Heinkel Flugzeugwerke Heinkel He-111 Bomber
| Role | Medium bomber |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Heinkel Flugzeugwerke |
| Designer | Siegfried and Walter Günter |
| First flight | 24 February 1935 |
| Introduction | 1935 |
| Retired | 1945 (Luftwaffe) 1958 (Spain) |
| Primary user | Luftwaffe |
| Produced | 1935–1944 |
| Number built | 32 prototype aircraft 12 civilian airliners 808 pre-war aircraft 5,656 aircraft (1939–1944) Total: 6,508 |
| Variants | CASA 2.111 |
.
History Heinkel Flugzeugwerke
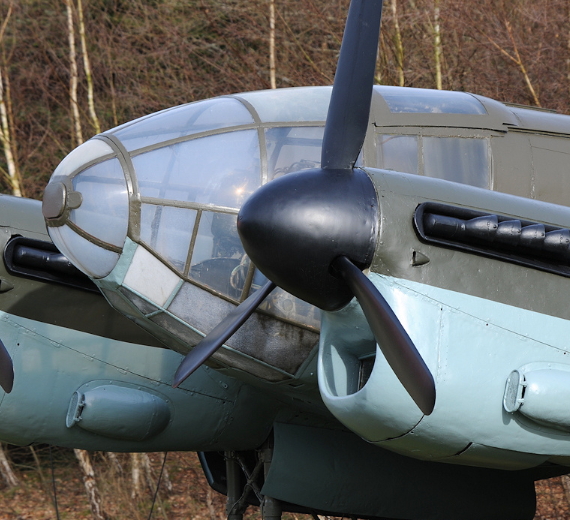
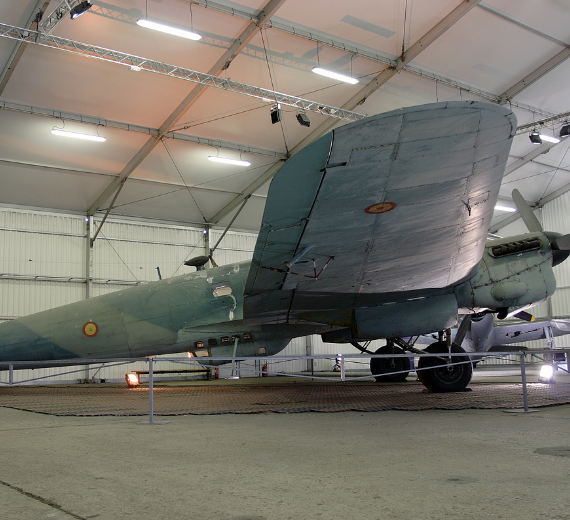
Heinkel He-111 "Greenhouse nose"
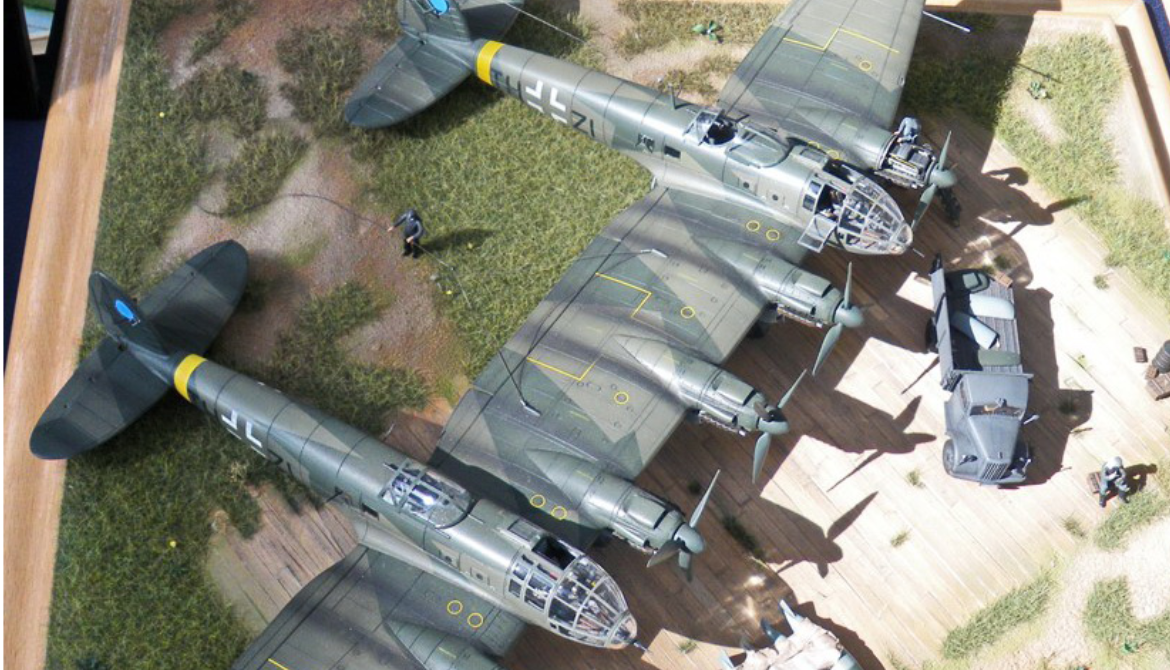
 The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a "wolf in sheep's clothing". Due to restrictions placed on Germany after the First World War prohibiting bombers, it was presented solely as a civil airliner, although from conception the design was intended to provide the nascent Luftwaffe with a heavy bomber
The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a "wolf in sheep's clothing". Due to restrictions placed on Germany after the First World War prohibiting bombers, it was presented solely as a civil airliner, although from conception the design was intended to provide the nascent Luftwaffe with a heavy bomber
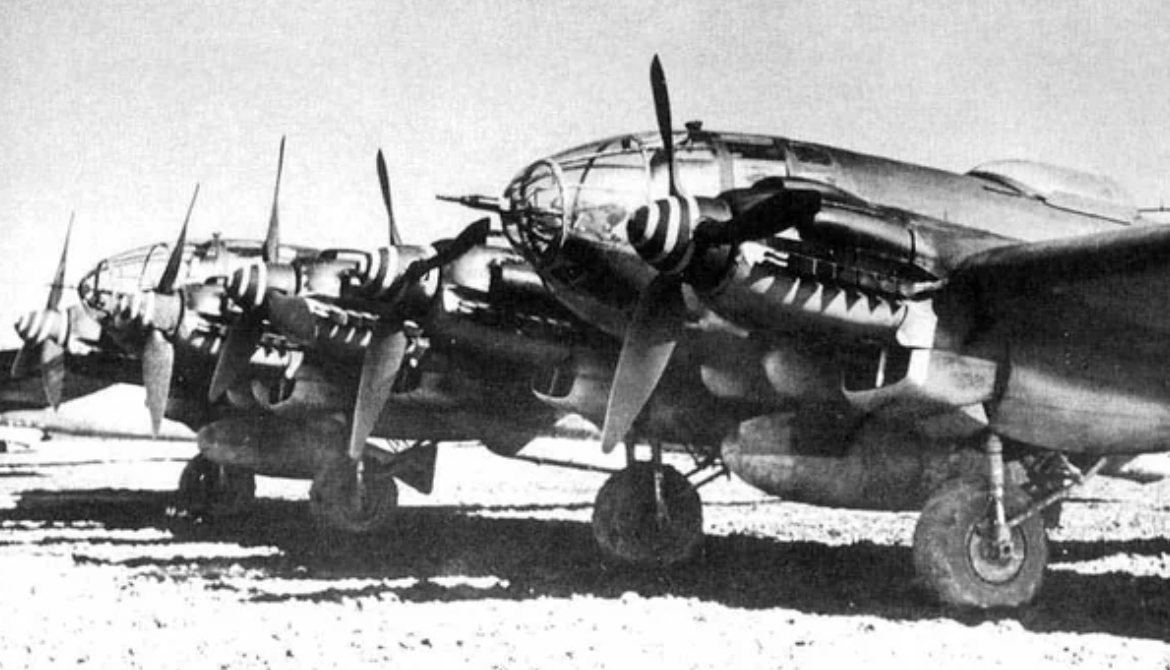
Perhaps the best-recognised German bomber of World War II due to the distinctive, extensively glazed "greenhouse" nose of the later versions, the Heinkel He 111 was the most numerous Luftwaffe bomber during the early stages of the war. It fared well until it met serious fighter opposition during the Battle of Britain, when its defensive armament was found to be inadequate
Basic design

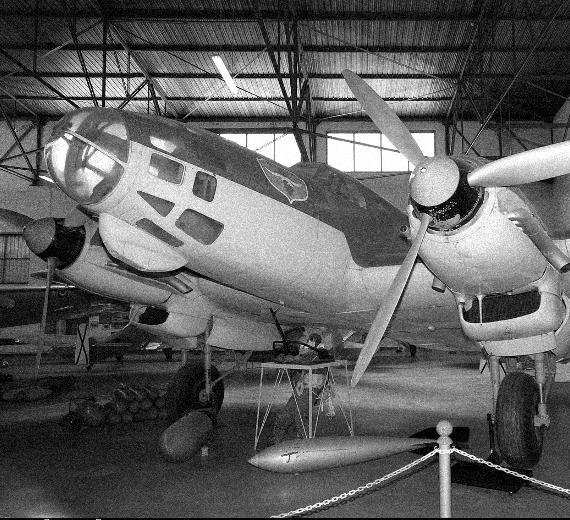
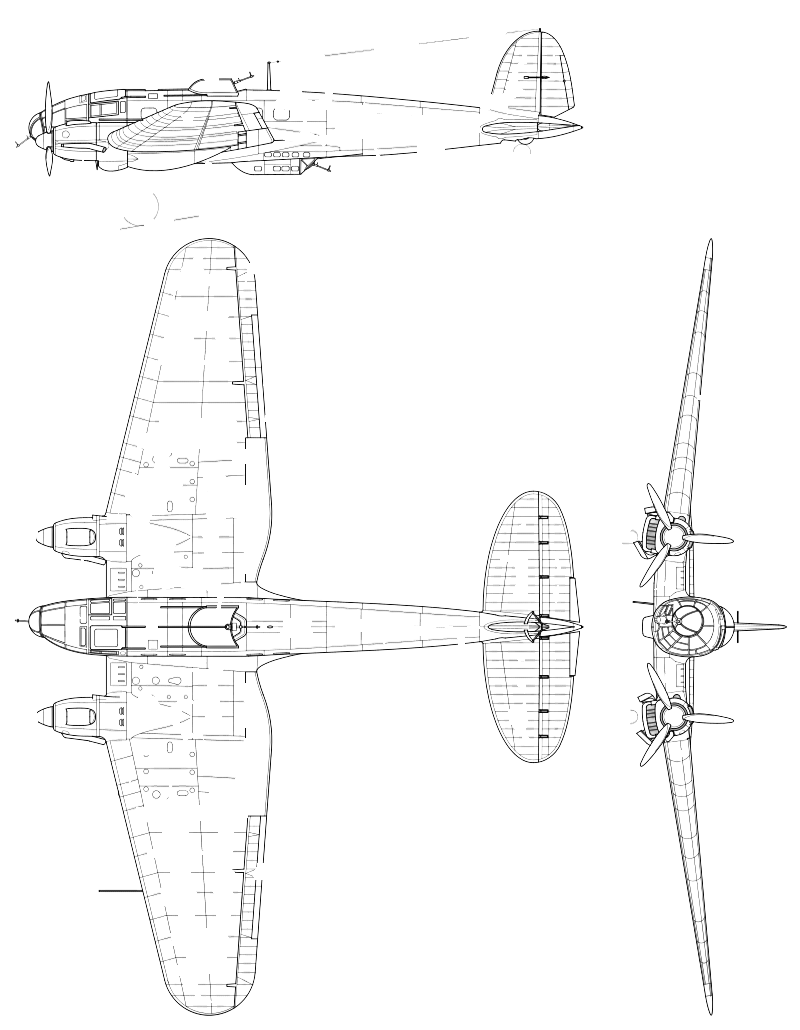
The design of the He 111 A-L initially had a conventional stepped cockpit, with a pair of windscreen-like panels for the pilot and co-pilot. The He 111P and subsequent production variants were fitted with fully glazed cockpits and a laterally asymmetric nose, with the port side having the greater curvature for the pilot, offsetting the bombardier to starboard. The resulting stepless cockpit, which was a feature on a number of German bomber designs during the war years in varying shapes and formats, no longer had the separate windscreen panels for the pilot. Pilots had to look outside through the same bullet-like glazing that was used by the bombardier and navigator. The pilot was seated on the left and the navigator/bomb aimer on the right. The navigator went forward to the prone bomb-aiming position or could tilt his chair to one side, to move into the rear of the aircraft. There was no cockpit floor below the pilot's feet—the rudder pedals being on arms—giving very good visibility below. Sliding and removable panels were manufactured into the nose glazing to allow the pilot, navigator and or bomb aimer to exit the aircraft quickly, without a time-consuming retreat into the fuselage

0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke
Heinkel He-111 "Greenhouse nose"


Heinkel Flugzeugwerke
Heinkel He-1111 "Greenhouse nose"
Info He-111 H-6
-
-
- Crew: 5 (pilot, navigator/bombardier/nose gunner, ventral gunner, dorsal gunner/radio operator, side gunner)
- Length: 16.4 m (53 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 22.6 m (74 ft 2 in)
- Height: 4 m (13 ft 1 in)
- Wing area: 87.6 m2 (943 sq ft)
-
Powerplant
-
- Empty weight: 8,680 kg (19,136 lb)
- Gross weight: 12,030 kg (26,522 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 14,000 kg (30,865 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Junkers Jumo 211F-1 or Junkers Jumo 211F-2 V-12 inverted liquid-cooled piston engines, 970 kW (1,300 hp) each (Jumo 211F-1)
-
-
- 1,000 kW (1,340 hp) (Jumo 211F-2)
-
-
-
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 440 km/h (270 mph,
- Range: 2,300 km (1,400 mi, 1,200 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 6,500 m (21,300 ft)
- Time to altitude: 5,185 m (17,000 ft) in 20 minutes
Armament
-
-
Guns:
- up to 7 × 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 15 machine guns or 7x MG 81 machine gun (2 in the nose, 1 in the dorsal, 2 in the side, 2 in the ventral), some of them replaced or augmented by
- 1 × 20 mm (0.787 in) MG FF cannon (central nose mount or forward ventral position)
- 1 × 13 mm (0.512 in) MG 131 machine gun (mounted dorsal and/or ventral rear positions)
-
Bombs:
- 2,000 kilograms (4,400 lb) in the main internal bomb bay
-
-
-
Guns:
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The inaccuracy of horizontal bombing during the Ural bomber program demonstrated weaknesses in German bombsights and created doubts about the effectiveness of level bombing of factories.
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke
Heinkel He-111 Bomber
During development, the anticipated weight of the He 177 increased so much that a main undercarriage design sufficient to handle the 32 metric tons.
Youtube Link
On 9 November 1939, the first prototype, the He 177 V1, was flown for the first time with Dipl. Ing. Leutnant Carl Francke, then chief of the Rechlin central flight test center, at the controls. T