Junkers Ju 88 Schnellbomber
Role
Tactical / dive / torpedo bomber
Night / heavy fighter
Reconnaissance aircraft
Manufacturer Junkers
Designer Ernst Zindel, W. H. Evers, and Alfred Gassner
First flight 21 December 1936
Introduction 1939
Retired 1951 (France)
Primary user Luftwaffe
Number built 15,183
Variants Junkers Ju 188
.
History Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG JFM
Junkers Ju 88 Schnellbomber

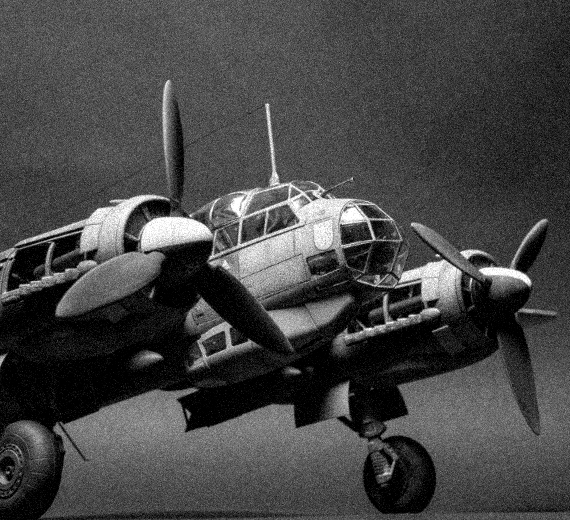
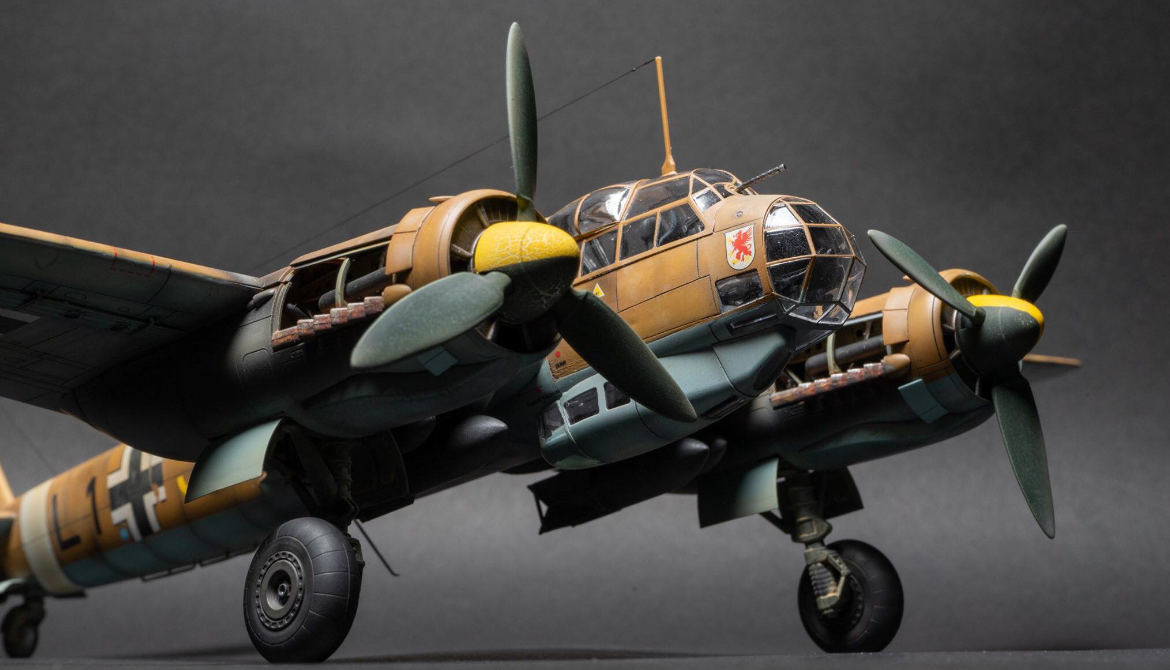
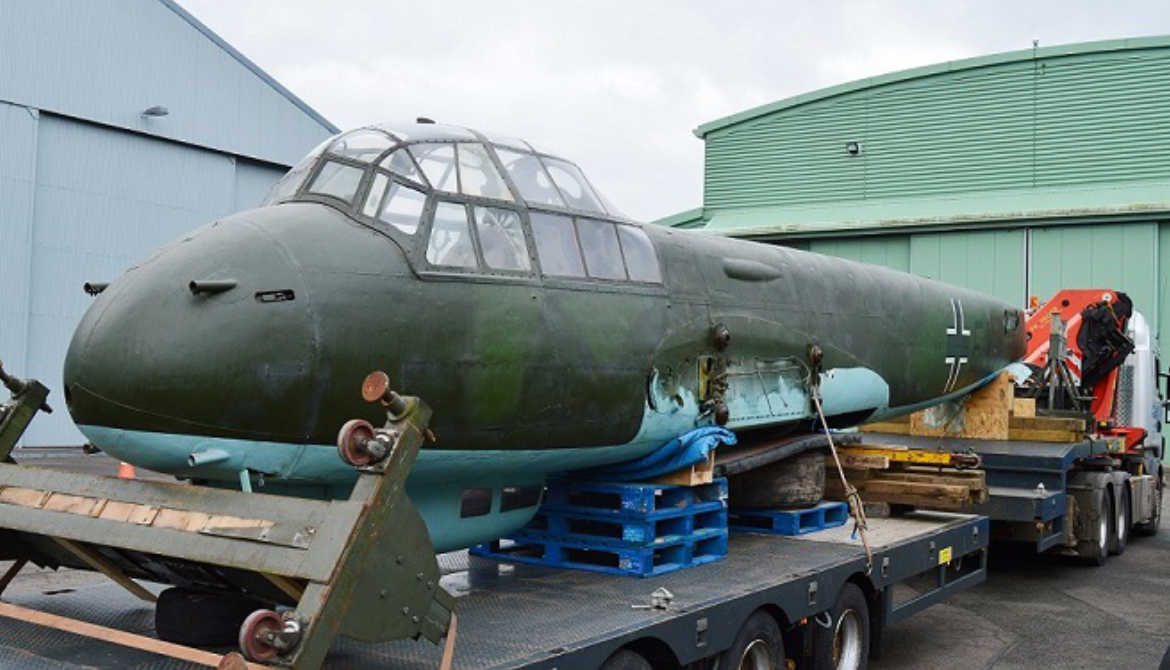
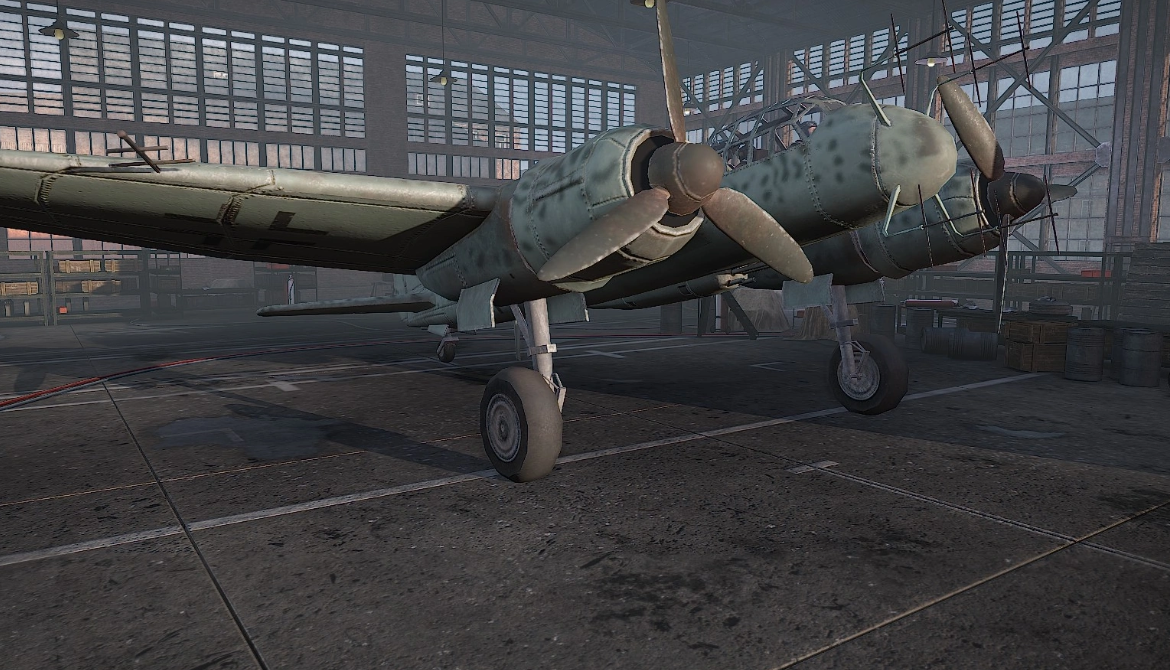
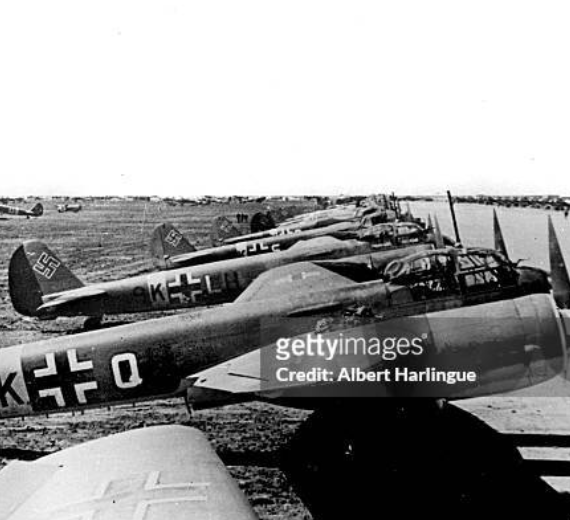
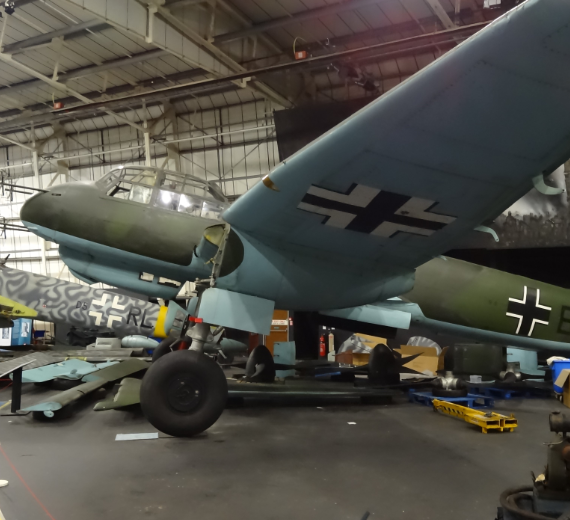
The Junkers Ju 88 is a German World War II Luftwaffe twin-engined multirole combat aircraft. Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works (JFM) designed the plane in the mid-1930s as a so-called Schnellbomber ("fast bomber") that would be too fast for fighters of its era to intercept. It suffered from technical problems during its development and early operational periods but became one of the most versatile combat aircraft of the war. Like a number of other Luftwaffe bombers, it served as a bomber, dive bomber, night fighter, torpedo bomber, reconnaissance aircraft, heavy fighter and at the end of the war, as a flying bomb
Design was initiated by Junkers chief designer Ernst Zindel. He was assisted by Wilhelm Heinrich Evers and American engineer Alfred Gassner. Evers and Gassner had worked together at Fokker Aircraft Corporation of America where Gassner had been Chief Engineer. Junkers presented their initial design in June 1936, and were given clearance to build two prototypes (Werknummer 4941 and 4942). The first two aircraft were to have a range of 2,000 km (1,200 mi) and were to be powered by two DB 600s. Three further aircraft, Werknummer 4943, 4944 and 4945, were to be powered by Jumo 211 engines. The first two prototypes, Ju 88 V1 and V2, differed from the V3, V4 and V5 in that the latter three models were equipped with three defensive armament positions to the rear of the cockpit, and were able to carry two 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) bombs, one under each inner wing panel.
Heavy fighter and night fighter

The Ju 88C was originally intended as a fighter-bomber and heavy fighter by adding fixed, forward-firing guns to the nose while retaining some bomb carrying ability of the A-series bomber. The C-series had a solid metal nose, typically housing one 20 mm (0.787 in) MG FF cannon and three 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 17 machine guns. The aircraft retained the ventral Bola gondola under the crew compartment though individual units sometimes removed this to reduce weight and drag to enhance performance. The Ju 88C was later used as a night fighter, and this became its main role.
The first version of the Ju 88C was the C-1 with 20 aircraft converted from A-1 airframes. Some of them entered service in the Zerstörerstaffel of KG 30 which became part of II./NJG 1 in July 1940. The C-1 was followed by the C-2 of which 20 aircraft were converted from A-5 airframes with enlarged wingspan. The C-4 became the first production version with 60 produced and 60 converted from A-5 airframes. The C-6, of which 900 aircraft were produced, was based on the A-4 airframe with more powerful engines and stronger defensive armament (single- or dual-mount belt-fed 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 81 or 13 mm (0.512 in) MG 131 instead of drum-fed MG 15 machine guns).


0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG JFM
Junkers Ju 88 Schnellbomber


Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG JFM
Junkers Ju 88 Schnellbomber
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 4 (pilot, bombardier/front gunner, radio operator/rear gunner, navigator/ventral gunner)
- Length: 14.4 m (47 ft 3 in)
- Wingspan: 20 m (65 ft 7 in)
- Height: 4.8 m (15 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 54.5 m2 (587 sq ft)
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Empty weight: 9,860 kg
- Gross weight: 12,105 kg
- Max takeoff weight: 14,000 kg
- Powerplant: 2 × Junkers Jumo 211J-1 or 211J-2 V-12 liquid-cooled inverted piston engine, 1,000 kW (1,340 hp) each for take-off
-
-
- 1,010 kW (1,350 hp) at 250 m
- 790 kW (1,060 hp) at 5,200 m (17,000 ft)
-
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 470 km/h (290 mph, 250 kn) at 5,300 m (17,390 ft) and 12,500 kg (27,557 lb)
- Cruise speed: 370 km/h (230 mph, 200 kn) at 5,300 m (17,390 ft) economical cruising speed
- Range: 1,790 km (1,110 mi, 970 nmi) with 2,896 L (765 US gal; 637 imp gal)
- Ferry range: 2,730 km (1,700 mi, 1,470 nmi) with 4,028 L
- Service ceiling: 8,200 m
- Time to altitude: 5,400 m (17,700 ft) in 23 minutes
Armament
-
-
Guns:
- Bombs: Up to 1,400 kilograms (3,100 lb) of ordnance internally in two bomb bays rated at 900 kg (2,000 lb) and 500 kg (1,100 lb) or up to 3,000 kg (6,600 lb) externally. Carrying bombs externally increased weight and drag and impaired the aircraft's performance. Carrying the maximum load usually required rocket-assisted take-off.
-
Guns:
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The Ju-88 design originated in 1935, as part of the Luftwaffe's goal of equipping its growing inventory with a fast medium bomber. The original design was by W.H. Evers and Alfred Gassner, who was an American citizen.
Junkers Ju 88 Schnellbomber
The Junkers Ju-88 was truly the backbone of the German Air Force, the Luftwaffe, in World War II.
Youtube Link
More than 9,000 were bombers, a total equal to the production of all other German bombers.