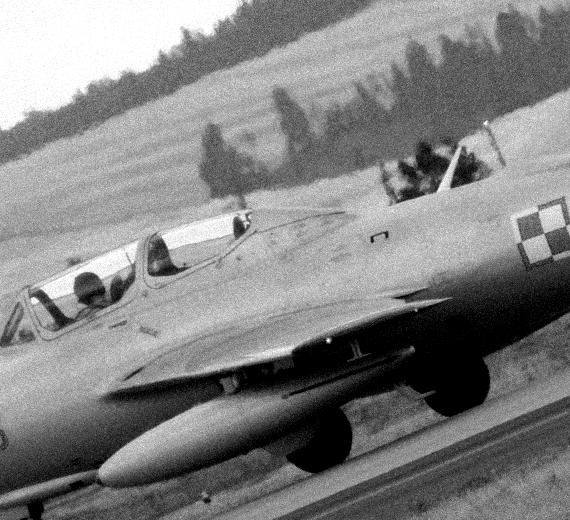
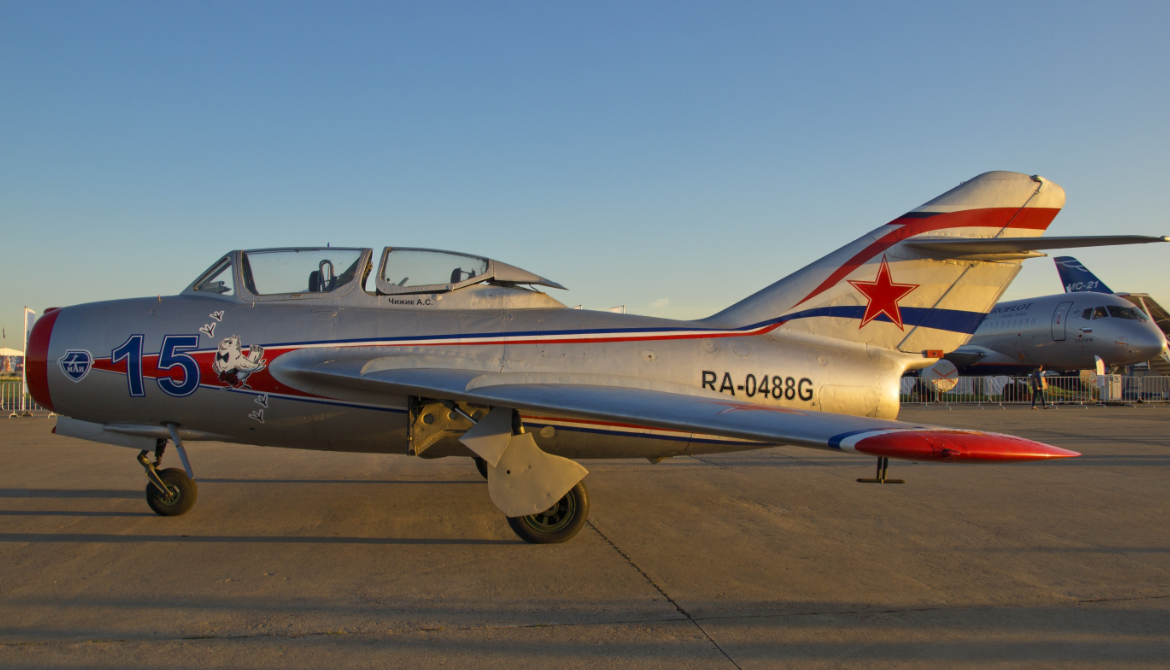
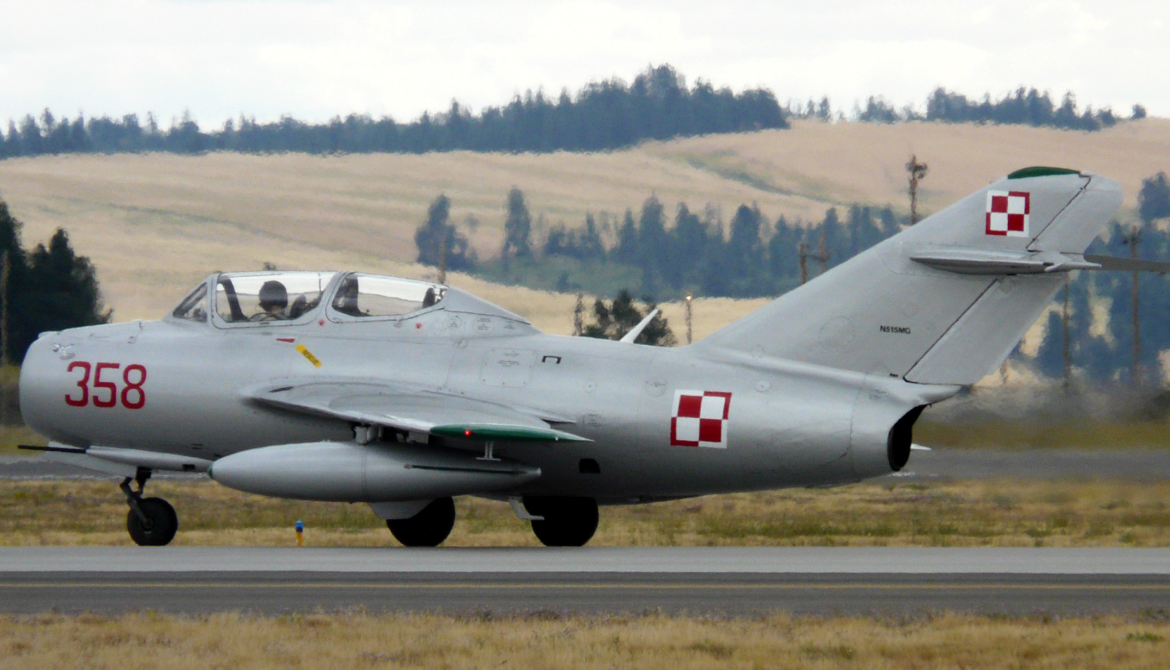
PZL Mielec
SBLim-2/MiG-15UTI
Role Fighter aircraft
National origin Soviet Union
Manufacturer Mikoyan-Gurevich
First flight 30 December 1947
Introduction 1949
Status In limited service with the
Korean People's Army Air Force
Primary users Soviet Air Forces
People's Liberation Army Air Force Korean People's Air Force
Number built 13,130 in the USSR
+ at least 4,180 under license
Developed into Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17
.
History WSK "PZL-Mielec
PZL Mielec
SBLim-2/MiG-15UTI

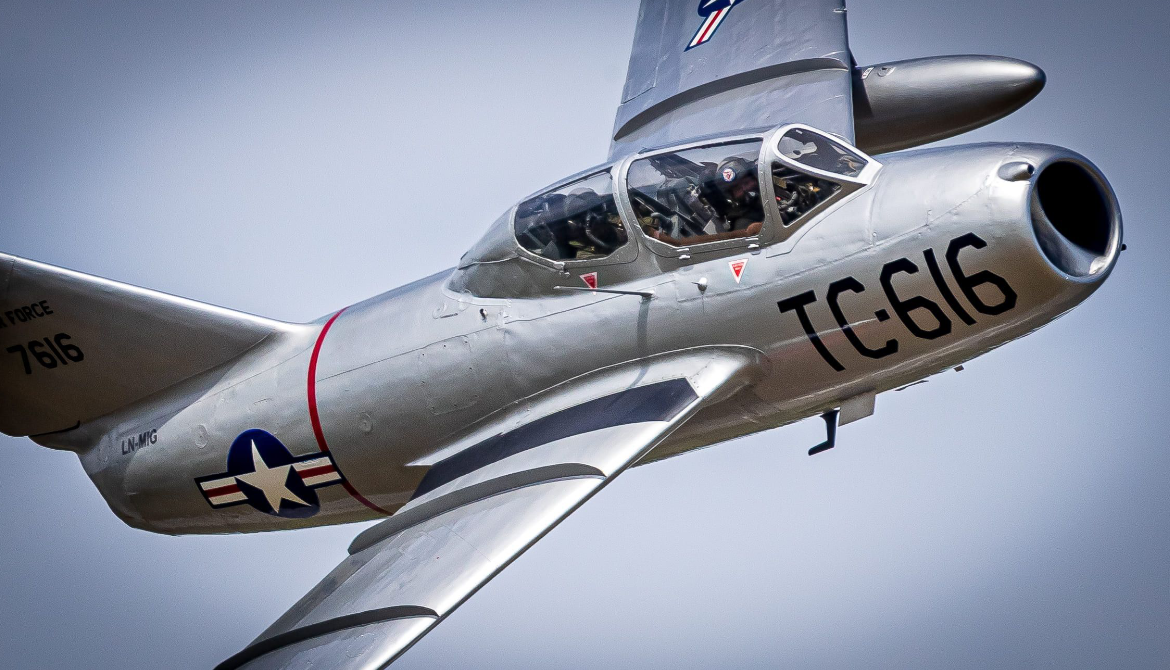
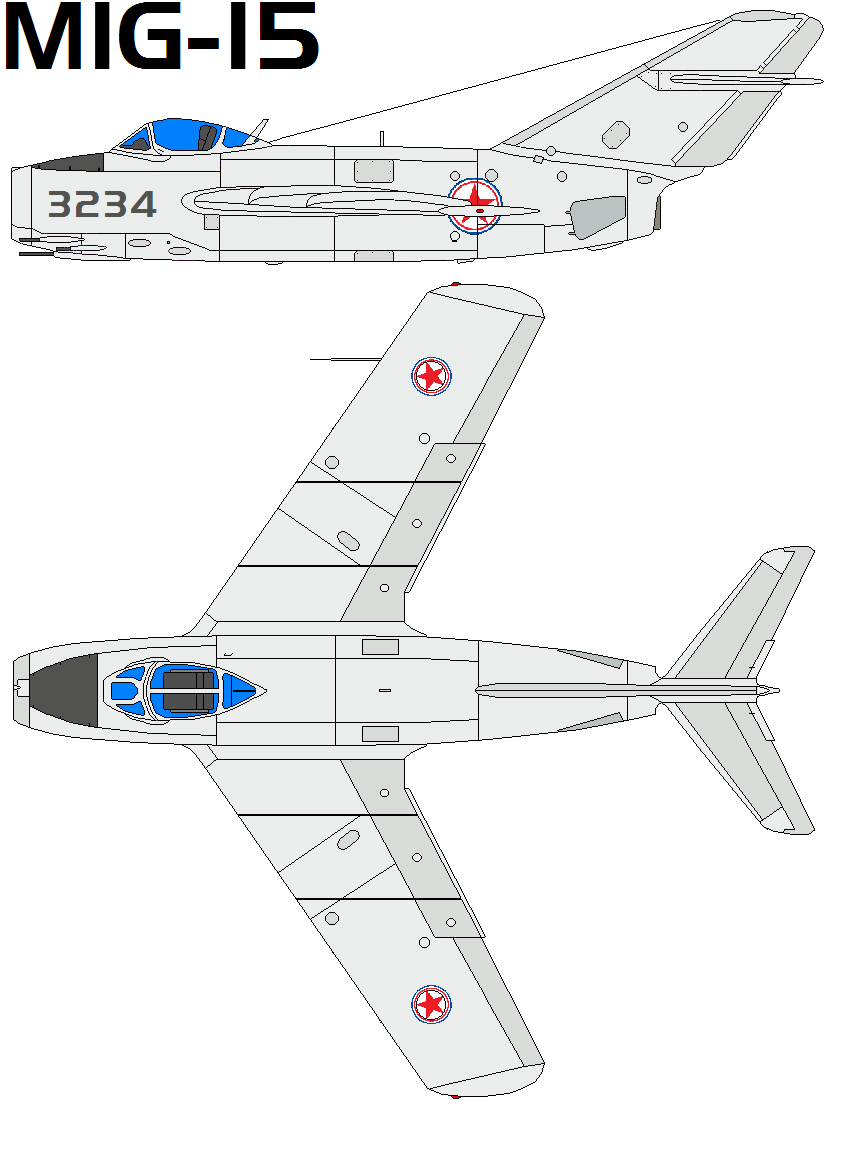
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15 (Russian: Микоя́н и Гуре́вич МиГ-15; USAF/DoD designation: Type 14; NATO reporting name: Fagot) is a jet fighter aircraft developed by Mikoyan-Gurevich for the Soviet Union. The MiG-15 was one of the first successful jet fighters to incorporate swept wings to achieve high transonic speeds. In aerial combat during the Korean War, it outclassed straight-winged jet day fighters, which were largely relegated to ground-attack roles. In response to the MiG-15's appearance and in order to counter it, the United States Air Force rushed the North American F-86 Sabre to Korea
The Germans had been unable to develop airworthy turbojets with thrust over 1,130 kilograms-force (11,100 N; 2,500 lbf) capable of running for more than a few hours at the time of the surrender in May 1945, which limited the performance of immediate Soviet postwar jet aircraft designs. The Soviet aviation minister Mikhail Khrunichev and aircraft designer A. S. Yakovlev suggested to Premier Joseph Stalin that the USSR buy the reliable, fully developed, Nene engines from Rolls-Royce (having been alerted to the fact that the U.K. Labour government wanted to improve post-war UK-Russia foreign relations) for the purpose of copying them in a minimum of time. Stalin is said to have replied, "What fool will sell us his secrets?

To take advantage of the new engine, the Council of Ministers ordered the Mikoyan-Gurevich OKB to build two prototypes for an advanced high-altitude daytime interceptor to defend against bombers. It was to have a top speed of 1,000 kilometres per hour (620 mph) and a range of 1,200 kilometres (750 mi).
Designers at MiG's OKB-155 started with the earlier MiG-9 jet fighter. The new fighter used Klimov's British-derived engines, swept wings, and a tailpipe going all the way back to a swept tail. The German Me 262 was the first fighter fitted with an 18.5° wing sweep, but it was introduced merely to adjust the center of gravity of its heavy Junkers Jumo 004 pioneering axial-compressor turbojet engines. Further experience and research during World War II later established that swept wings would give better performance at transonic speeds. At the end of World War II, the Soviets seized many of the assets of Germany's aircraft industry. The MiG team studied these plans, prototypes and documents, particularly swept-wing research and designs, even going so far as to produce a flying testbed in 1945 to investigate swept-wing design concepts as the piston-engined "pusher"-layout, MiG-8 Utka (Russian for "duck", from its tail-first canard design). The swept wing later proved to have a decisive performance advantage over straight-winged jet fighters when it was introduced into combat over Korea.0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
WSK "PZL-Mielec
PZL Mielec
SBLim-2/MiG-15UTI


WSK "PZL-Mielec
PZL Mielec
SBLim-2/MiG-15UTI
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 1
- Length: 10.102 m (33 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 10.085 m (33 ft 1 in)
- Height: 3.7 m (12 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 20.6 m2 (222 sq ft)
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Empty weight: 3,681 kg (8,115 lb)
- Gross weight: 5,044 kg (11,120 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 6,106 kg (13,461 lb) with 2x600 L (160 US gal; 130 imp gal) drop-tanks
- Fuel capacity: 1,420 L (380 US gal; 310 imp gal) internal
- Powerplant: 1 × Klimov VK-1 centrifugal-flow turbojet, 26.5 kN (5,950 lbf) thrust
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,076 km/h (669 mph, 581 kn) at sea level
-
-
-
- 1,107 km/h (688 mph; 598 kn) / M0.9 at 3,000 m (9,843 ft)
-
-
- Maximum speed: Mach 0.87 at sea level
- Cruise speed: 850 km/h (530 mph, 460 kn) Mach 0.69
- Ferry range: 2,520 km (1,570 mi, 1,360 nmi) at 12,000 m (39,370 ft) with 2x600 L (160 US gal; 130 imp gal) drop-tanks
- Service ceiling: 15,500 m (50,900 ft)
Armament
- Guns:
- 2 × 23 mm Nudelman-Rikhter NR-23 autocannon in the lower left fuselage (80 rounds per gun, 160 rounds total)
- 1 × 37 mm Nudelman N-37 autocannon in the lower right fuselage (40 rounds total)
- Hardpoints: 2 , with provisions to carry combinations of:
- Bombs: 100 kg (220 lb) bombs
- Other: drop tanks, or unguided rockets
.
Links to Youtube & Others
After the MiG-15 entered the war, it was shown to be clearly superior to the best straight-wing jets operated by other countries, including the Gloster Meteor, Lockheed F-80, Republic F-84 and Grumman F9F. In most measures of performance, the North American F-86 Sabre – which was also a swept-wing design – was the only close contemporary that could match the MiG-15.
PZL Mielec
SBLim-2/MiG-15UTI
The USAF has claimed that the F-86 had the advantage in combat kills over Korea between 1950 and 1953
Youtube Link
On 1 November 1950, the 50th IAD joined the war with its MiG-15s – their noses painted red and in North Korean markings. That day, eight MiG-15s intercepted about 15 USAF F-51D Mustangs