "superbomber" that could deliver 20,000 lb (9,100 kg) of bombs to a target 2,667 mi (4,292 km) away, and at a speed of 400 mph (640 km/h). Boeing's previous private venture studies formed the starting point for its response to the Air Corps formal specification.[0
KmCeiling
0
KmRange
0
Km/HAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
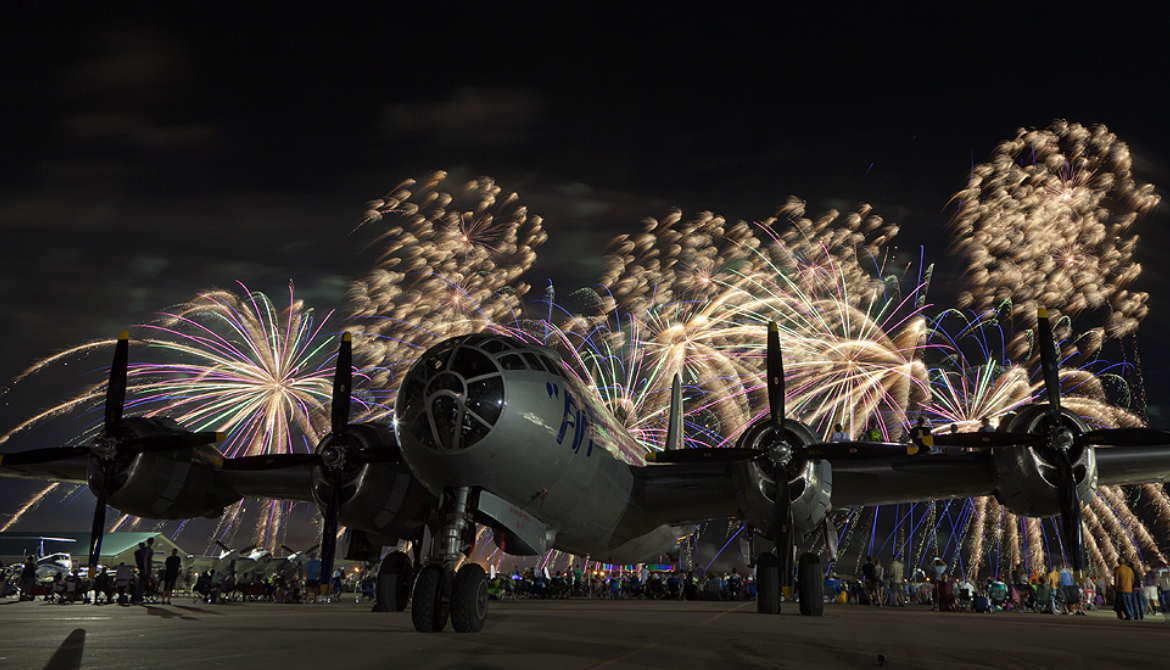
Photo Gallery
Boeing B-29 Super Fortress


Boeing Military Airplanes
Boeing B-29 Super Fortress
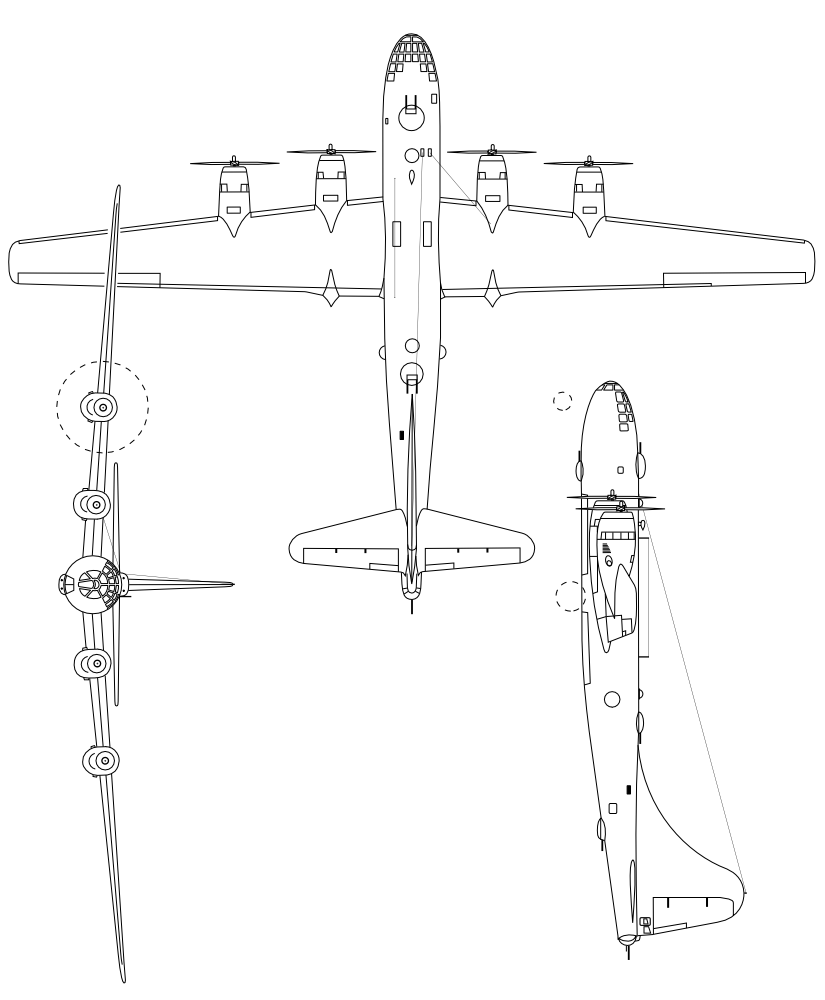
General characteristics
- Crew: 11 (Pilot, Co-pilot, Bombardier, Flight Engineer, Navigator, Radio Operator, Radar Observer, Right Gunner, Left Gunner, Central Fire Control, Tail Gunner)
- Length: 99 ft 0 in (30.18 m)
- Wingspan: 141 ft 3 in (43.05 m)
- Height: 27 ft 9 in (8.46 m)
- Wing area: 1,736 sq ft (161.3 m2)
Powerplant
- Frontal area: (3.824 m2)
- Empty weight: (33,793 kg)
- Gross weight: (54,431 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: (60,555 kg)
-
-
-
- (61,000 kg) combat overload
-
-
- Powerplant: 4 × Wright R-3350-23 Duplex-Cyclone 18-cylinder air-cooled turbosupercharged radial piston engines, 2,200 hp (1,600 kW) each
- Propellers: 4-bladed constant-speed fully-feathering propellers, 16 ft 7 in (5.05 m) diameter
Specifications
- Maximum speed: (575 km/h,
- Cruise speed: (350 km/h,
- Stall speed: 105 mph (169 km/h,
- Range: (5,230 km, 2,820 nmi)
- Ferry range: 5,600 mi (9,000 km,
- Service ceiling: 31,850 ft (9,710 m)
- Rate of climb: 900 ft/min (4.6 m/s)
Related development
-
Guns:
- 10 × .50 in (12.7 mm) Browning M2/ANs in remote-controlled turrets. (omitted from Silverplate B-29s)
- 2 × .50 BMG and 1× 20 mm M2 cannon in tail position (the cannon was later removed)
-
Bombs:
- 5,000 lb (2,300 kg) over 1,600 mi (2,600 km; radius at high altitude
- 12,000 lb (5,400 kg) over 1,600 mi (2,600 km; 1,400 nmi) radius at medium altitude
- 20,000 lb (9,100 kg) maximum over short distances at low altitude
- Could be modified to carry two 22,000 lb (10,000 kg) Grand Slam bombs
-
Boeing B-29 Super Fortress
Links to Youtube & Others
The General Electric Central Fire Control system on the B-29 directed four remotely controlled turrets armed with two .50 Browning M2 machine guns each.
Boeing
B-29 Superfortress
Manufacturing the B-29 was a complex task that involved four main-assembly factories
Youtube Link
Boeing provides comprehensive C-17 Globemaster III training solutions for aircrews and loadmasters with advanced simulation, courseware and computer-based training. C-17 operators can practice