.
History Curtiss-Wright AT-9 Jeep

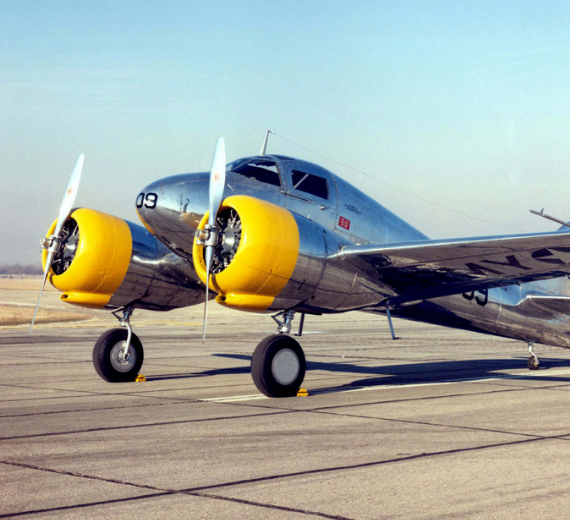
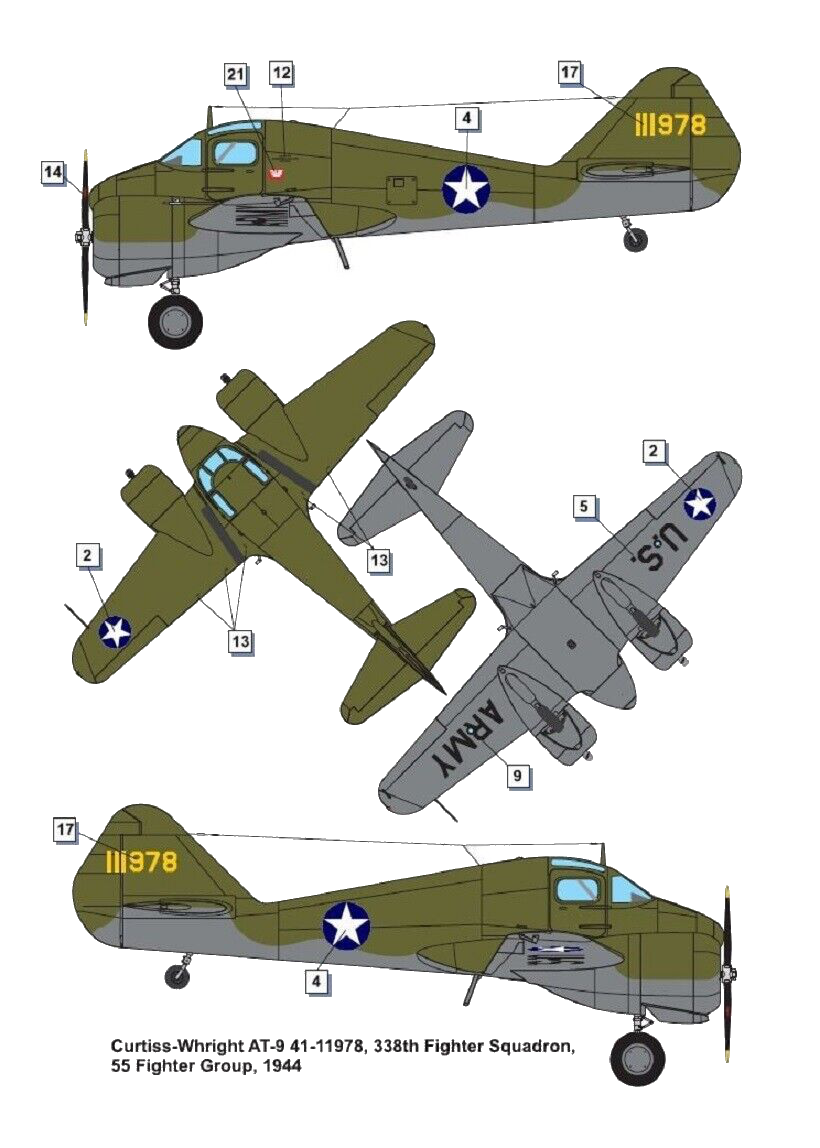
The Curtiss-Wright AT-9 Jeep was an American twin-engined advanced trainer aircraft used by the United States during World War II to bridge the gap between single-engined trainers and twin-engined combat aircraft. The AT-9 had a low-wing cantilever monoplane configuration, retractable landing gear and was powered by two Lycoming R-680-9 radial engines.
Curtiss-Wright anticipated the requirement for this type of "high-performance" aircraft and designed the Curtiss-Wright CW-25, a twin-engined trainer, which possessed the takeoff and landing characteristics of a light bomber. Using the same basic design as the larger Cessna AT-17 Bobcat, the new CW-25 was designed to simulate the demands of multi-engined operations. The design featured a small layout, grouping two Lycoming R-680-9 radial engines forward and using a retractable tailwheel landing gear to achieve the performance necessary to meet the requirements of an advanced trainer. The single CW-25 prototype acquired for evaluation had a welded steel-tube fuselage structure with the wings, fuselage and tail unit fabric-covered
Operational history

The first prototype Model 25 flew in 1941 and the production version entered service as the AT-9 in 1942. Named the "Fledgling" by Curtiss-Wright, it commonly became known as the "Jeep" in the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF). The prototype CW-25 had a fabric-covered steel tube fuselage and fabric-covered wings and tail units, but production AT-9s were of stressed metal skin construction.
The AT-9 was purposely designed to be less stable and proved to be difficult to fly or land, which made it particularly suitable for teaching new pilots to cope with the demanding flight characteristics of a new generation of high-performance, multi-engined aircraft such as the Martin B-26 Marauder and Lockheed P-38 Lightning.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Curtiss-Wright AT-9 Jeep


Curtiss-Wright AT-9 Jeep
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 2
- Length: 31 ft 8 in (9.65 m)
- Wingspan: 40 ft 4 in (12.29 m)
- Height: 9 ft 10 in (3.00 m)
- Wing area: 233 sq ft (21.6 m2)
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Empty weight: 4,494 lb (2,038 kg)
- Gross weight: 6,060 lb (2,749 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Lycoming R-680-9 , 295 hp (220 kW) each
- Propellers: 2-bladed propellers
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 197 mph (317 km/h
- Cruise speed: (282 km/h, 152 kn)
- Range: 750 mi (1,210 km, 650 nmi)
- Service ceiling: (5,800 m)
- Time to altitude: 10,000 ft (3,000 m) in 8 minutes 36 seconds
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The MB-339 was developed during the 1970s in response to an Italian Air Force requirement that sought a replacement for the service's existing fleet of Aermacchi MB-326s.
Curtiss-Wright
AT-9 Jeep
An Aermacchi MB-339 jet had just taken off in formation to head to Vercelli, where it should have perform an aerial exhibition.
Youtube Link
Learn all about the Aermacchi MB-339 with Curator of Aviation Eric Boehm.