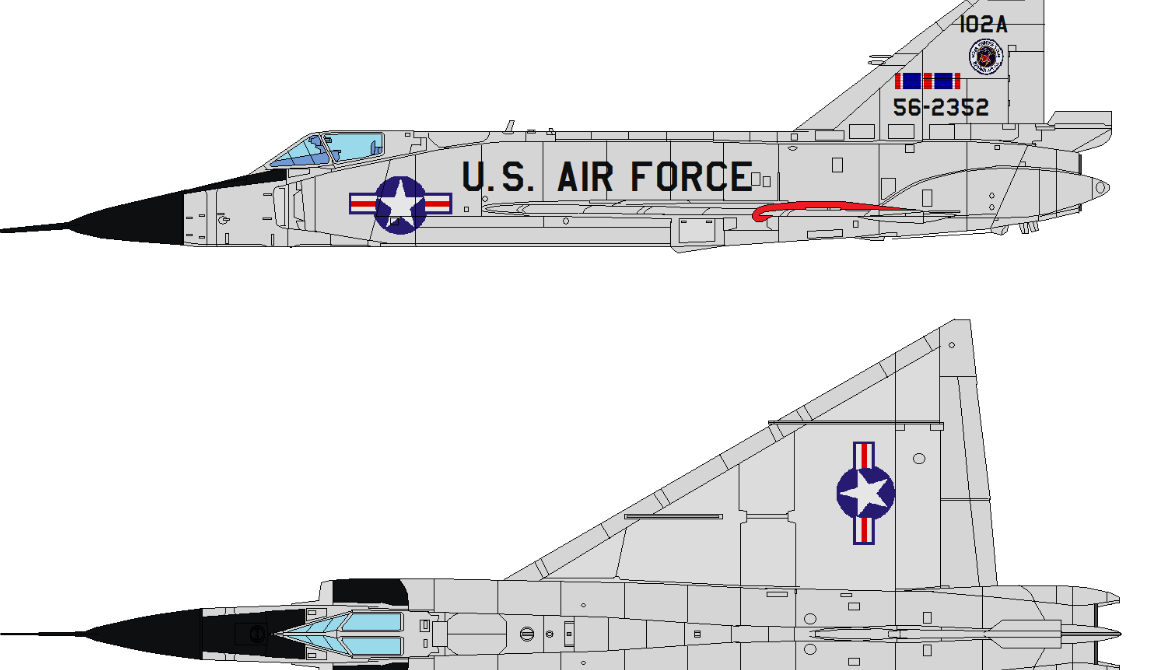
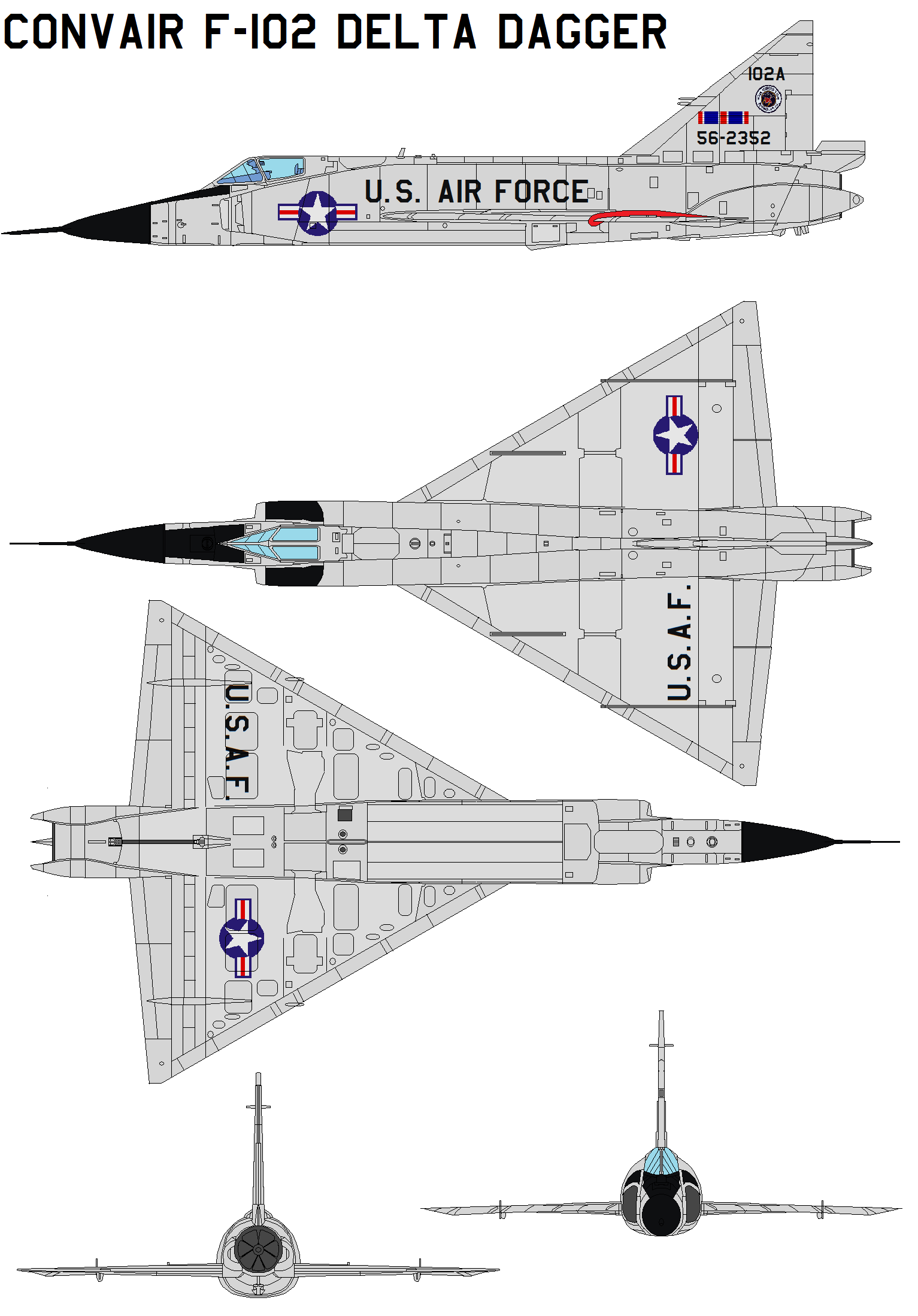
Consolidated / Convair
F-102 Delta Dagger
Role Interceptor aircraft
Manufacturer Convair
First flight 24 October 1953
Introduction April 1956
Retired 1979
Primary users United States Air Force
Greece
Turkey
Number built 1,000
Developed from Convair XF-92
Developed into F-106 Delta Dart
.
History Consolidated / Convair
Convair F-102 Delta Dagger

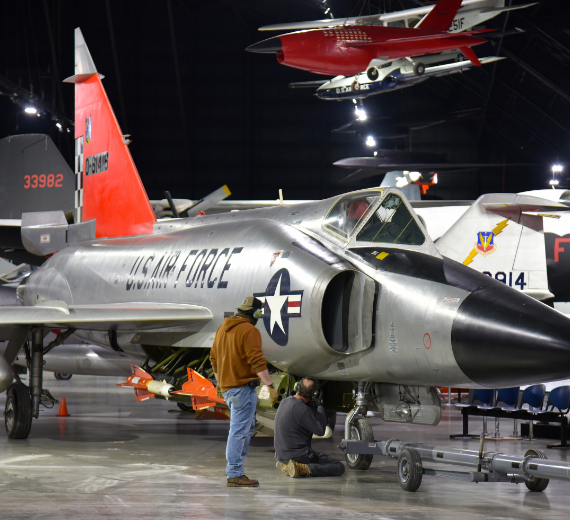
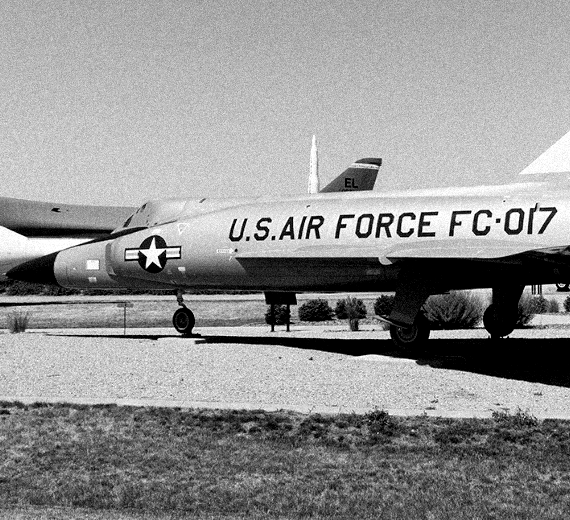
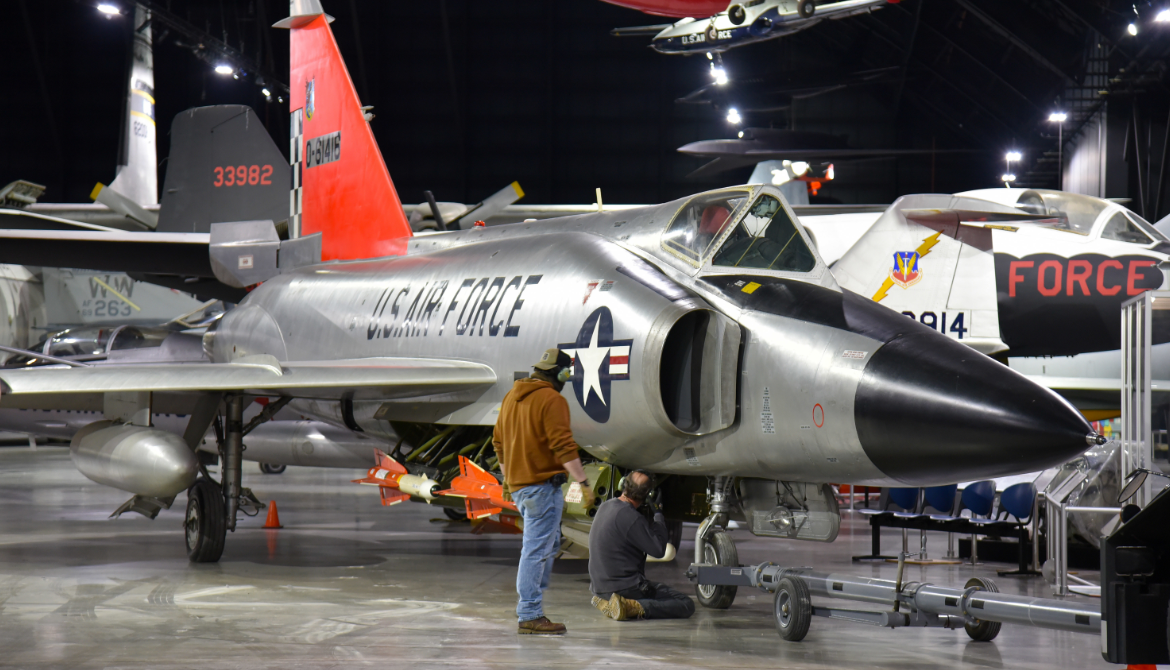
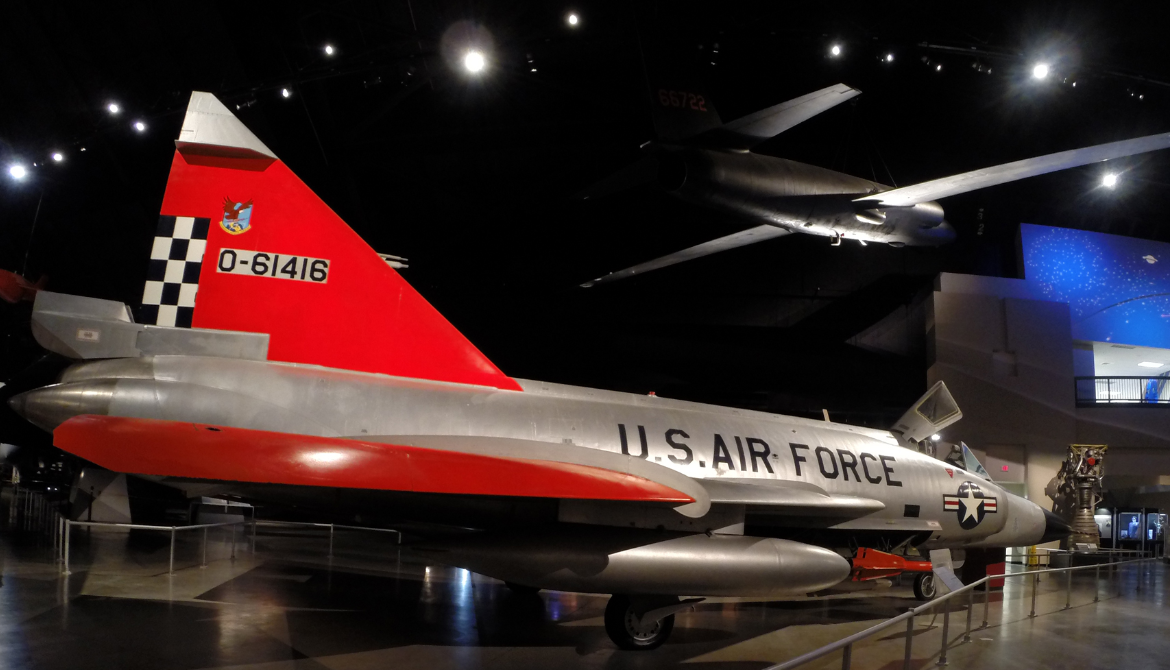
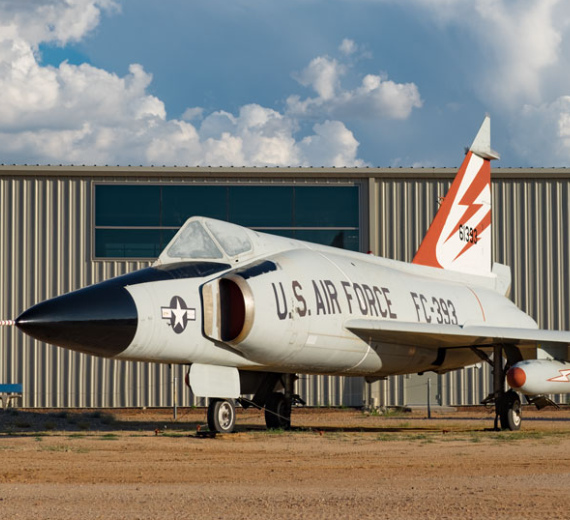
The Convair F-102 Delta Dagger was an interceptor aircraft designed and produced by the American aircraft manufacturer Convair. A member of the Century Series, the F-102 was the first operational supersonic interceptor and delta-wing fighter operated by the United States Air Force (USAF).
In 1921, Colonel Virginius Clark, chief designer of the Dayton-Wright Company, designed the Chummy sporting biplane.[1] The airframe was advanced in its use of the new Clark Y thick-section airfoil and a welded fuselage framework of chrome-molybdenum steel tubing. A departure from the all-wood structures found in other trainers, the structure proved sturdy and dependable. It was offered to the USAAS as a replacement for the Curtiss JN-4D trainer, with a choice of Le Rhone or Clerget rotary piston engines.
In 1922, the Army ordered three TA-3 (Trainer, Air-cooled, Type 3) machines for evaluation with the Le Rhone engine and dual controls. Evaluation showed that the type had the makings of a good trainer, but was somewhat lacking in power, so in 1923 Dayton-Wright modified one TA-3 with a more powerful 110 hp (82 kW) Le Rhone.
Background

On 8 October 1948, the board of senior officers of the United States Air Force (USAF) issued recommendations that the service organize a competition for a new interceptor scheduled to enter service in 1954; as such, the all-new design would initially be dubbed the "1954 Ultimate Interceptor". Four months later, on 4 February 1949, the USAF approved the recommendation and prepared to hold a corresponding competition during the following year. In November 1949, the USAF decided that the new aircraft would be built around a fire-control system (FCS). The FCS was to be designed before the airframe to ensure compatibility. The airframe and FCS together were called the weapon system.
In January 1950, the USAF's Air Materiel Command issued request for proposals (RFPs) to 50 companies for the FCS, of which 18 responded. By May, the list was revised downward to 10. Meanwhile, a board at the U.S. Department of Defense headed by Major General Gordon P. Saville reviewed the proposals, and distributed some to the George E. Valley-led Air Defense Engineering Committee. Following recommendations by the committee to the Saville Board, the proposals were further reduced to two competitors, Hughes Aircraft and North American Aviation. Although the Valley Committee thought it was best to award the contract to both companies, Hughes was chosen by Saville and his team on 2 October 1950
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Consolidated / Convair / Vultee
Convair F-102 Delta Dagger


Consolidated Convair Vultee
Convair F-102 Delta Dagger
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 68 ft 4 in (20.83 m)
- Wingspan: 38 ft 1 in (11.61 m)
- Height: 21 ft 2.5 in (6.464 m)
- Wing area: 695 sq ft (64.6 m2) conically cambered wing
-
-
-
- 661.5 sq ft (61.46 m2) YF-102
-
-
Powerplant
- Empty weight: 19,350 lb (8,777 kg)
- Gross weight: 24,494 lb (11,110 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 31,500 lb (14,288 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 1,085 US gal (903 imp gal; 4,110 L) internal + 2x 215 US gal (179 imp gal; 810 L) drop tanks
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney J57-P-25 afterburning turbojet engine, 11,700 lbf (52 kN) thrust dry, 17,000 lbf (76 kN) with afterburner
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 825 mph (1,328 km/h, 717 kn) at 40,000 ft (12,192 m)
- Maximum speed: Mach 1.25, Mach 0.95 with drop tanks
- Range: 1,350 mi (2,170 km, 1,170 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 53,400 ft (16,300 m)
- Rate of climb: 13,000 ft/min (66 m/s)
- Wing loading: 35 lb/sq ft (170 kg/m2)
Armament
- Rockets: 24 × 2.75 in (70 mm) FFAR (Folding Fin Aerial Rocket) unguided rockets in missile bay doors
- Missiles:
- 6 × AIM-4 Falcon air-to-air missiles or
- 3 × AIM-4 Falcon
- 1 × AIM-26 Falcon with conventional or nuclear warhead
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The "Camel" may be regarded as the prototype of the Consolidated response to the USAAS's 1924 requirement for a new primary trainer. In the early summer of 1924.
Convair F-102 Delta Dagger
In 1922, the Army ordered three TA-3 (Trainer, Air-cooled, Type 3) machines for evaluation with the Le Rhone engine and dual controls.
Youtube Link
The Consolidated PT-1 Trusty (company designation Model 1) was a biplane primary trainer used by the United States Army Air Service (USAAS)