.
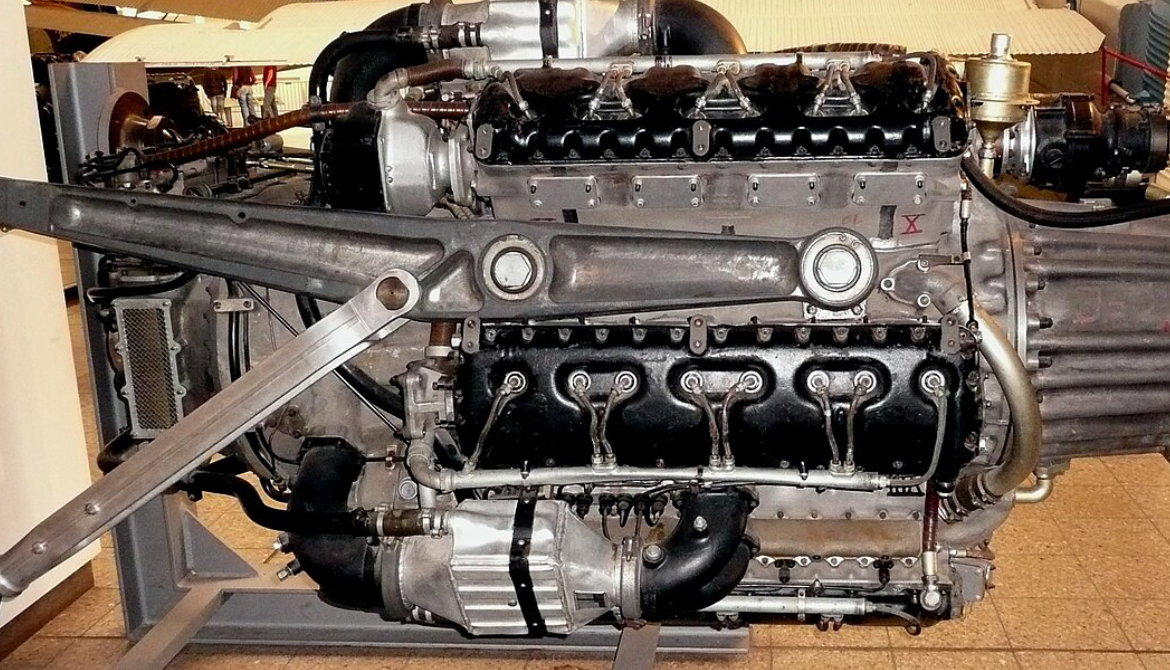
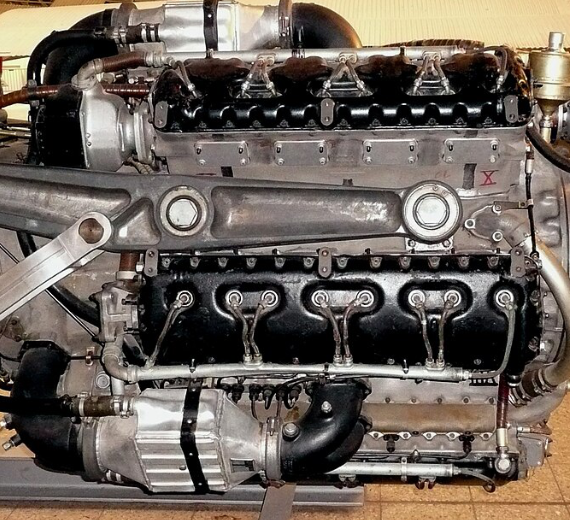
History Junkers Jumo 222 was a German
high-power multiple-bank in-line piston aircraft engine

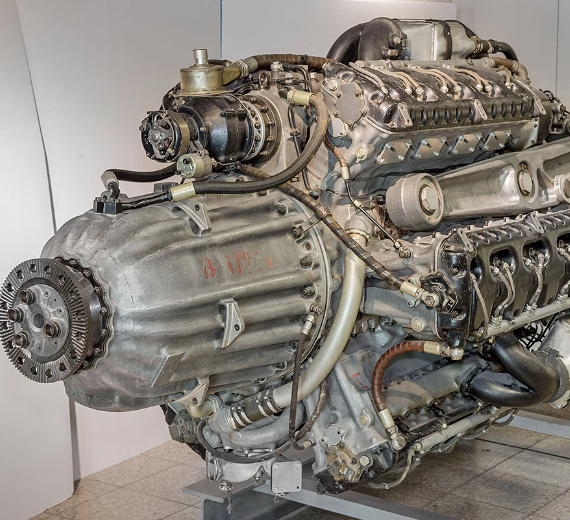
The Jumo 222 was a German high-power multiple-bank in-line piston aircraft engine from Junkers, designed under the management of Ferdinand Brandner of the Junkers Motorenwerke.
Such was the projected performance of the engine compared to contemporary designs that many developments of wartime Luftwaffe piston-engined aircraft designs were based on it, at least as an option. These included the entire Bomber B program, which looked to replace all existing Luftwaffe bombers with a new twin-engine design that was larger, faster and more heavily armed than any aircraft in their inventory.
The design failed to mature even after years of intensive development and several major design changes. The Bomber B program failed along with it, leaving the Luftwaffe with hopelessly outdated designs during the second half of the war. Only a small number of 222s were built, less than 300. They never left the prototype phase, but the design nevertheless continued appearing on proposals for new Luftwaffe multi-engined designs long after most had given up hope it would ever work..
Design

The comparison was even more favourable against other high-power engines under development. The cumbersome DB 606, the first-ever "high-output" powerplant developed in Germany, consisted of two DB 601's mounted to a single reduction gear case on their front ends, that delivered 1,790 kW (2,400 hp) with a weight of 1,515 kg (3,340 lb), and was 2.1 m × 1.6 m × 1.1 m (83 in × 63 in × 43 in)ft) in size. Their troubled use and deficient installation design in the He 177A, Germany's only heavy bomber aircraft to see production and front-line service, prompted Reichsmarschall Hermann Göring to derisively label them in the late summer of 1942 as "welded-together engines".[3] Conversely, the RLM was excited by the possibilities of the much more compact Jumo 222's design features, and the X engine configuration, 24 cylinder DB 604, of similar weight and displacement to the 222A but with somewhat lower specific power output. The RLM based their entire Bomber B program on pairs of these engines, which would deliver a bomber with the warload of the He 177 and even better speed than the Ju 88, a truly universal design.

By late 1941, Junkers decided the best course of action was to make more radical changes to the design, and introduced the 222C and 222D models. With a new bore and stroke of 145 mm × 140 mm (5.7 in × 5.5 in), the engine displacement increased a second time, to 55.5 L (3,386.8 in³), just very slightly larger than the contemporary Wright Duplex Cyclone American 18-cylinder air-cooled radial engine, which at the time was having its own significant problems ironed out, partially from the use of combustible magnesium-alloy metal for its crankcase. Back at the original 3,200 rpm, the Jumo 222 C/D models could deliver just under 2,200 kW (3,000 hp) when they started running in the summer of 1942. However, the problems were not cured, and only a handful were built. The RLM had been waiting for three years at this point, and eventually gave up and had all designs based on it look for alternate engines. Later that year, they gave up on that as well, and cancelled the entire Bomber B program outright.

0
HpHorse Power
0
Cilinder
0
KgWeight
0
MtrLength
Photo Gallery
Junkers Jumo 222 was a German
high-power multiple-bank in-line piston aircraft engine


Junkers Jumo 222 was a German high-power multiple-bank in-line piston aircraft engine
General characteristics
-
-
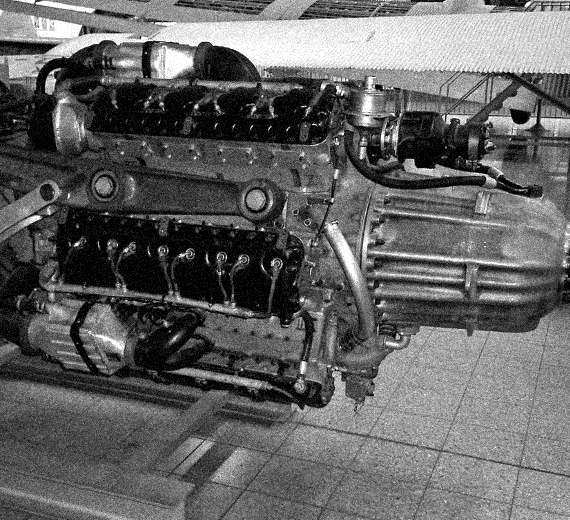
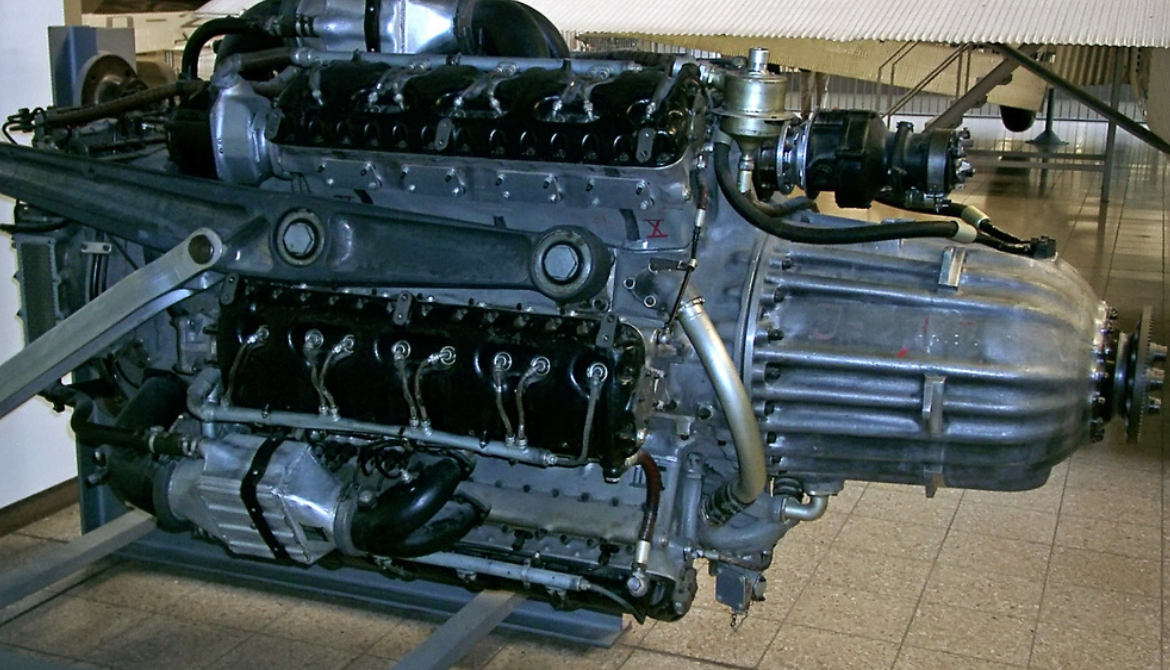
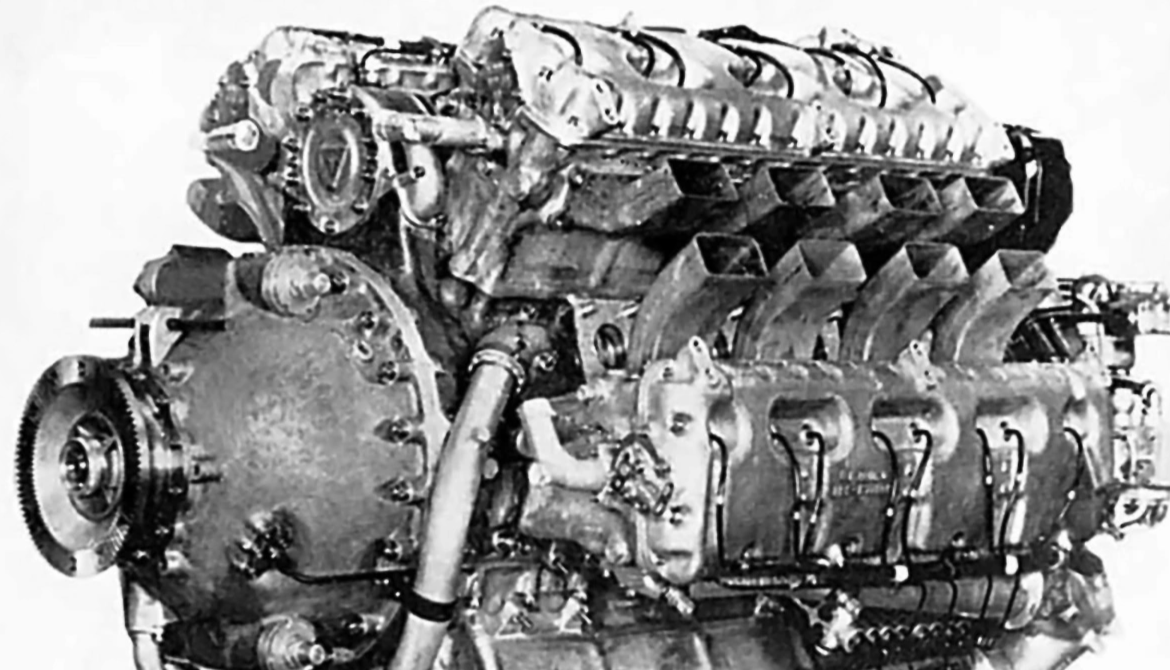
- Type: 6-bank, 24-cylinder supercharged liquid-cooled in-line aircraft engine
- Bore: 135 mm (5.3 in)
- Stroke: 135 mm (5.3 in)
- Displacement: 46.5 L (2,830 in³)
- Length: 2,400 mm (94 in)
- Diameter: 1,160 mm (46 in)
- Dry weight: 1,088 kg (2,399 lb)
-
Components
-
-
- Valvetrain: Two intake valves and one sodium-cooled exhaust valve per cylinder
- Supercharger: Single-stage two-speed centrifugal type supercharger
- Fuel system: Fuel injection
- Cooling system: Liquid-cooled
-
Performance
- Power output:
- (2,465 hp) at 3,200 rpm for takeoff
- 1,397 kW (1,873 hp) cruise
- Specific power: 39.5 kW/L
- Compression ratio: 6.5:1
- Specific fuel consumption: 0.29 kg/(kW·h) (0.477 lb/(hp·h))
- Power-to-weight ratio: (1.03 hp/lb)
.
Links to Youtube & Others
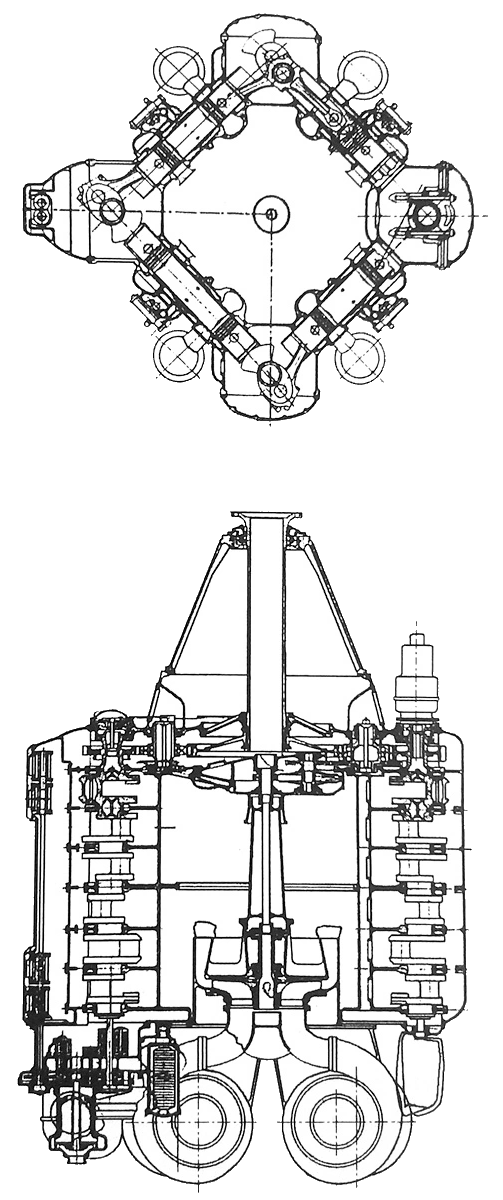
Since the Junkers Jumo 222 has six cylinder banks, it is one of the so-called Hexagon engines. Other examples of hexagon engines are rare - for example, the 24-cylinder water-cooled Dobrynin VD-4K and the 12-cylinder air-cooled Curtiss H-1640 Chieftain. Analogously, there were also octagon engines such as the Bristol Hydra with eight cylinder banks.
Junkers Jumo 222
piston aircraft engine
Design work on the Jumo 222 started in 1937. The engine was configured with six inline cylinder banks spaced at equal angles
Youtube Link
The Colombian Air Force used three Ju 52/3mde bombers equipped as floatplanes during the Colombia-Peru War in 1932–1933.