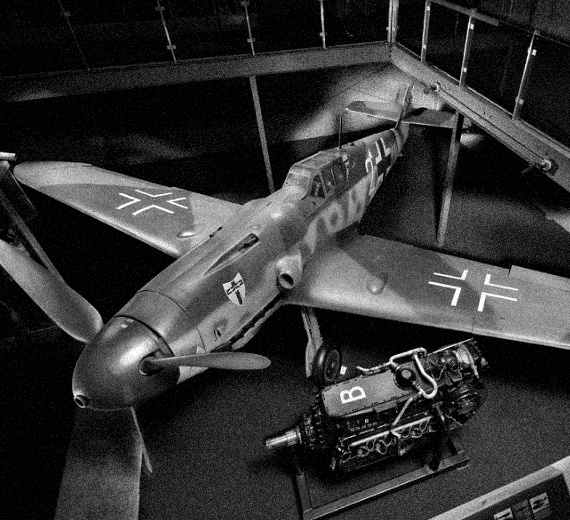
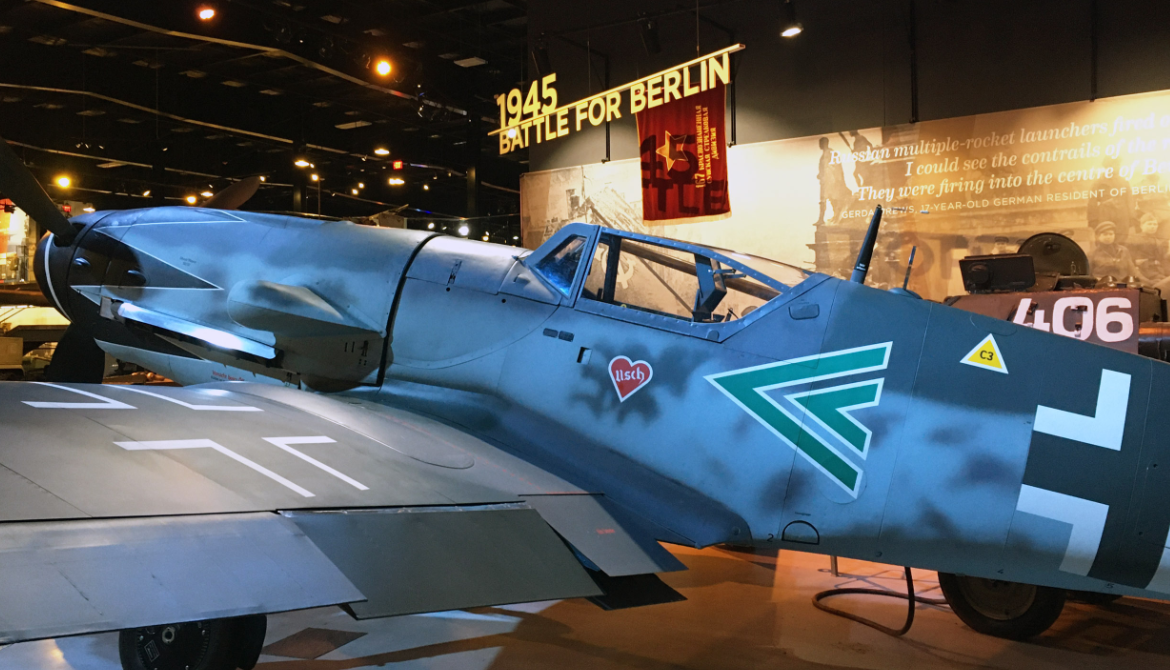
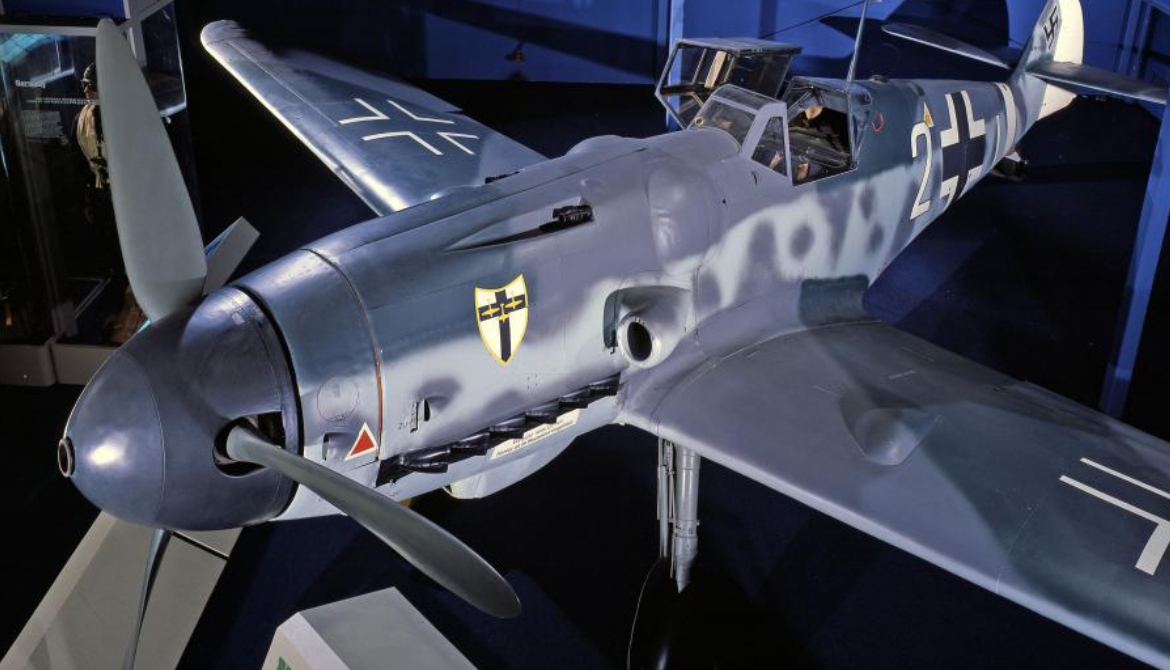
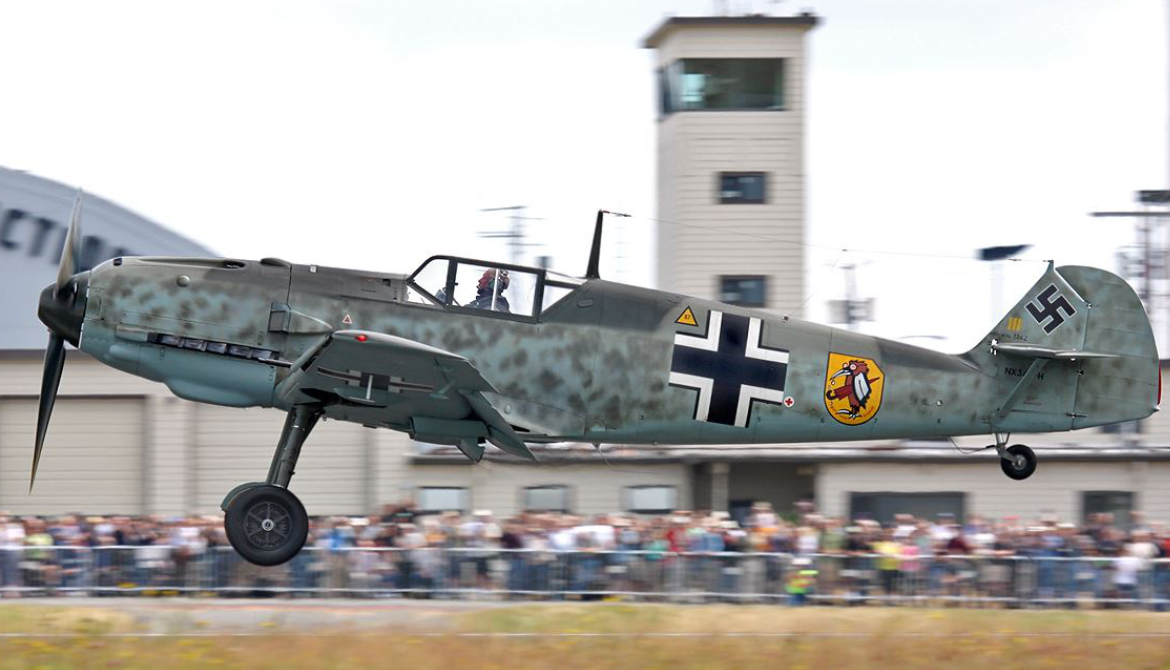
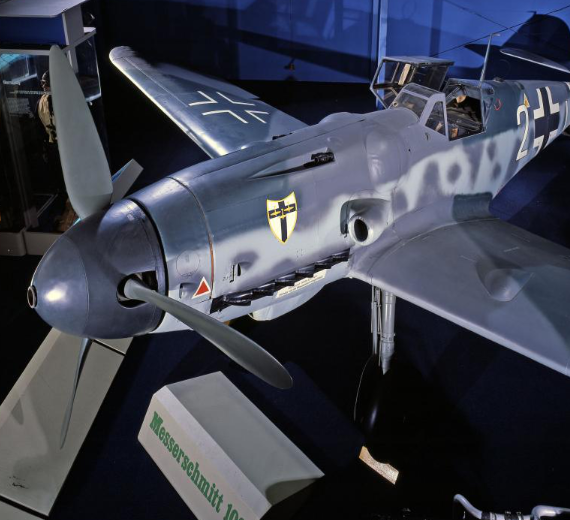
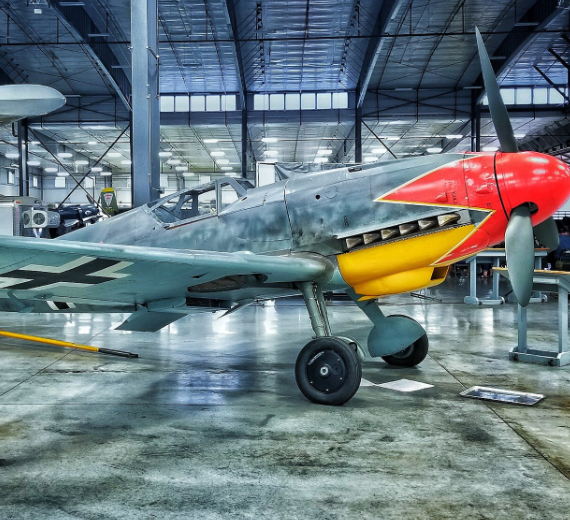
Messerschmitt
Bf 109G Gustaf
Role Fighter
Manufacturer Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW)
Messerschmitt AG
Designer Willy Messerschmitt,
First flight 29 May 1935
Introduction February 1937
Retired 9 May 1945, Luftwaffe
27
December 1965, Spanish Air Force
Primary users Luftwaffe
Royal Hungarian Air Force
National Republican Air Force
Royal Romanian Air Force
Number built 34,248 +603 Avia S-199
+239 HA-1112
Variants Avia S-99/S-199 Hispano Aviación HA-1112
.
History Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW)
Messerschmitt AG
Messerschmitt Bf 109 Gustaf

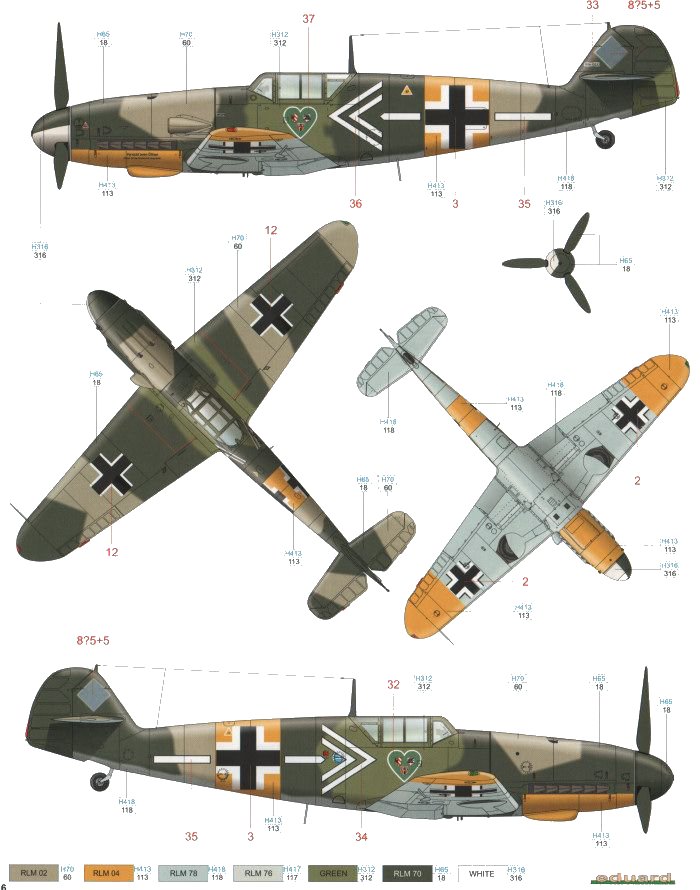
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a German World War II fighter aircraft that was, along with the Focke-Wulf Fw 190, the backbone of the Luftwaffe's fighter force. The Bf 109 first saw operational service in 1937 during the Spanish Civil War and was still in service at the end of World War II in 1945. It was one of the most advanced fighters when it first appeared, with an all-metal monocoque construction, a closed canopy, and retractable landing gear. It was powered by a liquid-cooled, inverted-V12 aero engine. It was called the Me 109 by Allied aircrew and some German aces, even though this was not the official German designation
The Bf 109 was flown by the three top-scoring fighter aces of all time, who claimed 928 victories among them while flying with Jagdgeschwader 52, mainly on the Eastern Front. The highest-scoring, Erich Hartmann, was credited with 352 victories. The aircraft was also flown by Hans-Joachim Marseille, the highest-scoring ace in the North African campaign who shot down 158 enemy aircraft (in about a third of the time). It was also flown by many aces from other countries fighting with Germany, notably the Finn Ilmari Juutilainen, the highest-scoring non-German ace. Pilots from Italy, Romania, Croatia, Bulgaria, and Hungary also flew the Bf 109. Through constant development, the Bf 109 remained competitive with the latest Allied fighter aircraft until the end of the war inspired by the design of the Messerschmitt Bf 109
Prototypes


Design work on Messerschmitt Project Number P.1034 began in March 1934, just three weeks after the development contract was awarded. The basic mock-up was completed by May, and a more detailed design mock-up was ready by January 1935. The RLM designated the design as type "Bf 109," the next available from a block of numbers assigned to BFW.
The first prototype (Versuchsflugzeug 1 or V1), with civilian registration D-IABI, was completed by May 1935, but the new German engines were not yet ready. To get the "R III" designs into the air, the RLM acquired four Rolls-Royce Kestrel VI engines by trading Rolls-Royce a Heinkel He 70 Blitz for use as an engine test-bed. Messerschmitt received two of these engines and adapted the engine mounts of V1 to take the V-12 engine upright. V1 made its maiden flight at the end of May 1935 at the airfield located in the southernmost Augsburg neighborhood of Haunstetten, piloted by Hans-Dietrich "Bubi" Knoetzsch. After four months of flight testing, the aircraft was delivered in September to the Luftwaffe's central test centre at the Erprobungsstelle Rechlin to take part in the design competition.
In 1935, the first Jumo engines became available, so V2 was completed in October using the 449 kW (610 PS; 602 hp) Jumo 210A engine. V3 followed, the first to be mounted with guns, but it did not fly until May 1936 due to a delay in procuring another Jumo 210 engine.0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW)
Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt Bf 109G Gustaf


Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW)
Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt Bf 109G Gustaf
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 1
- Length: 8.95 m (29 ft 4 in)
- Wingspan: 9.925 m (32 ft 7 in)
- Height: 2.6 m (8 ft 6 in)
- Wing area: 16.05 m2 (172.8 sq ft)
-
Powerplant
-
- Empty weight: 2,247 kg
- Gross weight: 3,148 kg
- Max takeoff weight: 3,400 kg
- Powerplant: 1 × Daimler-Benz DB 605A-1 V-12 inverted liquid-cooled piston engine 1,475 PS (1,455 hp; 1,085 kW)
- Propellers: 3-bladed VDM 9-12087, 3 m (9 ft 10 in) diameter light-alloy constant-speed propeller
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 520 km/h (320 mph,
-
-
- Cruise speed: 590 km/h (370 mph, 320 kn) at 6,000 m
- Range: 880–1,144 km
- Combat range: 440–572 km (273–355 mi, 238–309 nmi) 440-572 km to the front and back home
- Service ceiling: 12,000 m
Armament
-
Guns:
- 2 × 13 mm (.51 in) synchronized MG 131 machine guns 300
- 1 × 20 mm (.78 in) MG 151/20 cannon as centerline Motorkanone with 200
- 1 x 30 mm (1.18 in) MK 108 cannon as centerline Motorkanone with 65 rpg
- 2 × 20 mm MG 151/20 underwing cannon pods with 135 rpg
- Rockets: 2 × 21 cm (8 in)
- Bombs: 1 × 250 kg (551 lb) bomb or 4 × 50 kg (110 lb) bombs or 1 × 300-litre (79 US gal) drop tank
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The first Bf 109As served in the Spanish Civil War. By September 1939, the Bf 109 had become the main fighter of the Luftwaffe, replacing the biplane fighters, and was instrumental in gaining air superiority for the Wehrmacht during the early stages of the war.
Messerschnitt Bf
Bf 109G Gustaf
In February 1916, the south German engineering company MAN AG and several banks purchased the unprofitable aircraft builder Otto-Flugzeugwerke,
Youtube Link
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a German World War II fighter aircraft that was, along with the
Focke-Wulf Fw 190