.
History WSK "PZL-Mielec
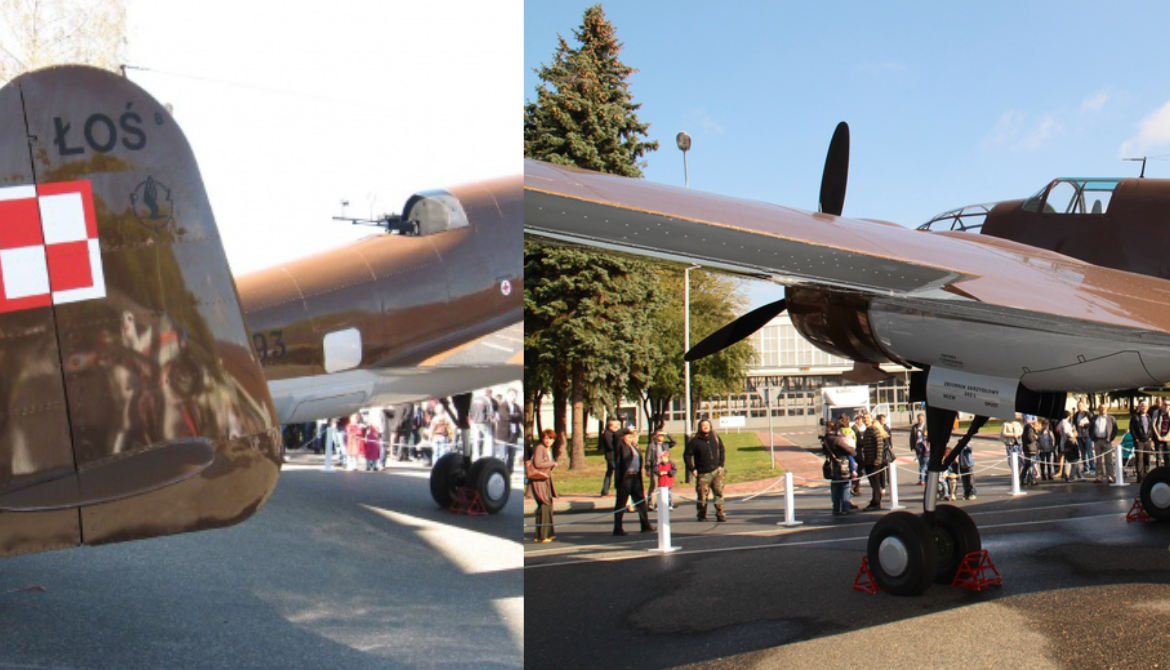
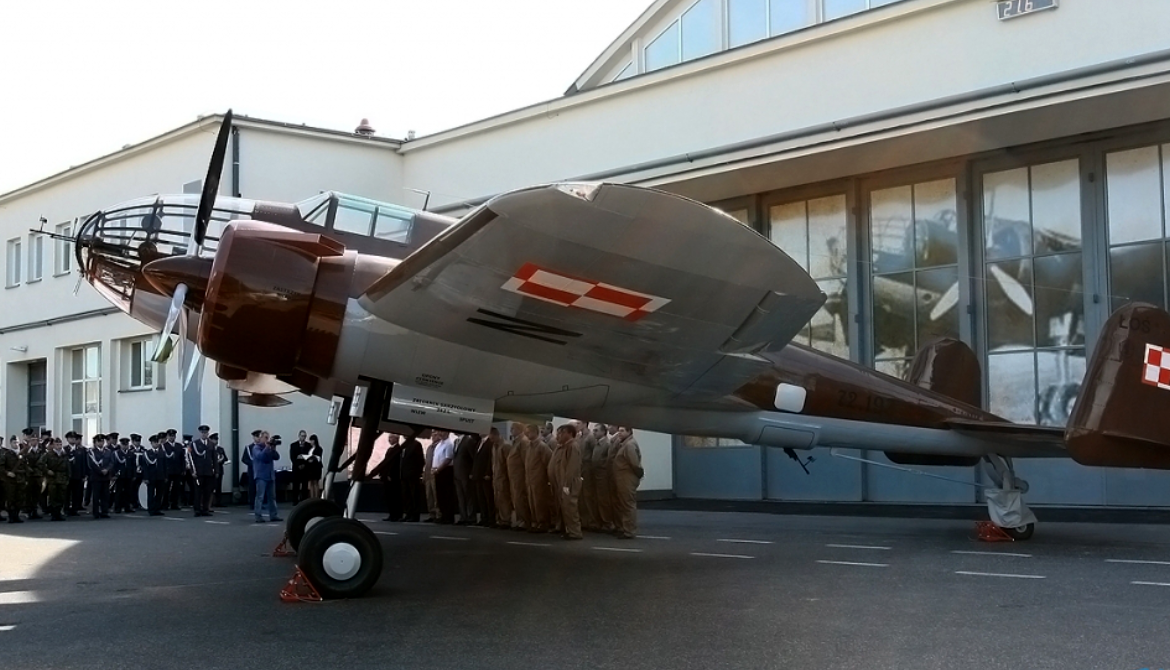
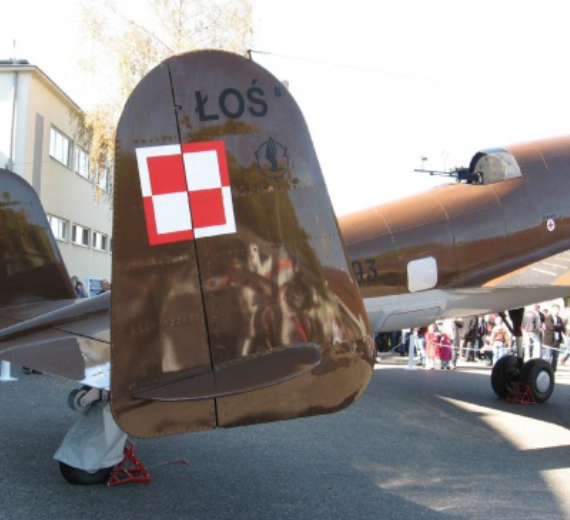
PZL.37 Łoś "Moose"

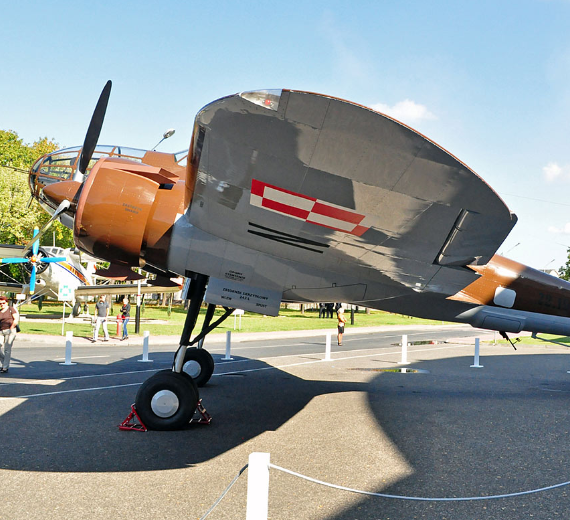
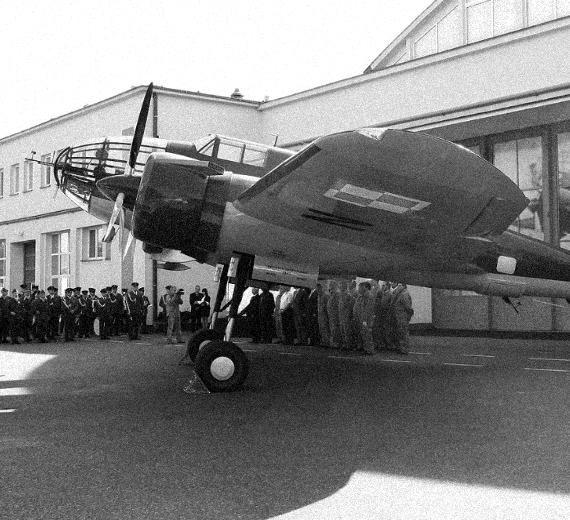
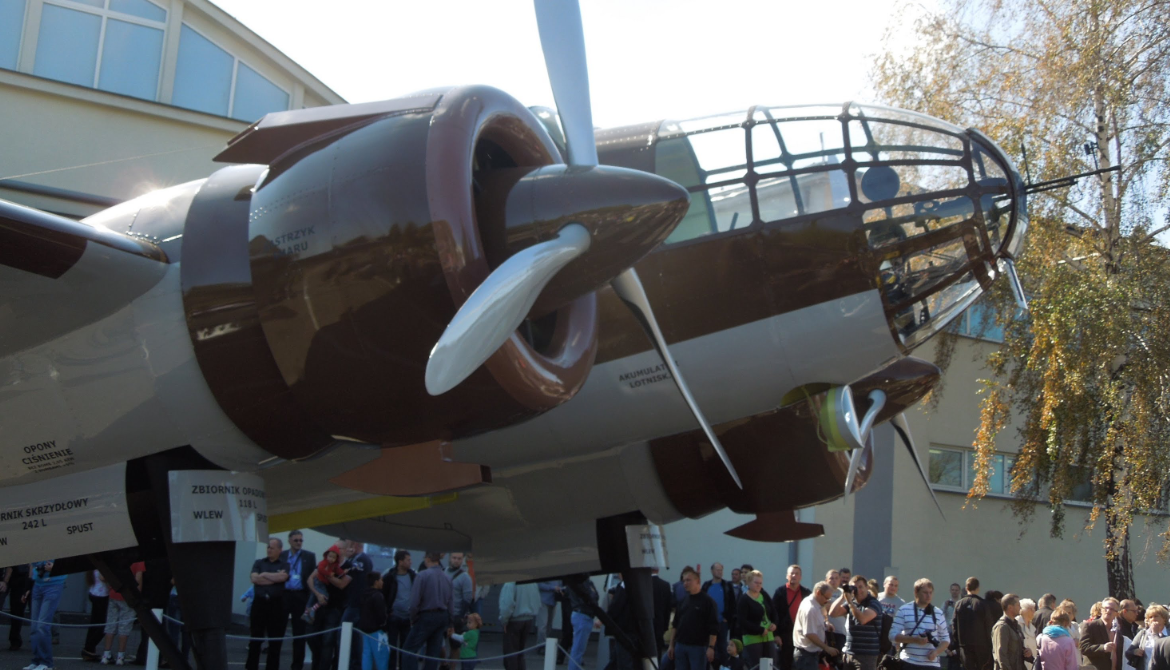
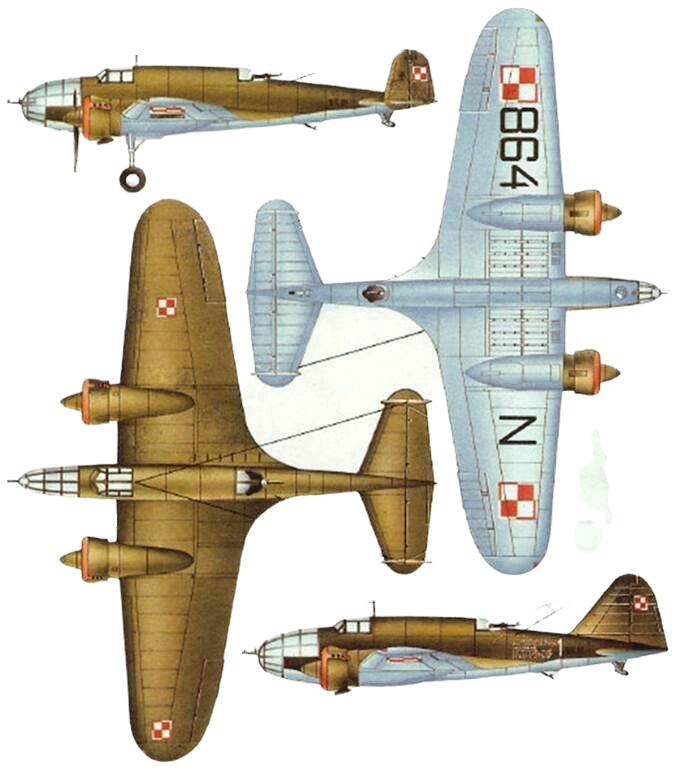
The PZL.37 Łoś (moose) was a Polish twin-engined medium bomber designed and manufactured by national aircraft company PZL. It is also known as "PZL P-37" or "PZL P.37", but the letter "P" was generally reserved for fighters of Zygmunt Puławski's design (such as the PZL P.11).
The Łoś was extensively used in the defense of Poland during the rapid invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany in September 1939. On 1 September 1939, the Polish Air Force had roughly 86 PZL.37s in total, but less than a half of those actually saw active combat use due to aircraft being used by training units, being in maintenance, or having been held in reserve. The bombers suffered from a high attrition rate due to lack of fighter protection, and the final Polish combat missions were performed on 19 September. During October 1940, around 26-27 of the PZL.37s that had been evacuated from Poland were seized by the Romanian government and 23 of these aircraft were subsequently used by the Royal Romanian Air Force, including offensive missions against the Soviet Union.
Design

0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
WSK "PZL-Mielec
PZL.37 Łoś "Moose"


WSK "PZL-Mielec
PZL.37 Łoś "Moose"
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 4
- Length: 12.92 m (42 ft 5 in)
- Wingspan: 17.93 m (58 ft 10 in)
- Height: 5.1 m (16 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 53.5 m2 (576 sq ft)
-
Powerplant
-
- Empty weight: 4,280 kg (9,436 lb)
- Gross weight: 8,865 kg (19,544 lb) basic combat loading
- Max takeoff weight: 9,105 kg (20,073 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × PZL Pegasus XX 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 723 kW (970 hp) each
- Propellers: 3-bladed variable-pitch propellers
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 412 km/h (256 mph, 222 kn) 2,800 m (9,186 ft) with 1,995 kg (4,398 lb) bomb load
- Range: 2,600 km (1,600 mi, 1,400 nmi)
- Combat range: 1,000 km (620 mi, 540 nmi) with 1,760 kg (3,880 lb) bomb load and extra fuel tanks
- Service ceiling: 7,000 m (23,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 4.7 m/s (930 ft/min)
Armament
- 3 x 7.92 mm observer's machine gun: 1 in the nose, 1 in the rear upper station, 1 in underbelly station
- Up to 2,580 kg (5,690 lb) of bombs (18 x 110 kg + 2 x 300 kg). Basic load 20 x 110 kg = 2,200 kg (4850 lb). Bomb load while operating from unprepared fields 880–1320 kg (1,940–2,910 lb) (8, 10 or 12 x 110 kg)
.
Links to Youtube & Others
Production of the Łoś commenced during the winter of 1936-1937.[14] During 1938, the first 10 serial aircraft were manufactured, designated as the PZL.37A; these were furnished with a single vertical stabilizer.
PZL.37 Łoś "Moose"
During early 1938, the Polish Air Force started to receive the Łos A variant;[19] it was followed by deliveries of the improved PZL.37B to operational units
Youtube Link
During early 1938, the Polish Air Force started to receive the Łos A variant;[19] it was followed by deliveries of the improved PZL.37B to operational units