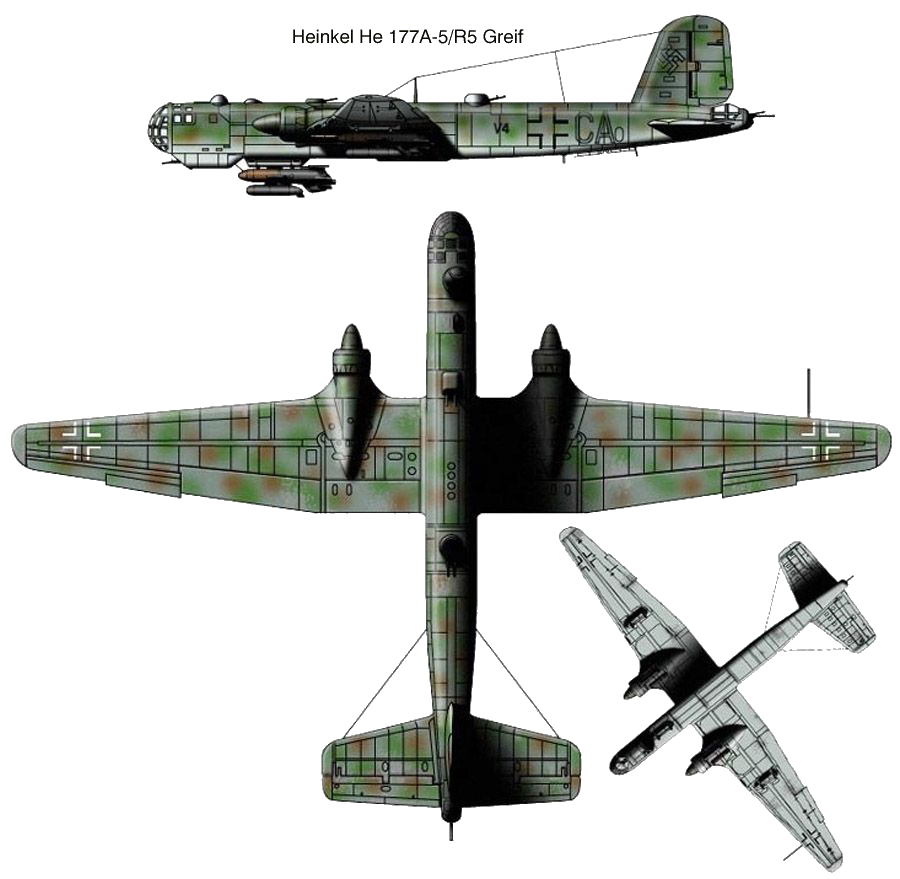
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke Heinkel He-177 "Greif"
 |
|
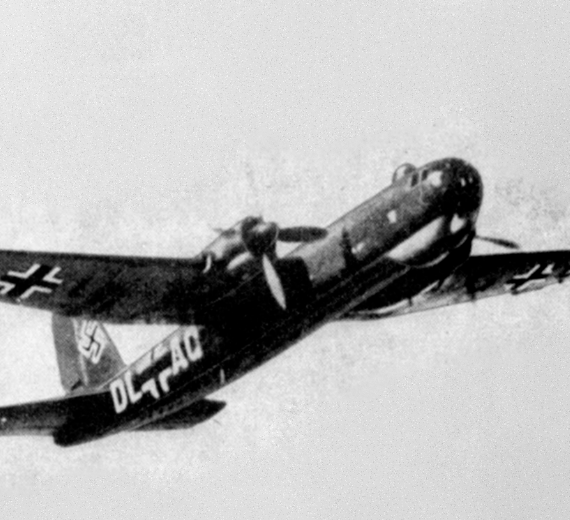
| The second He 177A-0 production prototype (A-02) with broad-bladed propellers, bearing radio code "DL+AQ | |
| Role | Long-range heavy bomber |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Heinkel Flugzeugwerke Licensed to Arado |
| First flight | 19 November 1937 |
| Introduction | 1942 |
| Retired | 1945 |
| Primary user | Luftwaffe |
| Number built | 1,169 |
| Variants | Heinkel He 274 Heinkel He 277 |
.
History Heinkel Flugzeugwerke
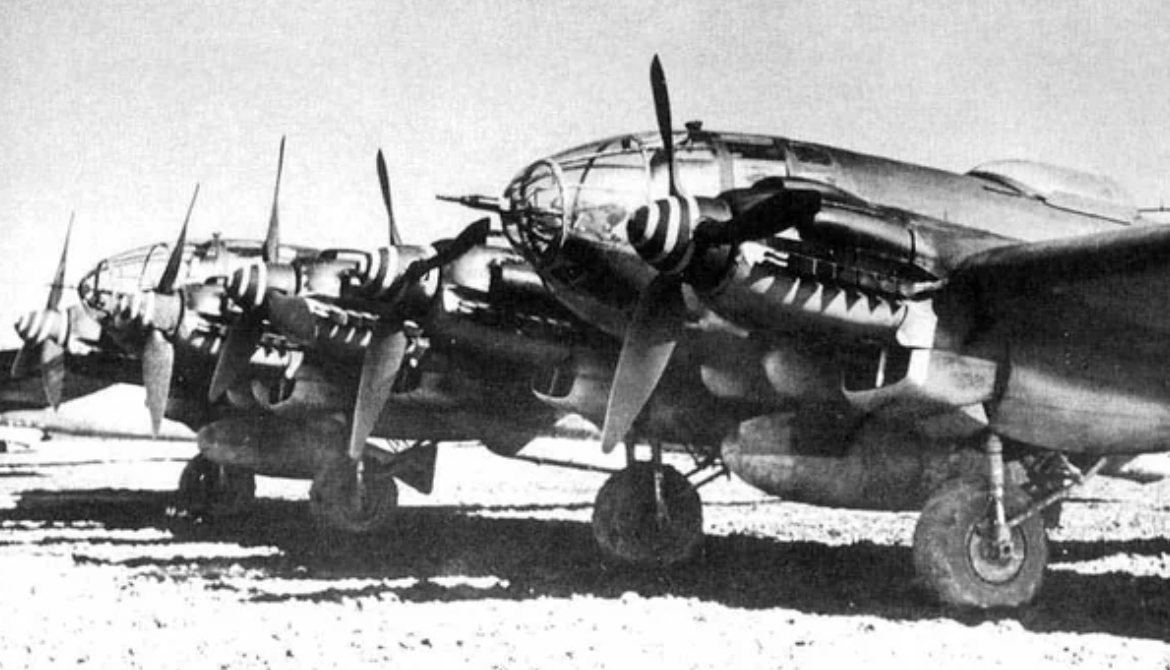
Heinkel He-177 A-3 Greif ("Reich's lighter")
 The Heinkel He 177 Greif (Griffin) was a long-range heavy bomber flown by the Luftwaffe during World War II. The introduction of the He 177 to combat operations was significantly delayed, by both problems with the development of its engines and frequent changes to its intended role. Nevertheless, it was the only long-range, heavy bomber to become operational with the Luftwaffe during the war. The He 177 had a payload/range capability similar to that of four-engined heavy bombers used by the Allies in the European theatre.
The Heinkel He 177 Greif (Griffin) was a long-range heavy bomber flown by the Luftwaffe during World War II. The introduction of the He 177 to combat operations was significantly delayed, by both problems with the development of its engines and frequent changes to its intended role. Nevertheless, it was the only long-range, heavy bomber to become operational with the Luftwaffe during the war. The He 177 had a payload/range capability similar to that of four-engined heavy bombers used by the Allies in the European theatre.
Work on the design began in response to a 1936 requirement known as Bomber A, issued by the RLM for a purely strategic bomber. Thus the He 177 was intended originally to be capable of a sustained bombing campaign against Soviet manufacturing capacity, deep inside Russia..
Engines

The He 177 required at least a pair of 2,000 PS (1,973 hp, 1,471 kW) engines to meet performance requirements. No engine in the German aviation power-plant industry at that time developed such power. A four-engine version would have been possible with engines like the Daimler-Benz DB 601 but the four-engine layout would impose higher propeller drag to the detriment of performance in dive bombing. The use of only two counter-rotating propellers on a heavy bomber offered many advantages, such as a substantial reduction in drag, reduction of dive instability and a marked improvement in maneuverability. The eight initial V-series prototypes, and the larger number of A-0 pre-production models of the He 177, displayed an airspeed and maneuverability comparable to many heavy fighters of the time.

0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
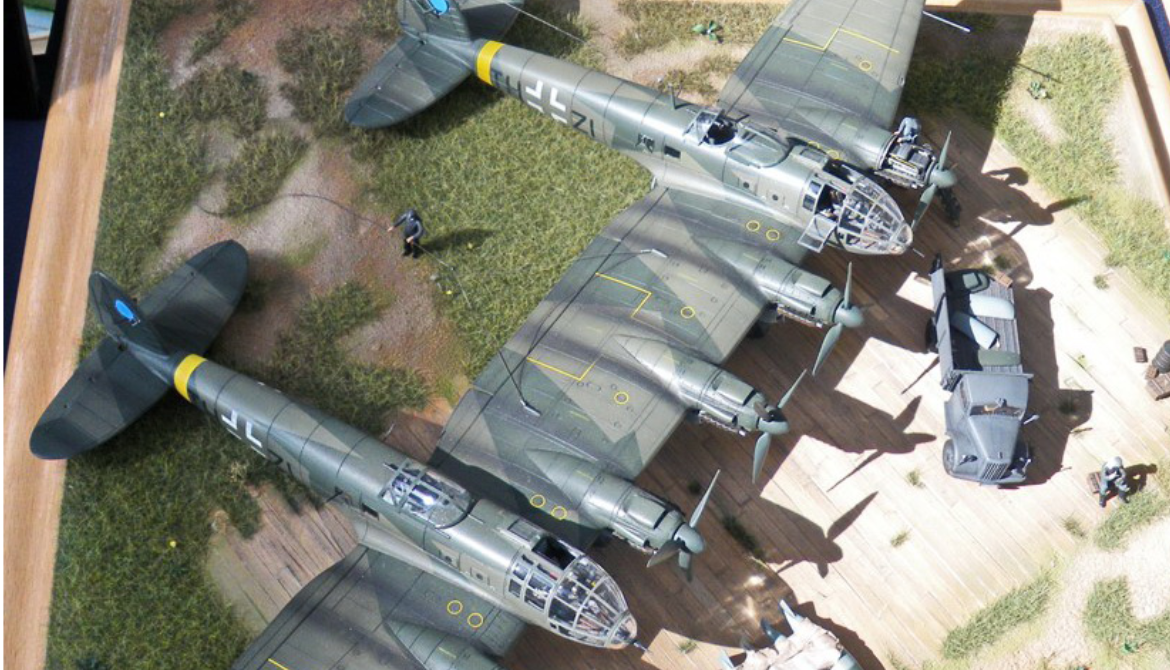
Photo Gallery
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke
Heinkel He-177 A-3 Greif "The Flaming Coffin"


Heinkel Flugzeugwerke
Heinkel He-177 Greif "The Flaming Coffin"
Info He-111 H-6
-
-
- Crew: 6
- Length: 22.00 m (72 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 31.44 m (103 ft 2 in)
- Height: 6.67 m (21 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 100 m2 (1,100 sq ft)
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Empty weight: 16,800 kg
- Gross weight: 32,000 kg
- Useful load: 15,200 kg
- Powerplant: 2 × Daimler-Benz DB 610 24-cylinder liquid-cooled piston engines, 2,218 kW (2,975 hp) each
- Propellers: 4-bladed VDM constant-speed propellers
-
-
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 488 km/h (303 mph at 6,000 m (19,685 ft) in level flight
- Cruise speed: 415 km/h at 6,000 m
- Stall speed: 135 km/h (84 mph
- Range: 6,000 km (3,700 mi
- Service ceiling: 8,000 m
- Rate of climb: (623.4 ft/min)
Armament
-
- Guns:
- One 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 81 machine gun in nose.
- One 20 mm (0.8 in) MG 151 cannon in forward belly gondola, and one in tail.
- Two 13 mm (0.5 in) MG 131 machine gun in FDL 131Z remotely operated forward dorsal turret, and one in rear belly gondola, one in manned HDL 131/1 aft dorsal turret
- Bombs: Up to 7,000 kilograms (15,000 lb) of ordnance internally, up to 2,500 kg (5,500 lb) externally on underwing racks.
-
- Guns:
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The inaccuracy of horizontal bombing during the Ural bomber program demonstrated weaknesses in German bombsights and created doubts about the effectiveness of level bombing of factories.
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke
Heinkel He-177 A-3 Greif
During development, the anticipated weight of the He 177 increased so much that a main undercarriage design sufficient to handle the 32 metric tons.
Youtube Link
On 9 November 1939, the first prototype, the He 177 V1, was flown for the first time with Dipl. Ing. Leutnant Carl Francke, then chief of the Rechlin central flight test center, at the controls. T