.
History Rockwell-Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm
MBB X-31 experimental jet

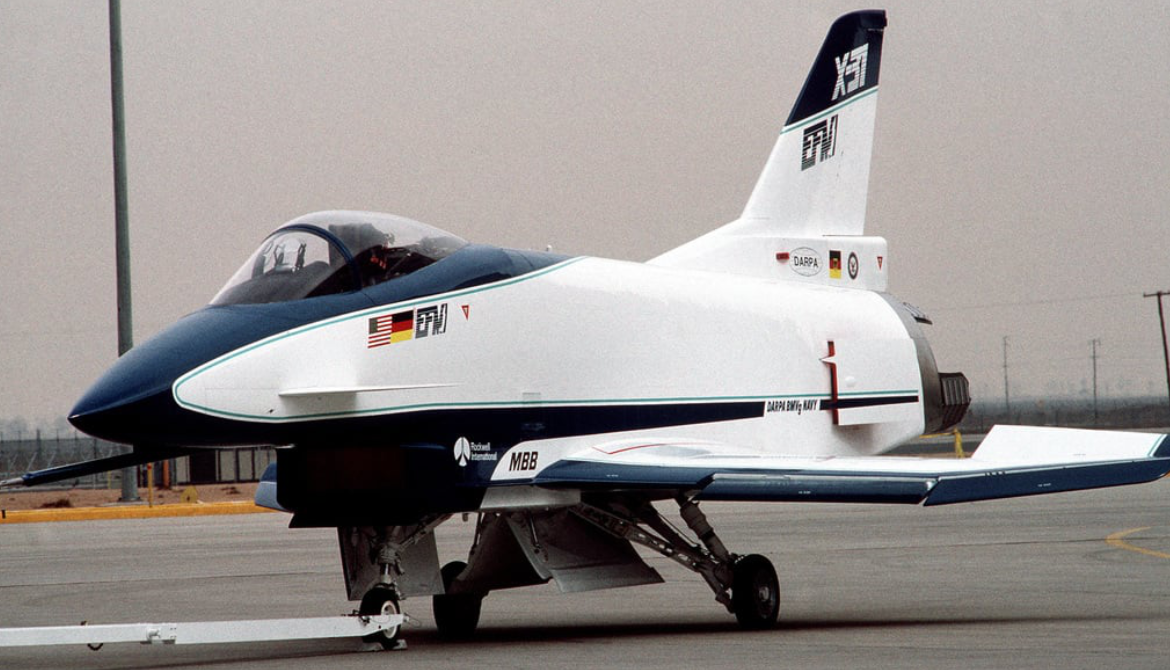
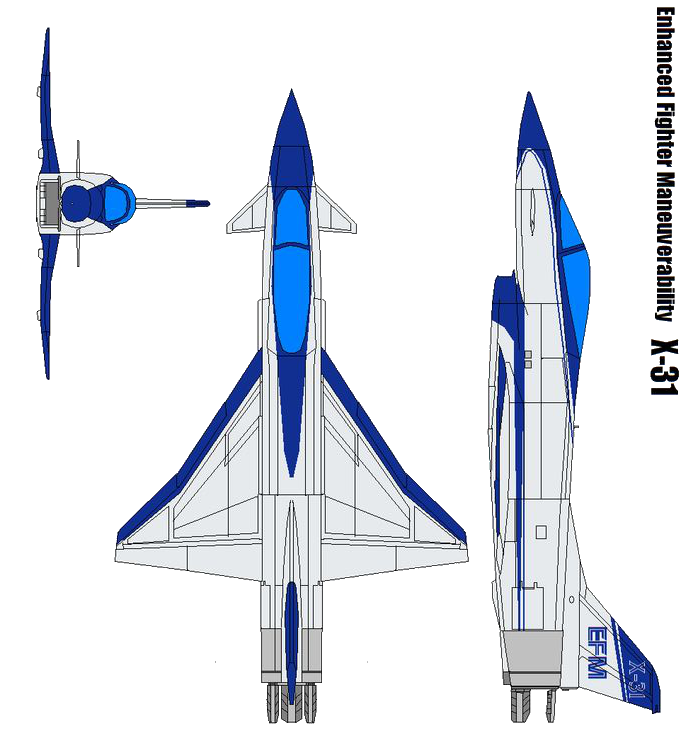
The Rockwell-Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm X-31 is an experimental jet fighter designed to test fighter thrust vectoring technology.
It was designed and built by Rockwell and Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB), as part of a joint US and German Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability program to provide additional control authority in pitch and yaw, for significantly more maneuverability than most conventional fighters. An advanced flight control system provided controlled flight at high angles of attack where conventional aircraft would stall or lose control. Two aircraft were built, of which only one has survived.
The X-31 design was essentially an all-new airframe design, although it borrowed heavily on design elements and sometimes actual parts of previous production, prototype, and conceptual aircraft designs, including the British Aerospace Experimental Airplane Programme (choice of wing type with canards, plus underfuselage intake), the German TKF-90 (wing planform concepts and underfuselage intake), F/A-18 Hornet (forebody, including cockpit, ejection seat, and canopy; electrical generators), F-16 Fighting Falcon (landing gear, fuel pump, rudder pedals, nosewheel tires, and emergency power unit), F-16XL (leading-edge flap drives), V-22 Osprey (control surface actuators), Cessna Citation (main landing gear's wheels and brakes), F-20 Tigershark (hydrazine emergency air-start system, later replaced) and B-1 Lancer (spindles from its control vanes used for the canards).
Prototypes

Aircraft built
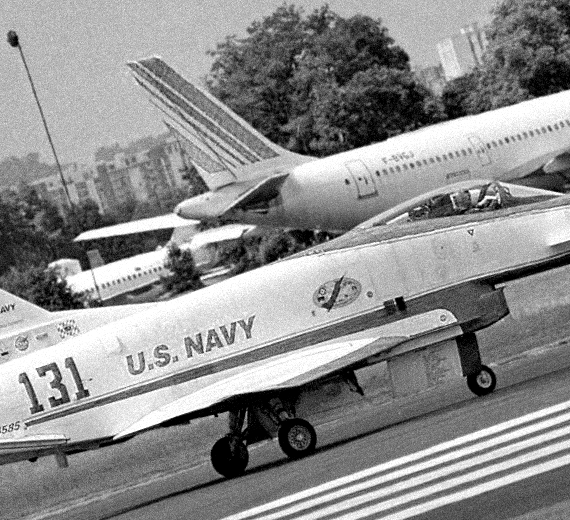
- BuNo 164584, 292 flights – crashed on January 19, 1995, north of Edwards AFB, California. The crash was caused by ice inside the pitot tube, sending incorrect airspeed data to the flight control computers. Contributing factors included the replacement of a heated pitot tube with an unheated Kiel probe, and ground crew/pilot ignorance of an option to override computer control. The pilot ejected safely. NASA issued in 2005 a film, "X-31: Breaking the Chain," reviewing the events. The novelty of the X-31 trials was computer control of its revolutionary flight controls (the canard wing and engine baffles) to effect maneuvers impossible for conventional jet fighters. The film discusses at length the combination of independent errors (e.g. that the accompanying chase pilot could not hear the test pilot's radio conversation with his base) in prompting loss of control, when the test pilot (correctly) ejected to save his life. Film of the crash shows the aircraft in unusual attitudes as the computer applied its false data to attempt to control flight after the pilot ejected.
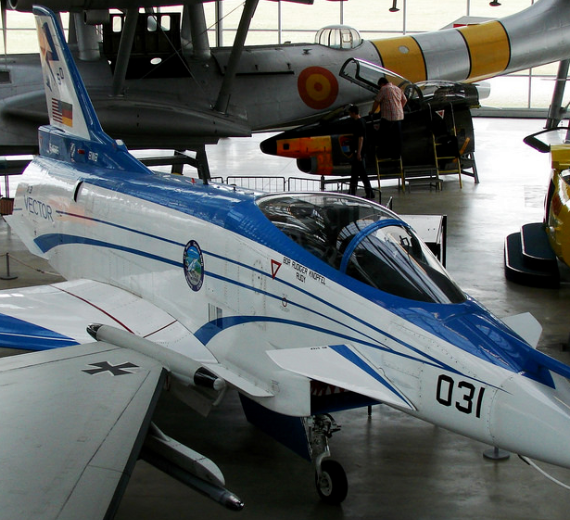
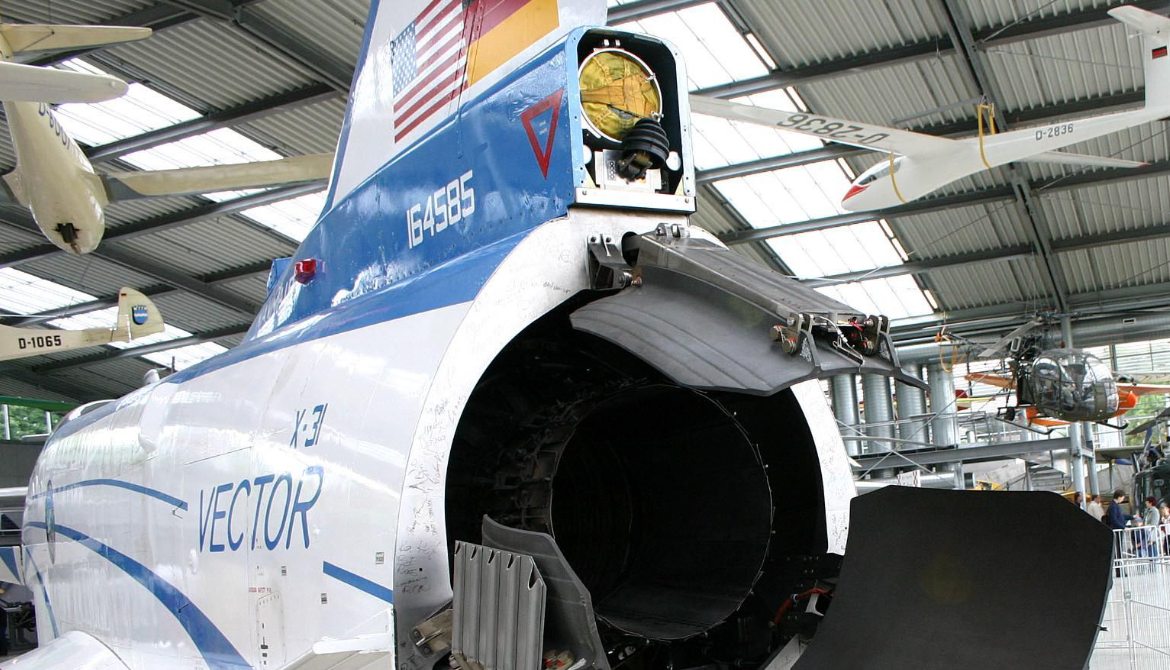
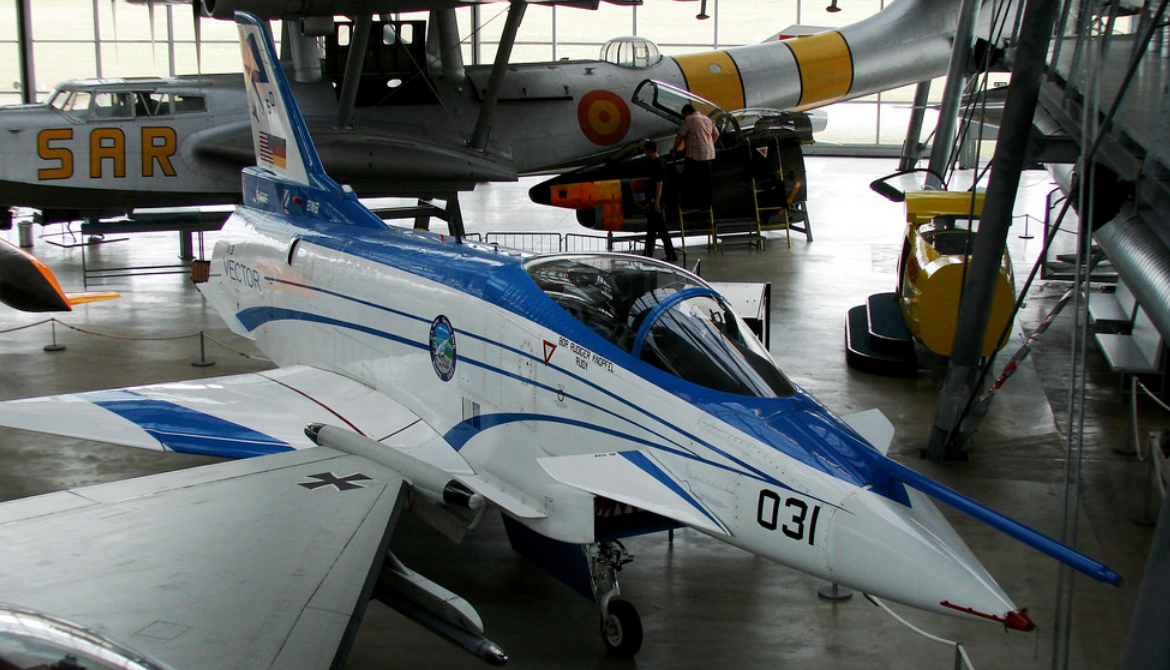
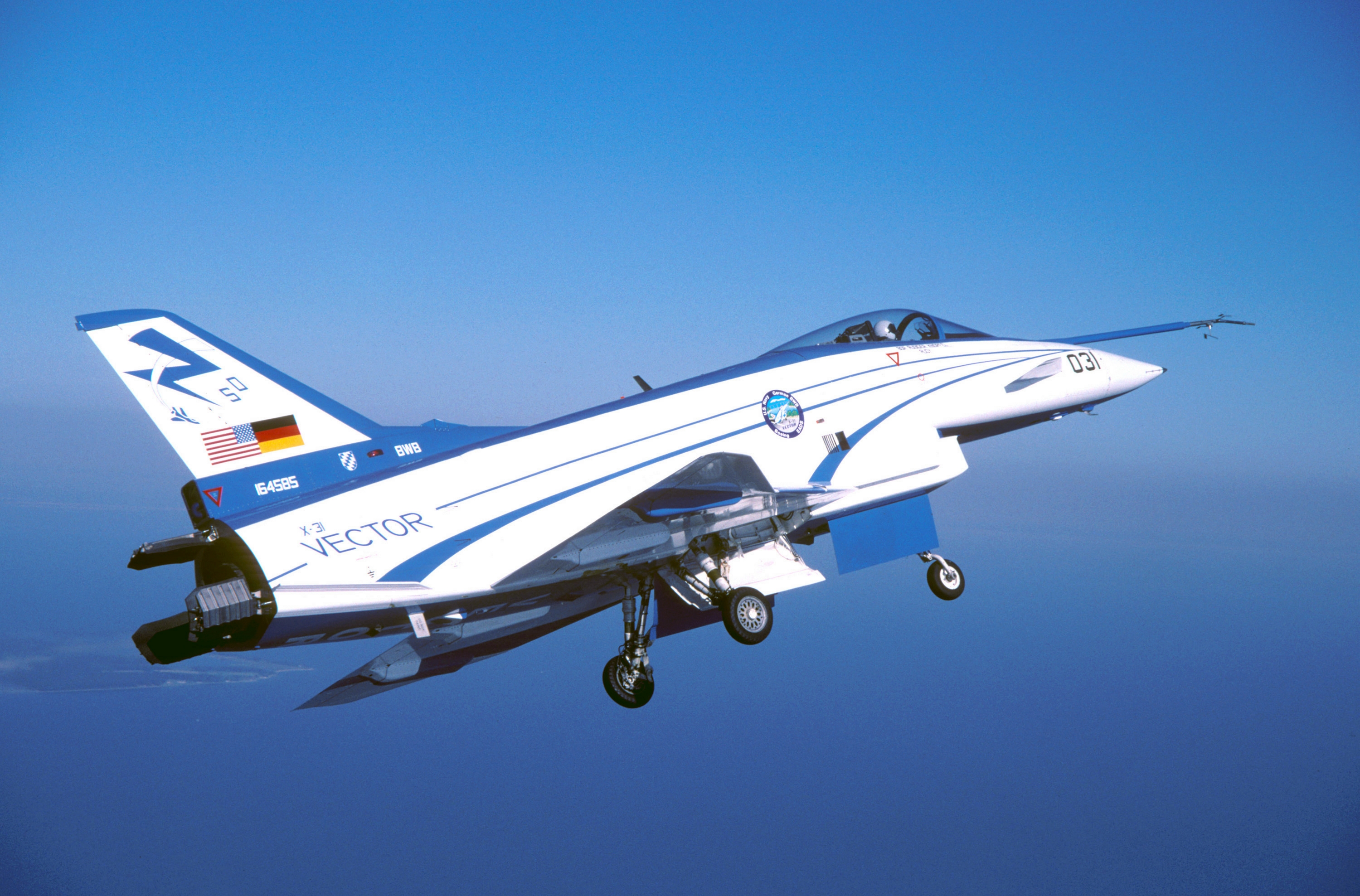
- BuNo 164585, 288 flights, the last one being in 2003. Put on permanent display at Deutsches Museum Flugwerft Schleissheim in Germany
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Rockwell-Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm X-31


Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW)
Messerschmitt
Rockwell-Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm X-31
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 1
- Length: 13.21 m (43 ft 4 in)
- Wingspan: 7.26 m (23 ft 10 in)
- Height: 4.44 m (14 ft 7 in)
- Wing area: 21.02 m2 (226.3 sq ft)
-
Powerplant
-
- Empty weight: 5,175 kg (11,409 lb)
- Gross weight: 6,622 kg (14,600 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 7,228 kg (15,935 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × General Electric F404-GE-400 turbofan engine, 71 kN (16,000 lbf) thrust
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,449 km/h (900 mph, 782 kn)
- Maximum speed: Mach 1.28
- Service ceiling: 12,200 m (40,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 218 m/s (42,900 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 315.0 kg/m2
.
Links to Youtube & Others
Two X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability demonstrators were test-flown during the early 1990s at NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, CA, to obtain data on control in the post-stall flight regime.
Rockwell-MBB
X-31 Demo
Angle of attack – AOA or alpha – describes the angle of an aircraft’s wings relative to the oncoming wind direction, or the path of the aircraft’s flight. In the X-31,
Youtube Link
During the program’s initial phase of operations at Rockwell International’s Palmdale facility, pilots flew the aircraft on 108 test missions.













