Kaman Aerospace
SH-2G Super Seasprite
| A Royal New Zealand Navy SH-2G | |
| Role | ASW helicopter |
|---|---|
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Kaman Aircraft |
| First flight | 2 April 1985 |
| Introduction | 1993 |
| Retired | US Navy in 2001; Royal Australian Navy in 2008 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary users | United States Navy (historical) Egyptian Navy Royal New Zealand Navy Polish Navy |
| Produced | 1985–1995 (also conversions) |
| Developed from | Kaman SH-2 Seasprite |
.
History Kaman Aerospace
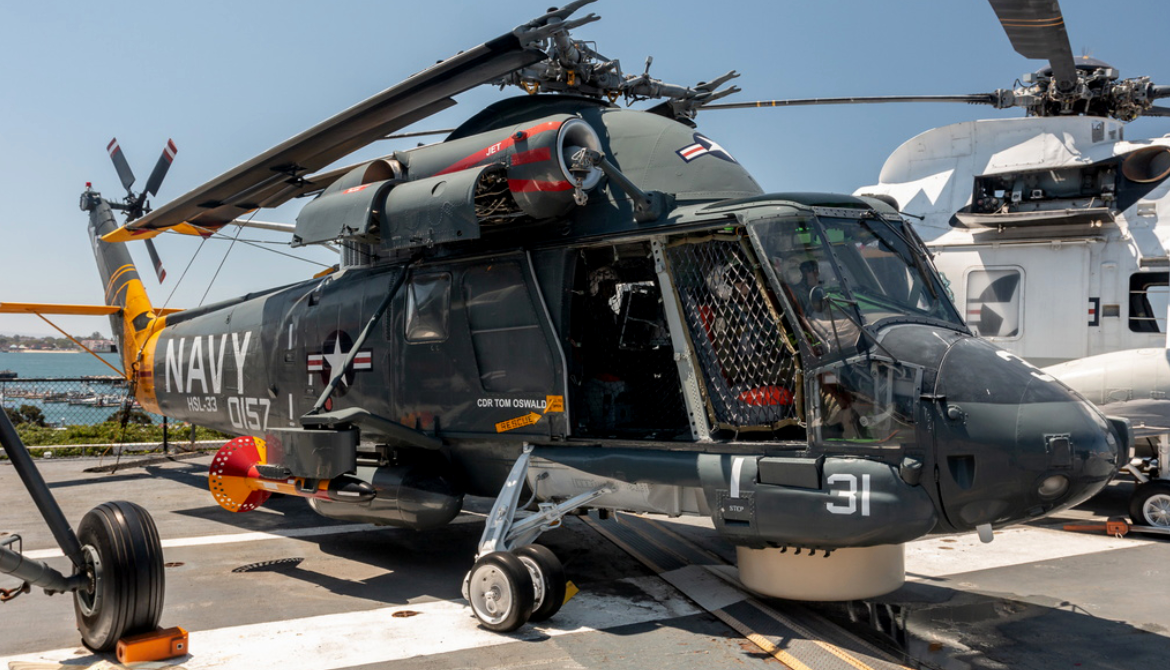
Kaman SH-2G Super Seasprite

The Kaman SH-2G Super Seasprite is an American ship-based helicopter with anti-submarine, anti-surface threat capability, including over-the-horizon targeting. This aircraft extends and increases shipboard sensor and weapon capabilities against several types of enemy threats, including submarines of all types, surface ships, and patrol craft that may be armed with anti-ship missiles. It was originally developed for the United States Navy in the 1980s as a reengined and updated version of the older Kaman SH-2 Seasprite which had been serving since the 1960s in a variety of versions, and G model was an evolution of the SH-2F, which was an important ASW aircraft naval vessels that could not manage a larger helicopter. The SH-2G entered service in the 1980s and 90s, and served to 2001 with the U.S. Navy, but went on to serve in several other Naval forces into the 2st Century and is still in active in service in several Navy's
The SH-2G's primary missions include anti-submarine and anti-surface warfare, anti-ship missile defense, and anti-ship surveillance and targeting. Secondary missions may include medical evacuation, search and rescue, personnel and cargo transfer, as well as small boat interdiction, amphibious assault air support, gun fire spotting, mine detection and battle damage assessment.
Design and development

In 1985, the SH-2G program was started. The US Navy wanted better anti-submarine capabilities and felt upgrading existing helicopters would be a more cost-effective approach; moreover legacy Knox-class and early "short-hull" Perry-class frigates operating the SH-2F could not operate the larger SH-60B Seahawk. The prototype YSH-2G first flew on 2 April 1985. The prototype was a modified SH-2F fitted with two more powerful General Electric T700-GE-401/401C engines.
The G-model has a reinforced upper fuselage to support the heavier new engines. The SH-2G also has multifunctional displays and new avionic systems. The Navy began receiving Airborne Mine Counter Measures (AMCM) hardware with the Kaman Magic Lantern laser mine detection system in December 1996.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Kaman Aerospace
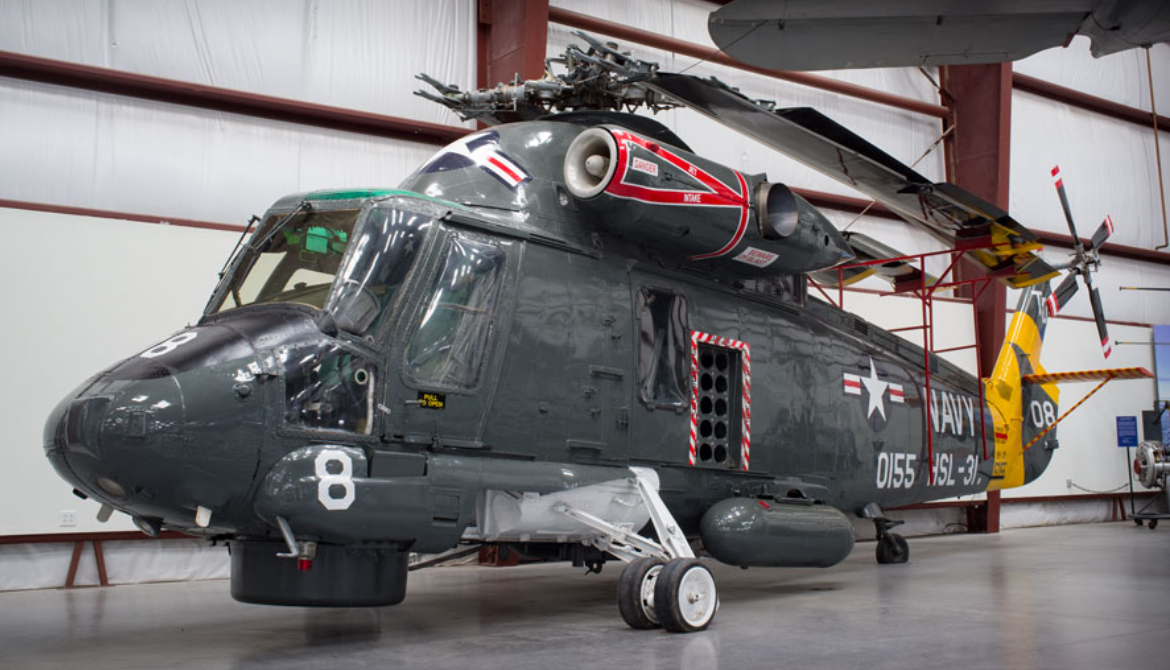
Kaman SH-2G Super Seasprite


Kaman Aerospace
Kaman SH-2G Super Seasprite
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 3 (USN: pilot, co-pilot/tactical coordinator (TACCO), sensor operator (SENSO)) (RNZN: pilot, observer and helicopter loadmaster)
- Capacity: 4,390 lb (1,991 kg) load
- Length: 52 ft 9 in (15.9 m)
- Height: 15 ft 0 in (4.5 m)
- Empty weight: 9,200 lb (4,170 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 13,500 lb (6,120 kg)
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Rotor systems: 4 blades on main rotor and tail rotor. Main rotor blades are controlled by servo flaps rather than a swashplate
- Powerplant: 2 × T700-GE-401/401C turboshaft, 1,723 shp each
- Main rotor diameter: (13.4 m)
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 256 km/h
- Cruise speed: 222 km/h
- Never exceed speed: 278 km/h
- Range: ,000 km
- Endurance: 5 hr with 2 external tanks
- Service ceiling: (3,000 m
Related development
-
- Guns: FN MAG General-purpose machine gun x 1 (equipped on the right door only for the Royal New Zealand Navy)
- Hardpoints: Two bomb racks behind the main landing gear (for drop tanks and depth charges)
- Missiles: Export type only, equipped with 2 AGM-65D air-to-ground missiles
.
Links to Youtube & Others
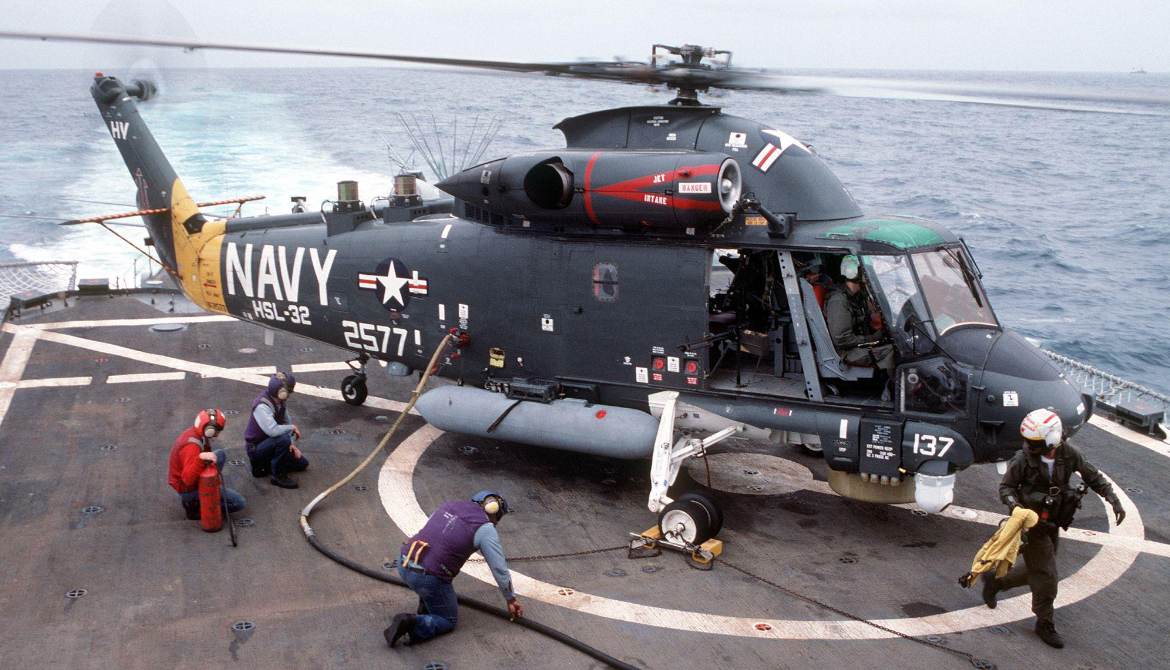
Beginning in 1991, the US Navy received 24 SH-2Gs, which were assigned to US Navy Reserve units. The Super Seasprite entered service with HSL-84 in 1993.The SH-2 served in some 600 Navy deployments and flew 1.5 million flight hours. The Navy Reserve squadron HSL-84 retired the last of the helicopters in June 2001
Kaman Aerospace
SH-2G Super Seasprite
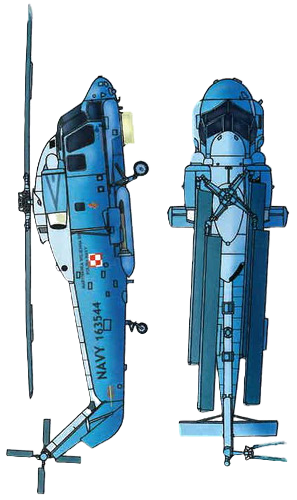
The Polish Navy operates four of these aircraft, which were included in the purchase of two Oliver Hazard Perry-class frigates from the United States Navy.
Youtube Link
In the 1990s, the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) decided that it needed an intermediate helicopter to operate from the Anzac-class frigates and the planned offshore patrol vessel