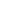Heading 3
World's aircraft enginesWikipedia link
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system
The Aircraft engines
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors.
Lockheed Martin Corp.
In commercial aviation the major Western manufacturers of turbofan engines are Pratt & Whitney (a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies), General Electric, Rolls-Royce, and CFM International (a joint venture of Safran Aircraft Engines and General Electric). Russian manufacturers include the United Engine Corporation, Aviadvigatel and Klimov. Aeroengine Corporation of China was formed in 2016 with the merger of several smaller companies. The largest manufacturer of turboprop engines for general aviation is Pratt & Whitney. General Electric announced in 2015 entrance into the market.
Created in 1917

| Part of a series on |
| Aircraft propulsion |
|---|
| Shaft engines: driving propellers, rotors, ducted fans or propfans |
|
|
|---|
Lockheed aircraft current and former.
Engines Types: from 1848 - present. 1848:
.
1848: John Stringfellow made a steam engine for a 10-foot wingspan model aircraft which achieved the first powered flight, albeit with negligible payload.
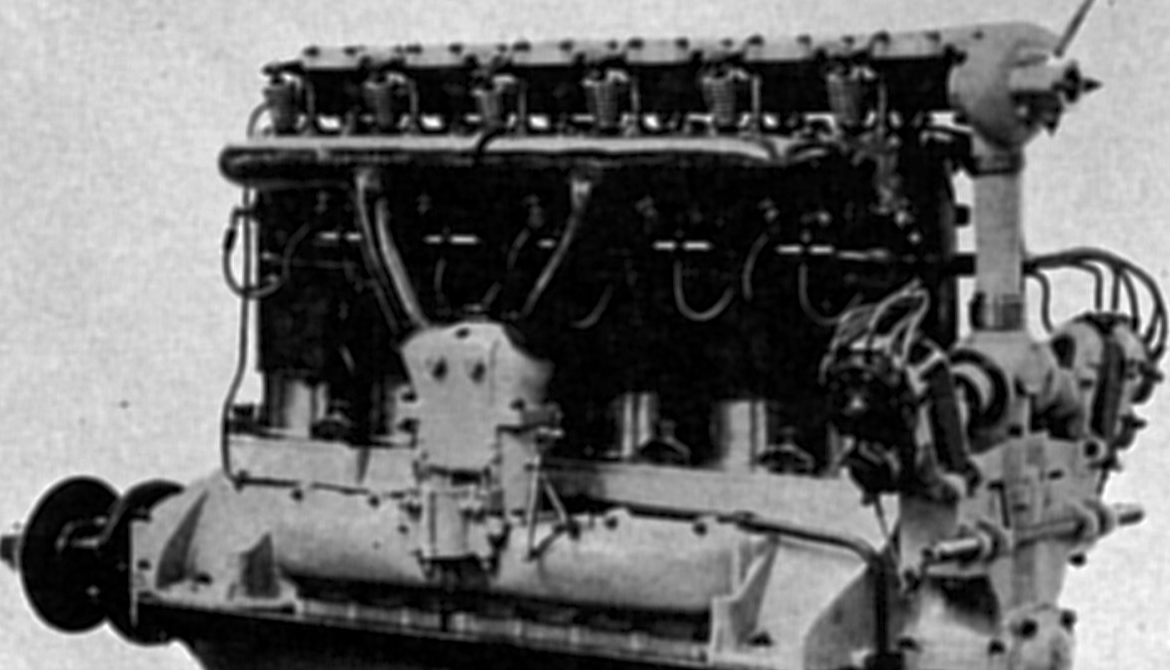
1903: Charlie Taylor built an inline engine, mostly of aluminum, for the Wright Flyer (12 horsepower).
1903: Manly-Balzer engine sets standards for later radial engines.
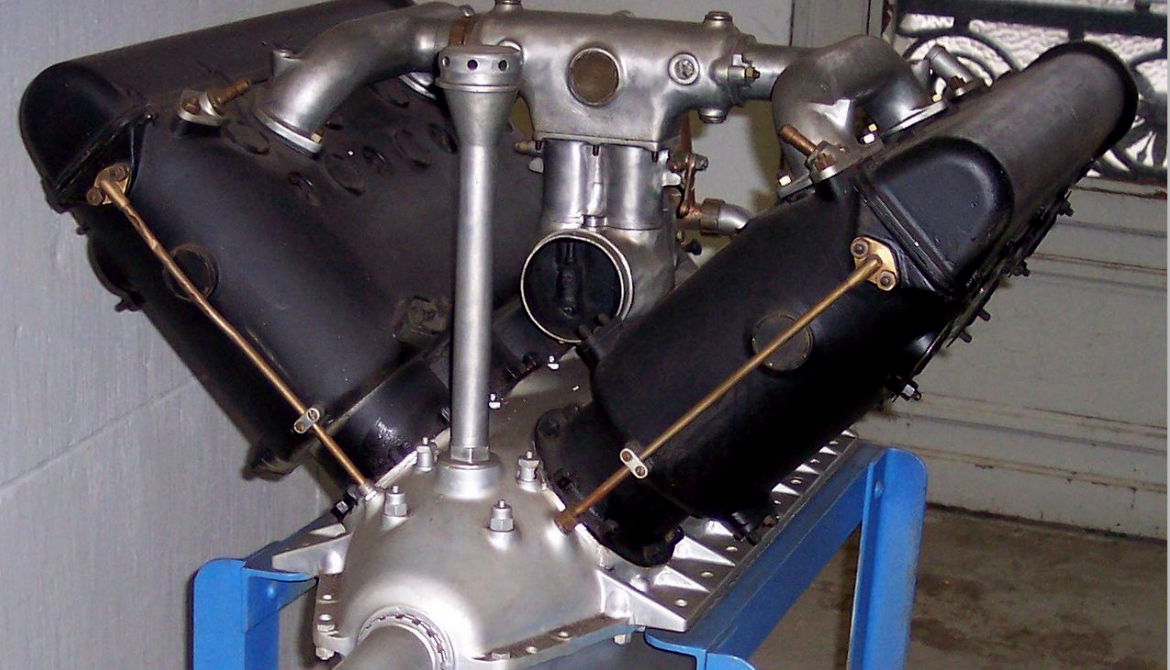
1906: Léon Levavasseur produces a successful water-cooled V8 engine for aircraft use.
1908: René Lorin patents a design for the ramjet engine.
1908: Louis Seguin designed the Gnome Omega, the world's first rotary engine to be produced in quantity. In
1909 a Gnome powered Farman III aircraft won the prize for the greatest non-stop distance flown at the Reims Grande Semaine d'Aviation setting a world record for endurance of 180 kilometres
(110 mi).
1910: Coandă-1910, an unsuccessful ducted fan aircraft exhibited at Paris Aero Salon,
powered by a piston engine. The aircraft never flew, but a patent was filed for
routing exhaust gases into the duct to augment thrust.
1914: Auguste Rateau suggests using exhaust-powered compressor – a turbocharger – to improve high-altitude performance; not accepted after the tests
1917-18: The Idflieg-numbered R.30/16 example of the Imperial German Luftstreitkräfte's Zeppelin-Staaken R.VI heavy bomber becomes the earliest known supercharger-equipped aircraft to fly,
with a Mercedes D.II straight-six engine in the central fuselage driving a Brown-Boveri mechanical supercharger for the R.30/16's four Mercedes D.IVa engines.
1918: Sanford Alexander Moss picks up Rateau's idea and creates the first successful turbocharger
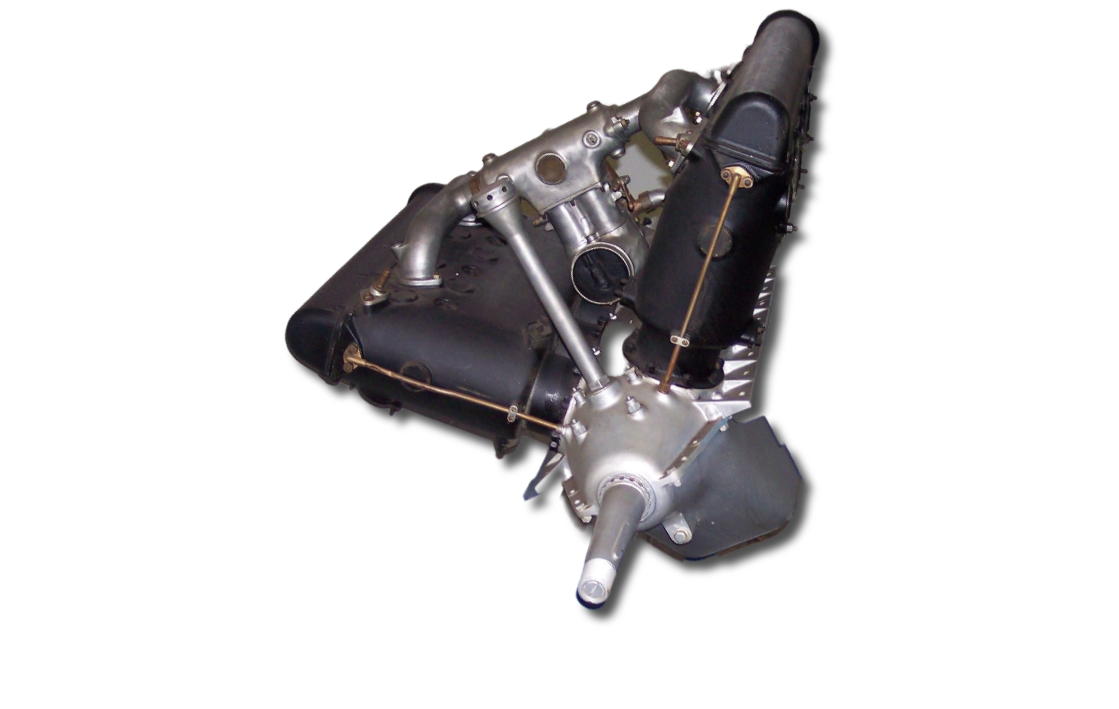
1926: Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar IV (S), the first series-produced supercharged engine for aircraft use;] two-row radial with a gear-driven centrifugal supercharger.
1930: Frank Whittle submitted his first patent for a turbojet engine.
June
1939: Heinkel He 176 is the first successful aircraft to fly powered solely by a liquid-fueled rocket engine.
Commercial aircraft
Photo Gallery
Aircraft engines
The Heinkel HeS 3 (HeS - Heinkel Strahltriebwerke) was the world's first operational jet engine to power an aircraft.
TheTurbofan engines.
August 1939: Heinkel HeS 3 turbojet propels the pioneering German Heinkel He 178 aircraft.
1940: Jendrassik Cs-1, the world's first run of a turboprop engine. It is not put into service.
1943 Daimler-Benz DB 670, first turbofan runs
1944: Messerschmitt Me 163B Komet, the world's first rocket-propelled combat aircraft deployed.
1945: First turboprop-powered aircraft flies, a modified Gloster Meteor with two Rolls-Royce Trent engines.
1947: Bell X-1 rocket-propelled aircraft exceeds the speed of sound.
1948: 100 shp 782, the first turboshaft engine to be applied to aircraft use; in 1950 used to develop the larger 280 shp (210 kW) Turbomeca Artouste.
1949: Leduc 010, the world's first ramjet-powered aircraft flight.
1950: Rolls-Royce Conway, the world's first production turbofan, enters service.
1968: General Electric TF39 high bypass turbofan enters service delivering greater thrust and much better efficiency.
2002: HyShot scramjet flew in dive.
2004: NASA X-43, the first scramjet to maintain altitude.
2020: Pipistrel E-811 is the first electric aircraft engine to be awarded a type certificate by EASA. It powers the Pipistrel Velis Electro, the first fully electric EASA type-certified aeroplane
Pratt & Whitney
Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company is a major unit of Lockheed Martin with in Fort Worth, Texas.

Whright Aeronautica
The Vickers VC10 is a mid-sized, narrow-body long-range British jet airliner.

Lockheed F-104 Starfighter
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nullam vitae congue tortor.

Lockheed Vega 5
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nullam vitae congue tortor.

Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nullam vitae congue tortor.

Lockheed C-5M Galaxy
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur<br> adipiscing elit. Nullam vitae congue



PRATT & WHITNEY
R-2000 TWIN WASP
General characteristics
Date
Country of Origin
United States of America)
Powerplant
Type
PROPULSION-
Radial engine
Specifications
Type: Twin-row radial engine, 14 cylinder
Bore: 5.75 in (146 mm)
Stroke: 5.5 in (140 mm)
Displacement: 2,004 in3 (32.84 L
Dimensions
Length: 61.02 in (1,550 mm)
Diameter: 49.49 in (1,257 mm)
Dry weight: 1,570 lb (710 kg)