Messerschmitt
Me 321 Glider
Role Cargo glider
Manufacturer Messerschmitt
First flight 25 February 1941
Introduction 1941
Status Retired
Primary user Luftwaffe
Produced June 1941 – April 1942
Number built 200
Developed into Messerschmitt Me 323
.
History Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW)
Messerschmitt AG
Messerschmitt Me 321 Glider

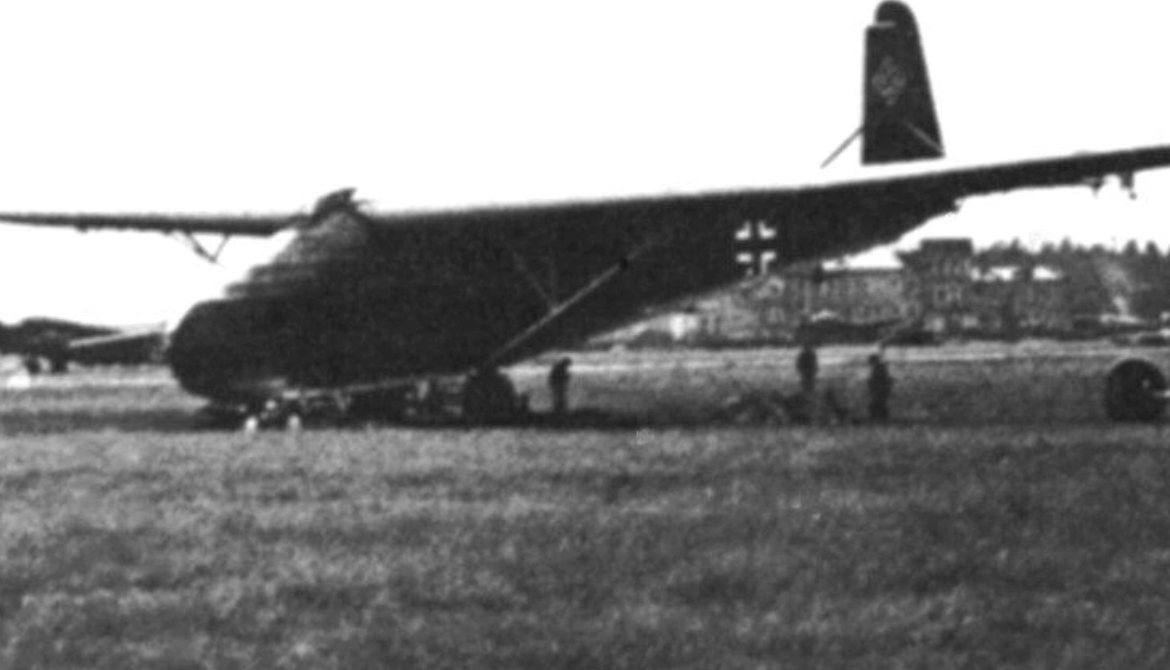
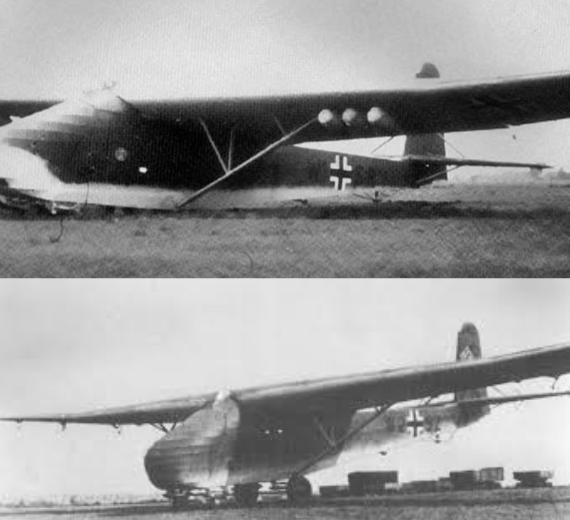
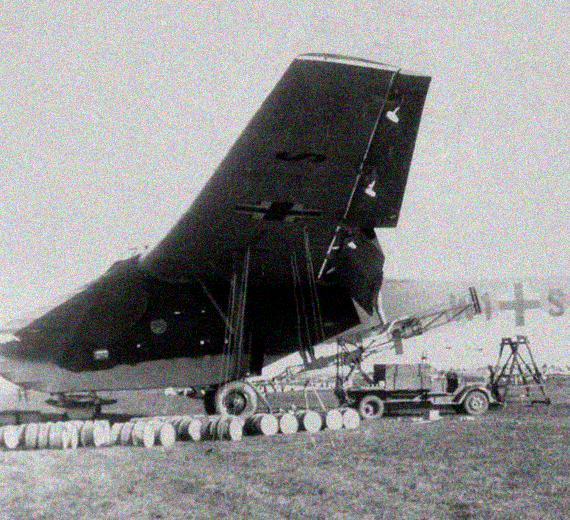
The Messerschmitt Me 321 Gigant was a large German cargo glider developed and used during World War II. Intended to support large-scale invasions, the Me 321 had very limited use due to the low availability of suitable tug aircraft, high vulnerability whilst in flight, and its difficult ground handling, both at base and at destination landing sites. The Me 321 was developed, in stages, into the six-engined Messerschmitt Me 323 Gigant, which removed some of the problems with ground handling, although the payload was reduced. Vulnerability to ground fire and aerial attack remained a constant problem during operations of all variants
During the preparations for a possible invasion of Britain during World War II (Operation Sea Lion) the Luftwaffe's Transport Command saw an obvious need existed for a larger-capacity cargo- and troop-carrying aircraft than its mainstay, the Junkers Ju 52. When the plans for Operation Sea Lion were shelved in December 1940, and planning began for the invasion of the USSR (Operation Barbarossa), the most cost-effective solution to the need for transport aircraft was found to be to use gliders. Accordingly, the Technical Bureau of the Luftwaffe issued a tender for rapid development of a Grossraumlastensegler ("large-capacity transport glider") to the aircraft manufacturers Junkers and Messerschmitt. The specification called for the glider to be capable of carrying either an 88 mm gun plus its tractor, or a medium tank. The codename Projekt Warschau (Project Warsaw) was used, with Junkers being given the codename Warschau-Ost and Messerschmitt Warschau-Süd.
Prototypes

Variants
- Me 321 A-1: single-pilot version; 100 built
-
Me 321 B-1: had a crew of three (including co-pilot) and was armed with 2–4 × 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 15 machine-guns; 100 built
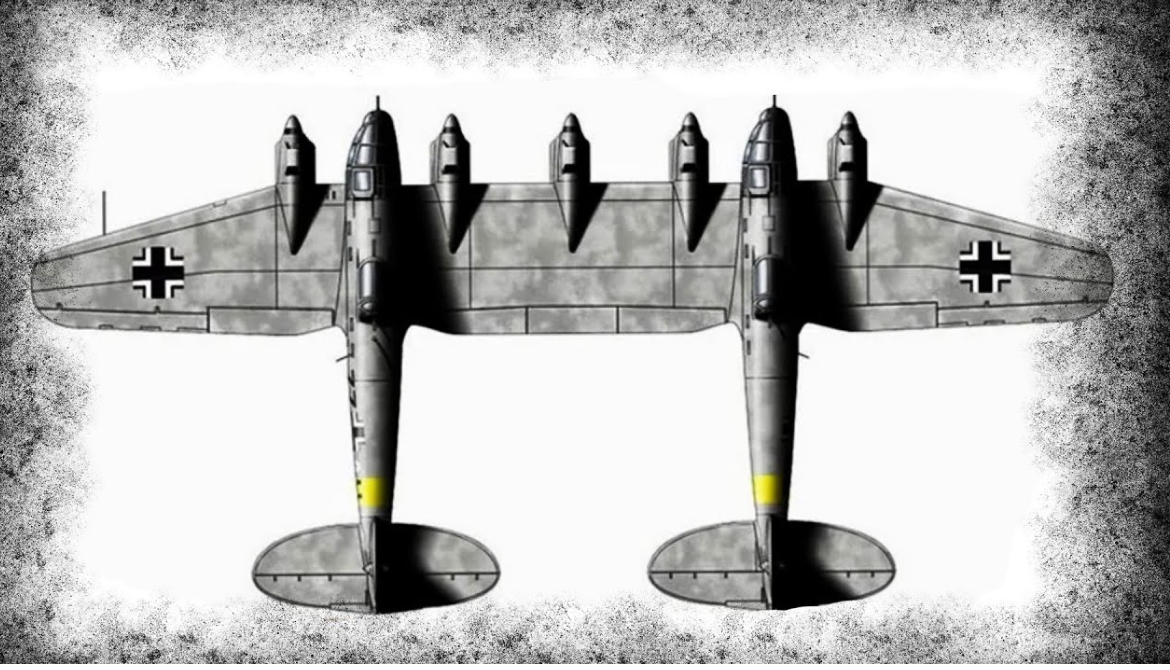
Towing the Me 321 Luftwaffe used the Heinkel He-111Z Zwilling
0
KmCeiling
0
KmWith Troika-schlepp
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW)
Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt Me 321 Glider


Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW)
Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt Me 321 Glider
General Info
-
-
-
- Me 321 A-1: single-pilot version; 100 built
- Me 321 B-1: had a crew of three (including co-pilot) and was armed with 2–4 × 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 15 machine-guns; 100 built
-
-
Dimensions
-
- Height: 10.15 m (33 ft 4 in)
- Wing area: 300 m2 (3,200 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 12,200 kg (26,896 lb)
- Gross weight: 34,400 kg (75,839 lb)
-
Performance
-
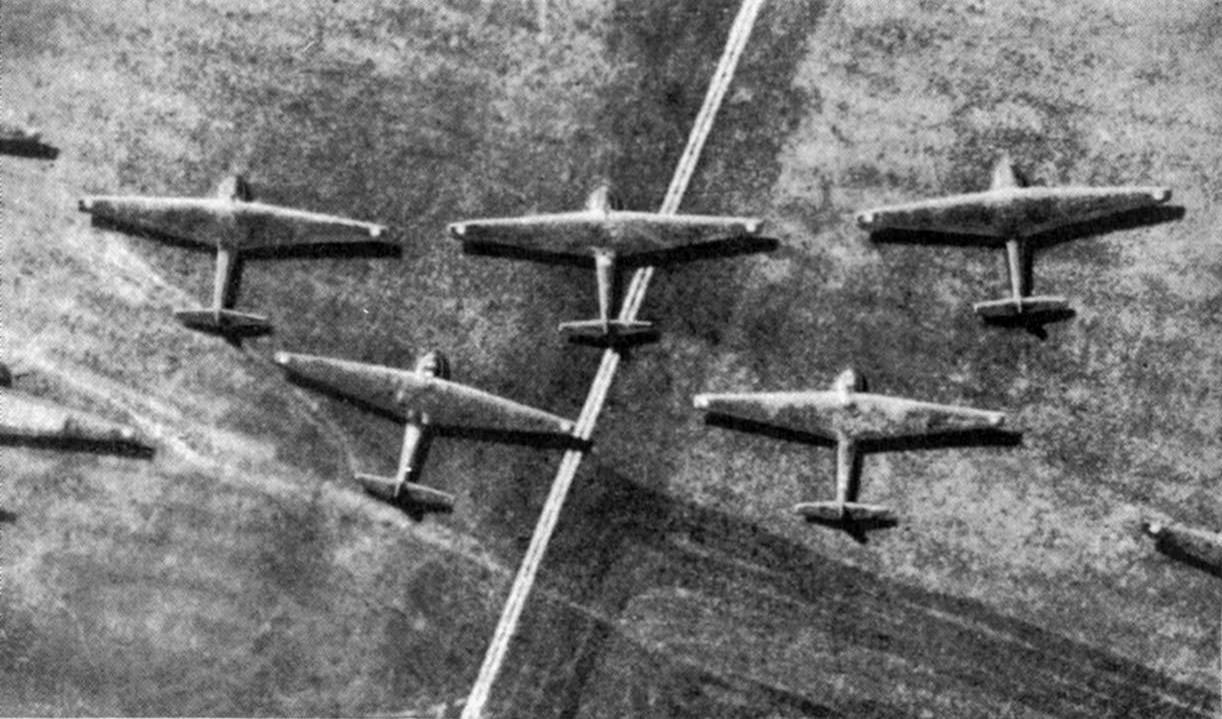
Rate of climb: 2.5 m/s (490 ft/min) when towed by three Messerschmitt Bf 110 aircraft in a Troika-schlepp (triple-tow) or
He 111 Zwilling - Maximum tow speed: 180 km/h (110 mph; 97 kn)
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The first Me 321 A-1 production aircraft entered service in May 1941 with Grossraumlastensegler 321 at Leipheim, initially towed by Ju 90s and later by the He 111Z and the Troikaschlepp arrangement of three Bf 110s.
Messerschmitt Me 321 Glider
The later Me 321 B-1 variant had a crew of three and was armed with four 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 15 machine guns.
Youtube Link
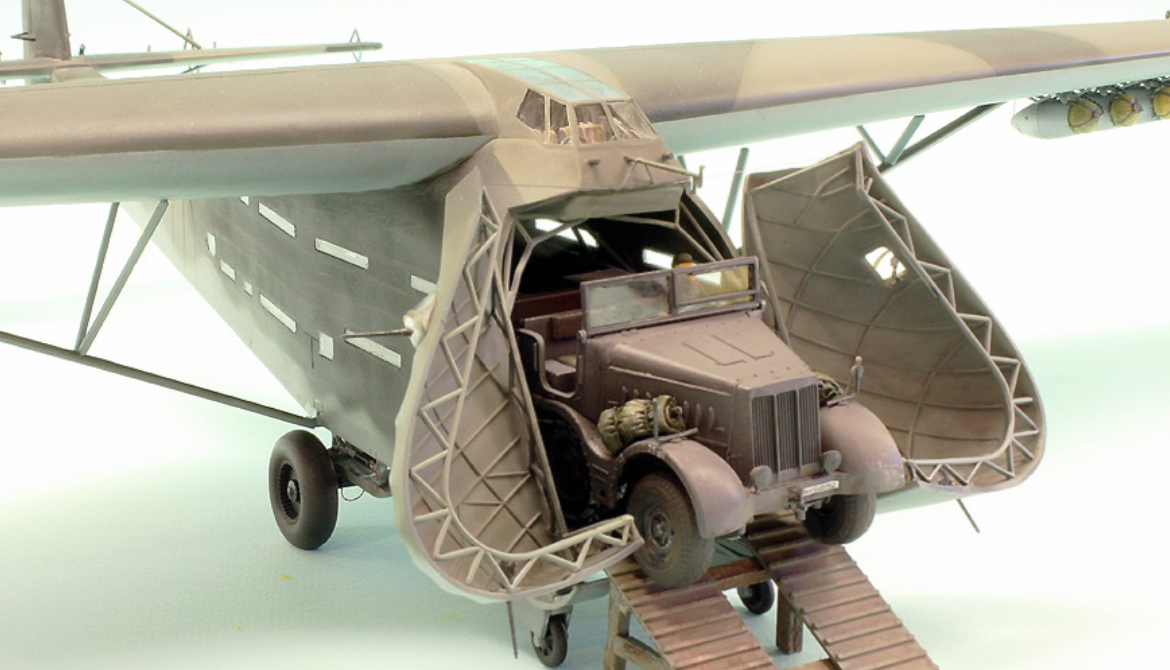
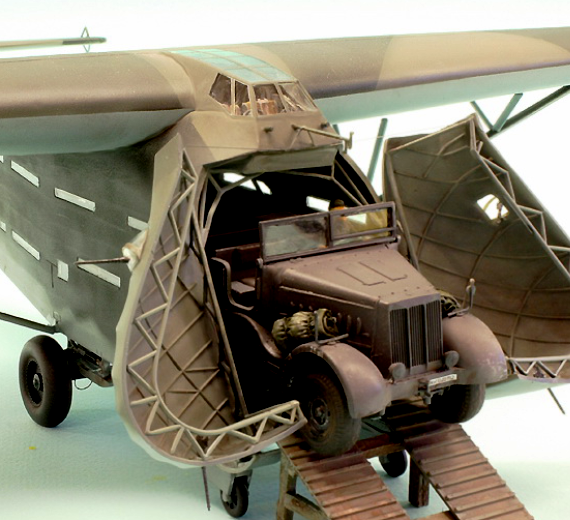
The Me 321 was fitted with a jettisonable undercarriage comprising two Bf 109 mainwheels at the front and two Junkers Ju 90 main wheels at the rear and was intended to land on four extendable skids.