Vickers Limited
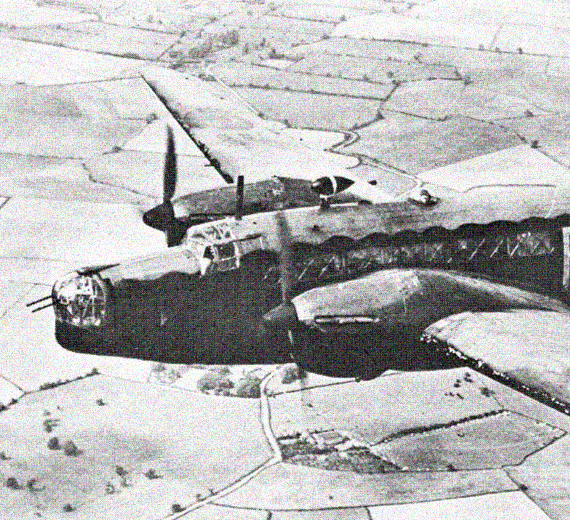
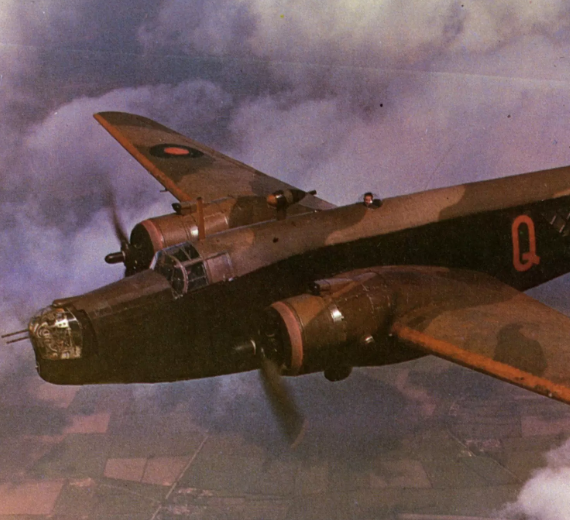
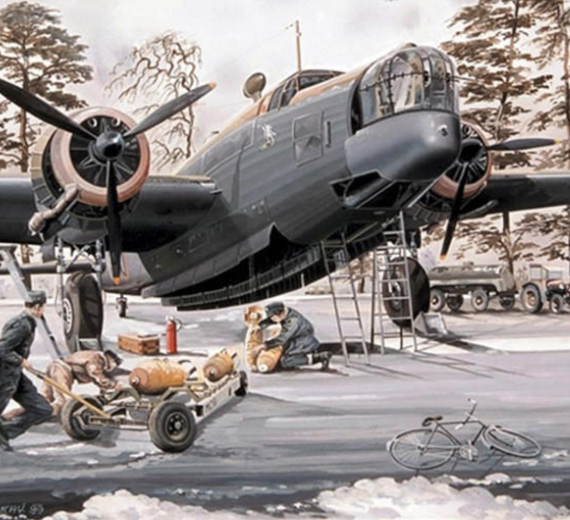
Wellington B Mark 1A
| Role | Medium bomber anti-submarine aircraft |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Vickers-Armstrongs |
| First flight | 15 June 1936 |
| Introduction | October 1938 |
| Retired | March 1953 |
| Primary users | Royal Air Force Royal Australian Air Force Royal Canadian Air Force Fleet Air Arm |
| Produced | 1936–1945 |
| Number built | 11,461 or 11,462 |
| Developed into | Vickers Warwick Vickers VC.1 Viking |
.
History Vickers Limited Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd
Wellington B Mark 1A the "Wimpey"

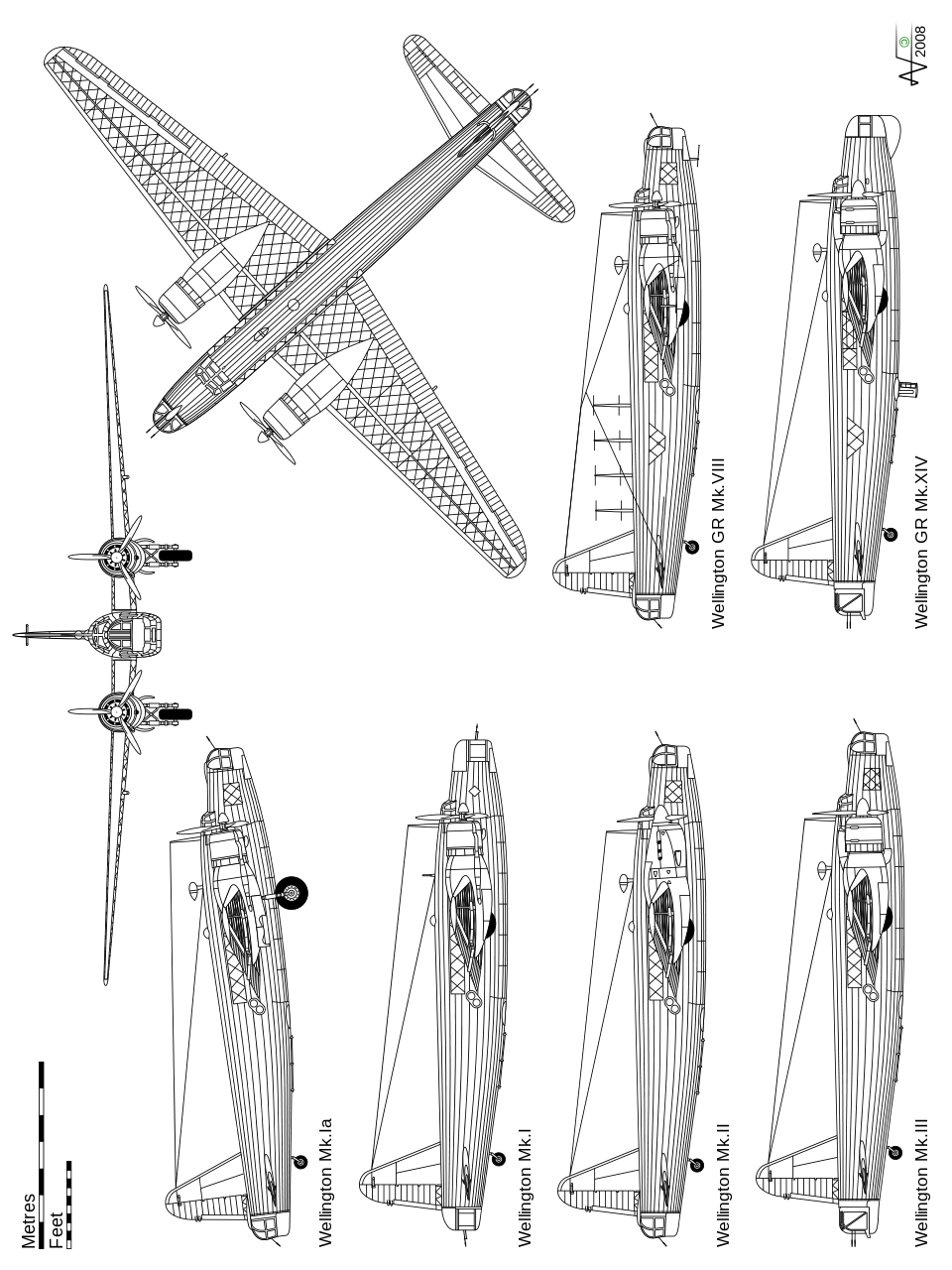
The Vickers Wellington was a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson; a key feature of the aircraft is its geodetic airframe fuselage structure, which was principally designed by Barnes Wallis. Development had been started in response to Air Ministry Specification B.9/32, issued in the middle of 1932, for a bomber for the Royal Air Force.
A larger heavy bomber aircraft designed to Specification B.1/35, the Vickers Warwick, was developed in parallel with the Wellington; the two aircraft shared around 85% of their structural components. Many elements of the Wellington were also re-used in a civil derivative, the Vickers VC.1 Viking.
Development


In October 1932, the British Air Ministry invited Vickers to tender for the recently issued Specification B.9/32, which sought a twin-engine medium daylight bomber. In response, Vickers conducted a design study, led by Chief Designer Rex Pierson. Early on, Vickers' chief structures designer Barnes Wallis proposed the use of a geodetic airframe, inspired by his previous work on airships and the single-engined Wellesley light bomber. During structural testing performed at the Royal Aircraft Establishment, Farnborough, the proposed structure demonstrated not only the required strength factor of six, but reached 11 without any sign of failure, proving the geodetic airframe to possess a strength far in excess of normal levels. This strength allowed for the structure design to be further developed to reduce the size of individual members and adopt simplified standard sections of lighter construction..

0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Vickers Limited Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd
Wellington B Mark 1A


Vickers Limited Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd
Vickers Wellington B Mark 1A
General Info
-
-
- Crew: five or six
- Length: 64 ft 7 in (19.69 m)
- Wingspan: 86 ft 2 in (26.26 m)
- Height: 17 ft 5 in (5.31 m)
- Wing area: 840 sq ft (78 m2)
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Empty weight: 18,556 lb (8,417 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: (12,927 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Bristol Pegasus Mark XVIII radial engines, 1,050 hp (780 kW) each
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 235 mph (378 km/h, 204 kn) at 15,500 ft (4,700 m)
- Range: 2,550 mi (4,100 km, 2,220 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 18,000 ft (5,500 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,120 ft/min (5.7 m/s)
Armament
-
-
Guns: 6–8× .303 (7.7 mm) "Browning .303 Mk II" machine guns:
- 2× in nose turret
- 2× in tail turret
- 2× in waist positions
- Bombs: 4,500 lb (2,000 kg) bombs
-
Guns: 6–8× .303 (7.7 mm) "Browning .303 Mk II" machine guns:
.
Links to Youtube & Others
In late 1960, the People's Republic of China had begun negotiations with Vickers for as many as 40 Viscounts, but negotiations were protracted due to political tensions
Vickers Ltd.
Wellington B Mark 1A
BEA, and its nationalised successor British Airways (BA), vigorously operated the Viscount on Britain's domestic routes
Youtube Link
The first airline in Latin America to operate the Viscount was Cubana de Aviación. Cubana's −755D Viscounts, delivered in 1956,